Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to compare the efficacy of radiotherapy (RT) combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) with RT alone for the treatment of bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods
We included in this retrospective study 25 RCC patients (28 bone metastases), who were treated with RT at our institution. Patients were divided into two groups: patients treated with RT alone (monotherapy group; n = 17) and those treated with RT combined with TACE (combined therapy group; n = 11). The administered median RT dose was 30 Gy in 10 fractions. Anti-cancer agents used in TACE were cisplatin (median dose, 50 mg) and carboplatin (median dose, 240 mg) for patients with reduced renal function. We evaluated the objective response, post-RT-skeletal-related event (PR-SRE)–free rate, and adverse events associated with treatment for each group.
Results
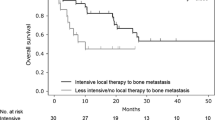
The objective response rates for bone metastases in the monotherapy and combined therapy groups were 33% and 82%, respectively (p = 0.009). The 2-year PR-SRE-free rate in the monotherapy and combined therapy groups was 41.8% and 100%, respectively (p = 0.009). The objective response and PR-SRE-free rates were significantly superior in the combined therapy than in the monotherapy group. There were no significant differences in adverse events or survival between the two groups.
Conclusion
RT combined with TACE is a promising treatment for bone metastases from RCC, as it results in higher objective response, and PR-SRE-free rates compared with RT alone.
Key Points
• Skeletal-related events (SREs) are common in patients with bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
• Radiotherapy (RT) provides pain relief in patients with bone metastases from RCC, but rarely achieves objective response.
• Combination of RT with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization results in higher objective response and post-RT-SRE-free rates compared with RT alone and is a promising treatment for bone metastases from RCC, as it.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMA:
-
Bone-modifying agent
- CR:
-
Complete response
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- ICI:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MTT:
-
Molecularly targeted therapy
- PD:
-
Progressive disease
- PR:
-
Partial response
- PR-SRE:
-
Post-radiotherapy-skeletal-related event
- QOL:
-
Quality of life
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- SR:
-
Stable response
- SRE:
-
Skeletal-related event
- TACE:
-
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization
- TAE:
-
Transcatheter arterial embolization
References
Woodward E, Jagdev S, McParland L et al (2011) Skeletal complications and survival in renal cancer patients with bone metastases. Bone 48:160–166
Bianchi M, Sun M, Jeldres C et al (2012) Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: a population-based analysis. Ann Oncol 23:973–980
Beuselinck B, Oudard S, Rixe O et al (2011) Negative impact of bone metastasis on outcome in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Ann Oncol 22:794–800
Santoni M, Conti A, Procopio G et al (2015) Bone metastases in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: are they always associated with poor prognosis? J Exp Clin Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0122-0
McKay RR, Kroeger N, Xie W et al (2014) Impact of bone and liver metastases on patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy. Eur Urol 65:577–584
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P et al (2009) Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:3584–3590
Escudier B, Eiseen T, Stadler WM et al (2009) Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: final efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol 27:3312–3318
Calvo E, Escudier B, Motzer RJ et al (2012) Everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: subgroup analysis of patients with 1 or 2 previous vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies enrolled in the phase III RECORD-1 study. Eur J Cancer 48:333–339
Bedke J, Stuhler V, Stenzl A, Brehmer B (2018) Immunotherapy for kidney cancer: status quo and the future. Curr Opin Urol 28:8–14
Teyssonneau D, Gross-Goupil M, Domblides C et al (2018) Treatment of spinal metastases in renal cell carcinoma: a critical review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 125:19–29
Lipton A, Zheng M, Seaman J (2003) Zoledronic acid delays the onset of skeletal-related events and progression of skeletal disease in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 98:962–969
Jung ST, Ghert MA, Harrelson JM, Scully SP (2003) Treatment of osseous metastases in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res 409:223–231
Lee J, Hodgson D, Chow E et al (2005) A phase II trial of palliative radiotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 104:1894–1900
Kijima T, Fujii Y, Suyama T et al (2008) Radiotherapy to bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma with or without zoledronate. BJU Int 103:620–624
Hosaka S, Katagiri H, Niwakawa M et al (2018) Radiotherapy combined with zoledronate can reduce skeletal-related events in renal cell carcinoma patients with bone metastasis. Int J Clin Oncol 23:1127–1133
Sun S, Lang EV (1998) Bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma: preoperative embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:263–269
Wirbel RJ, Roth R, Schlte M, Kramann B, Mutschler W (2005) Preoperative embolization in spinal and pelvic metastases. J Orthop Sci 10:253–257
Gupta P, Gamanagatti S (2012) Preoperative transarterial embolisation in bone tumors. World J Radiol 4:186–192
Radeleff B, Eiers M, Lopez-Benitez R et al (2006) Transarterial embolization of primary and secondary tumors of the skeletal system. Eur J Radiol 58:68–75
Forauer AR, Kent E, Cwikiel W, Esper P, Redman B (2007) Selective palliative transcatheter embolization of bony metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol 46:1012–1018
Nagata Y, Mitsumori M, Okajima K et al (1998) Transcatheter arterial embolization for malignant osseous and soft tissue sarcomas. II. Clinical results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 21:208–213
Chiras J, Adem C, Vallee JN, Spelle L, Cormier E, Rose M (2004) Selective intra-arterial chemoembolization of pelvic and spine bone metastases. Eur Radiol 13:1774–1780
Koike Y, Takizawa K, Ogawa Y et al (2011) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or embolization (TAE) for symptomatic bone metastases as a palliative treatment. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:793–801
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, Berg W, Amsterdam A, Ferrara J (1999) Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 17:2530–2540
Diamond E, Molina AM, Carbonaro M et al (2015) Cytotoxic chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in the era of targeted therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 96:518–526
Hussain M, Vaishampayan U, Du W, Redman B, Smith DC (2001) Combination paclitaxel, carboplatin, and gemcitabine is an active treatment for advanced urothelial cancer. J Clin Oncol 19:2527–2533
Hosogoe S, Hatakeyama S, Kusaka A et al (2018) Platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy improves oncological outcomes in patients with locally advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus 4:946–953
Drooz AT, Lewis CA, Allen TE et al (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transcatheter embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S237–S242
Mizumoto M, Hrada H, Asakura H et al (2009) Radiotherapy for patients with metastases to the spinal column: a review of 603 patients at Shizuoka Cancer Center Hospital. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79:208–213
Soo CS, Wallace S, Chuang VP, Carrasco CH, Phillies G (1982) Lumbar artery embolization in cancer patients. Radiology 145:655–659
Uemura A, Fujimoto H, Yasuda S et al (2001) Transcatheter arterial embolization for bone metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol 11:1457–1462
Yamaura H, Yamada K, Matsuzawa T (1976) Radiation effect on the proliferating capillaries in rat transparent chambers. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 30:179–187
Yamaura H, Matsuzawa T (1979) Tumor regrowth after irradiation: an experimental approach. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 35:201–219
Coldwell DM, Stokes KR, Yakes WF (1994) Embolotherapy: agents, clinical applications and techniques. Radiographics 14:623–643
Kato T, Nemoto R, Mori H, Takahashi M, Harada M (1981) Arterial chemoembolization with mitomycin C microcapsules in the treatment of primary or secondary carcinoma of the kidney, liver bone and intrapelvic organs. Cancer 48:674–680
Funding
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid of the Uruma Fund for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Sadayuki Murayama.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heianna, J., Makino, W., Ariga, T. et al. Concomitant radiotherapy and transarterial chemoembolization reduce skeletal-related events related to bone metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 30, 1525–1533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06454-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06454-8