Abstract
Objectives
To develop a fast, high-resolution T1-mapping sequence dedicated to skeletal muscle imaging, and to evaluate the potential of T1 as a robust and sensitive biomarker for the monitoring of chronic fatty degenerations in a dystrophic disease.
Methods
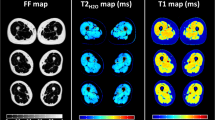
The magnetic resonance imaging sequence consisted of the acquisition of a 1,000-radial-spokes FLASH echo-train following magnetisation inversion, resulting in 10s scan time per slice. Temporal image series were reconstructed using compressed sensing and T1 maps were computed using Bloch simulations. Ten healthy volunteers and 30 patients suffering from Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) participated in this prospective study, in order to evaluate the repeatability, the precision and the sensitivity of the proposed approach. Intramuscular fat fraction (FF) was also measured using a standard three-point Dixon method. The protocol was approved by a local ethics committee.
Results
The mean T1 evaluated in the thighs muscles of healthy volunteers was 1,199 ± 45 ms, with a coefficient of reproducibility of 2.3%. Mean T1 values were statistically decreased in the thighs of BMD patients and were linearly correlated with intramuscular FF (R = -0.98).
Conclusions
T1-mapping is a good candidate for fast, sensitive and quantitative monitoring of fatty infiltrations in neuromuscular disorders.
Key Points
• A T1 mapping sequence dedicated to skeletal muscle imaging was implemented.
• The acquisition time was 10 s per slice.
• Muscle T1 values were significantly decreased in dystrophic muscles compared to healthy muscles.
• T1 values correlated with intramuscular fat fraction measured by three-point Dixon.
• T1 represents an alternative biomarker for monitoring fatty infiltrations in neuromuscular disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMD :
-
Becker muscular dystrophy
- ES :
-
Echo spacing
- FA :
-
Flip angle
- FF :
-
Fat fraction
- FLASH :
-
Fast low angle shot
- GA :
-
Golden angle
- MRI :
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NMD :
-
Neuromuscular disorder
- T1 :
-
Longitudinal relaxation time
- T2 :
-
Transverse relaxation time
- Tacq :
-
Acquisition time
- TD :
-
Delay time
- TE :
-
Echo time
References
Hollingsworth KG, de Sousa PL, Straub V, Carlier PG (2012) Towards harmonization of protocols for MRI outcome measures in skeletal muscle studies: consensus recommendations from two TREAT-NMD NMR workshops, 2 May 2010, Stockholm, Sweden, 1-2 October 2009, Paris, France. Neuromuscul Disord 22(Suppl 2):S54–S67
Carlier PG, Marty B, Scheidegger O et al (2016) Skeletal muscle quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy as an outcome measure for clinical trials. J Neuromuscul Dis 3:1–28
Fischmann A, Hafner P, Gloor M et al (2013) Quantitative MRI and loss of free ambulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol 260:969–974
Gaeta M, Messina S, Mileto A et al (2012) Muscle fat-fraction and mapping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: evaluation of disease distribution and correlation with clinical assessments. Skeletal Radiol 41:955–961
Kim HK, Laor T, Horn PS et al (2010) T2 Mapping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: distribution of disease activity and correlation with clinical assessments. Radiology 255:899–908
Hernando D, Kellman P, Haldar JP, Liang Z-P (2009) Robust water/fat separation in the presence of large field inhomogeneities using a graph cut algorithm. Magn Reson Med 63:79–90
Sharma SD, Artz NS, Hernando D et al (2015) Improving chemical shift encoded water-fat separation using object-based information of the magnetic field inhomogeneity. Magn Reson Med 73:597–604
Arpan I, Forbes SC, Lott DJ et al (2013) T2 mapping provides multiple approaches for the characterization of muscle involvement in neuromuscular diseases: a cross-sectional study of lower leg muscles in 5-15-year-old boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. NMR Biomed 26:320–328
Forbes SC, Willcocks RJ, Triplett WT et al (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy assessment of lower extremity skeletal muscles in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a multicenter cross sectional study. PLoS One 9:e106435
