Abstract
Objectives
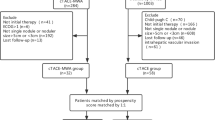
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical outcome of patients receiving microwave ablation (MWA), either after downstaging of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), or without downstaging when meeting initially the Milan criteria.
Methods
From January 2012 to January 2018, 66 patients with HCC beyond the Milan criteria who were downstaged by TACE previous to MWA comprised the study group. The control group comprised 190 patients who underwent MWA as first-line treatment as they met initially the Milan criteria. Cumulative overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates were compared. The propensity score analysis was performed to reduce potential bias.
Results
Baseline characteristics were balanced between the two groups after 1:1 propensity score matching. The OS rates were 100%, 79%, and 73% at 1, 3, and 5 years in the downstaging group and 95%, 83%, and 72%, respectively, in the Milan group. The corresponding RFS rate were 77%, 40%, and 31% in the downstaging group and 76%, 45%, and 34% in the Milan group. There were no significant differences in the OS and RFS rates between the two groups (p = 0.981 and p = 0.586).
Conclusions
The long-term therapeutic outcomes of MWA for downstaged HCC with TACE were similar to HCC that initially met the Milan criteria.
Key Points
• Patients treated with MWA of HCC after downstaging with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) were similar to those with HCC that initially met Milan criteria.
• Microwave ablation (MWA) can be an effective treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) that is downstaged to the Milan criteria.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- TACE:
-
Transarterial chemoembolization
References
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R et al (1996) Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 334:693–699
Kulik L, Heimbach JK, Zaiem F et al (2018) Therapies for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 67:381–400
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2018) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 69:182–236
Uhlig J, Sellers CM, Stein SM, Kim HS (2019) Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: contemporary treatment trends and outcomes from the United States National Cancer Database. Eur Radiol 29:2679–2689
Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M (2016) Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 150:835–853
Liu W, Zheng Y, He W et al (2018) Microwave vs radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a propensity score analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 48:671–681
(2019) National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (NCCN) Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hepatobiliary.pdf Accessed 6 Mar 2019
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X et al (2002) Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 359:1734–1739
Peng Z, Wei M, Chen S et al (2018) Combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation versus hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after initial surgery: a propensity score matching study. Eur Radiol 28:3522–3531
Zhang R, Shen L, Zhao L, Guan Z, Chen Q, Li W (2018) Combined transarterial chemoembolization and microwave ablation versus transarterial chemoembolization in BCLC stage B hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Interv Radiol 24:219–224
Li W, Ni CF (2019) Current status of the combination therapy of transarterial chemoembolization and local ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44:2268–2275
Chapman WC, Majella Doyle MB, Stuart JE et al (2008) Outcomes of neoadjuvant transarterial chemoembolization to downstage hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation. Ann Surg 248:617–625
Samuel D, Coilly A (2018) Management of patients with liver diseases on the waiting list for transplantation: a major impact to the success of liver transplantation. BMC Med 16:113
Rudnick SR, Russo MW (2018) Liver transplantation beyond or downstaging within the Milan criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:265–275
Yao FY, Mehta N, Flemming J et al (2015) Downstaging of hepatocellular cancer before liver transplant: long-term outcome compared to tumors within Milan criteria. Hepatology 61:1968–1977
Toso C, Mentha G, Kneteman NM, Majno P (2010) The place of downstaging for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 52:930–936
Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS et al (2018) AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67:358–380
Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM, Riaz A et al (2009) A comparative analysis of transarterial downstaging for hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization versus radioembolization. Am J Transplant 9:1920–1928
Allard MA, Sebagh M, Ruiz A et al (2015) Does pathological response after transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with cirrhosis predict outcome after liver resection or transplantation? J Hepatol 63:83–92
Kim BK, Kim SU, Kim KA et al (2015) Complete response at first chemoembolization is still the most robust predictor for favorable outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 62:1304–1310
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL et al (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update. Radiology 273:241–260
Xu Y, Shen Q, Liu P et al (2017) Microwave ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma that met up-to-seven criteria: feasibility, local efficacy and long-term outcomes. Eur Radiol 27:3877–3887
Liu S, Li H, Guo L et al (2019) Tumor size affects efficacy of adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and microvascular invasion. Oncologist 24:513–520
Majno PE, Adam R, Bismuth H et al (1997) Influence of preoperative transarterial lipodol chemoembolization on resection and transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 226:688–701
De LW, Sze DY, Ahmed A et al (2009) Transarterial chemoinfusion for hepatocellular carcinoma as downstaging therapy and a bridge toward liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 9:1158–1168
Yu CY, Ou HY, Huang TL et al (2012) Hepatocellular carcinoma downstaging in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 44:412–414
Lei J, Wang W, Yan L (2013) Downstaging advanced hepatocellular carcinoma to the Milan criteria may provide a comparable outcome to conventional Milan criteria. J Gastrointest Surg 17:1440–1446
Chen QF, Jia ZY, Yang ZQ, Fan WL, Shi HB (2017) Transarterial chemoembolization monotherapy versus combined transarterial chemoembolization-microwave ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma tumors ≤5 cm: a propensity analysis at a single center. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40:1748–1755
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Xiaoming Chen.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors (SL) has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committees of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Methodology
• Retrospective
• prognostic study
• Multicenter study
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, F., Lian, S., Mai, Q. et al. Microwave ablation after downstaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: outcome was similar to tumor within Milan criteria. Eur Radiol 30, 2454–2462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06604-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06604-y