Wokke BH, van den Bergen JC, Versluis MJ et al (2014) Quantitative MRI and strength measurements in the assessment of muscle quality in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 24:409–416
Murphy W, Totty W, Carroll J (1986) MRI of normal and pathological skeletal muscle. AJR Am J Roentgenol 146:565–574
Mercuri E, Pichiecchio A, Allsop J et al (2007) Muscle MRI in inherited neuromuscular disorders: past, present, and future. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:433–440
Bulluck H, Maestrini V, Rosmini S et al (2015) Myocardial T1 mapping. Circ J 79:487–494
Varghese J, Scandling D, Joshi R et al (2015) Rapid assessment of quantitative T 1, T 2 and T 2 * in lower extremity muscles in response to maximal treadmill exercise. NMR Biomed 28:998–1008
Li K, Dortch RD, Welch EB et al (2014) Multi-parametric MRI characterization of healthy human thigh muscles at 3.0 T—relaxation, magnetization transfer, fat/water, and diffusion tensor imaging. NMR Biomed 27:1070–1084
Winkelmann S, Schaeffter T, Koehler T et al (2007) An optimal radial profile order based on the golden ratio for time-resolved MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:68–76
Glover GH, Schneider E (1991) Three-point Dixon technique for true water/fat decomposition with B0 inhomogeneity correction. Magn Reson Med 18:371–383
Song HK, Dougherty L (2000) k-space weighted image contrast (KWIC) for contrast manipulation in projection reconstruction MRI. Magn Reson Med 44:825–832
Ehses P, Seiberlich N, Ma D et al (2013) IR TrueFISP with a golden-ratio-based radial readout: fast quantification of T1, T2, and proton density. Magn Reson Med 69:71–81
Gensler D, Mörchel P, Fidler F et al (2015) Myocardial T1: quantification by using an ECG-triggered radial single-shot inversion-recovery MR imaging sequence. Radiology 274:879–887
Marty B, Coppa B, Carlier PG (2018) Fast, precise, and accurate myocardial T1 mapping using a radial MOLLI sequence with FLASH readout. Magn Reson Med 79:1387–1398
Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM (2007) Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 58:1182–1195
Hargreaves BA, Vasanawala SS, Pauly JM, Nishimura DG (2001) Characterization and reduction of the transient response in steady-state MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 46:149–158
Marty B, Vignaud A, Greiser A et al (2015) BLOCH equations-based reconstruction of myocardium t1 maps from modified look-locker inversion recovery sequence. PLoS One 10:e0126766
Ma D, Gulani V, Seiberlich N et al (2013) Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 495:187–192
Wokke BH, Van Den Bergen JC, Hooijmans MT et al (2016) T2 relaxation times are increased in Skeletal muscle of DMD but not BMD patients. Muscle Nerve 53:38–43
De Sousa PL, Vignaud A, Fleury S, Carlier PG (2011) Fast monitoring of T(1), T(2), and relative proton density (M(0) ) changes in skeletal muscles using an IR-TrueFISP sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:921–930
Idilman IS, Aniktar H, Idilman R et al (2013) Hepatic steatosis: quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology 267:767–775
Gold GE, Han E, Stainsby J et al (2004) Musculoskeletal MRI at 3.0 T: relaxation times and image contrast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:343–351
Kellman P, Herzka DA, Hansen MS (2014) Adiabatic inversion pulses for myocardial T1 mapping. Magn Reson Med 71:1428–1434
Bryant ND, Li K, Does MD et al (2014) Multi-parametric MRI characterization of inflammation in murine skeletal muscle. NMR Biomed 27:716–725
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Benjamin Marty, Ph.D.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• prospective
• experimental
• performed at one institution
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 304 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marty, B., Coppa, B. & Carlier, P.G. Monitoring skeletal muscle chronic fatty degenerations with fast T1-mapping. Eur Radiol 28, 4662–4668 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5433-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5433-z