Abstract
Purpose
Accommodating a novel semi-implantable bone conduction hearing device within the temporal bone presents challenges for surgical planning. This study describes the utility of CT in pre-operative assessment of such an implant.
Methods
Retrospective review of pre-operative CT, clinical and surgical records of 16 adults considered for device implantation. Radiological suitability was assessed on CT using 3D simulation software. Antero-posterior (AP) dimensions of the mastoid bone and minimum skull thickness were measured. CT planning results were correlated with operative records.
Results
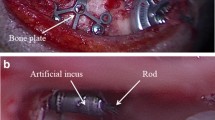
Eight and five candidates were suitable for device placement in the transmastoid and retrosigmoid positions, respectively, and three were radiologically unsuitable. The mean AP diameter of the mastoid cavity was 14.6 mm for the transmastoid group and 4.6 mm for the retrosigmoid group (p < 0.05). Contracted mastoid and/or prior surgery were predisposing factors for unsuitability. Four transmastoid and five retrosigmoid positions required sigmoid sinus/dural depression and/or use of lifts due to insufficient bone capacity.
Conclusion
A high proportion of patients being considered have contracted or operated mastoids, which reduces the feasibility of the transmastoid approach. This finding combined with the complex temporal bone geometry illustrates the importance of careful CT evaluation using 3D software for precise device simulation.
Key points
• Preoperative temporal bone CT is essential for determining Bonebridge device suitability.
• Mastoid under-pneumatisation and prior mastoidectomy predict a retrosigmoid Bonebridge position.
• 3D simulation software is recommended for precise device positioning.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dun CA, Faber HT, de Wolf MJ, Cremers CW, Hol MK (2011) An overview of different systems: the bone-anchored hearing aid. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 71:22–31
Kiringoda R, Lustig LR (2013) A meta-analysis of the complications associated with osseointegrated hearing aids. Otol Neurotol 34:790–794
Barbara M, Perotti M, Gioia B, Volpini L, Monini S (2013) Transcutaneous bone-conduction hearing device: audiological and surgical aspects in a. Acta Otolaryngol 133:1058–1064
Canis M, Ihler F, Blum J, Matthias C (2013) CT-assisted navigation for retrosigmoidal implantation of the Bonebridge. HNO 61:1038–1044
Huber AM, Sim JH, Xie YZ, Chatzimichalis M, Ullrich O, Röösli C (2013) The Bonebridge: preclinical evaluation of a new transcutaneously-activated bone anchored hearing device. Hear Res 301:93–99
Lo JF, Tsang WS, Yu JY, Ho OY, Ku PK, Tong MC (2014) Contemporary hearing rehabilitation options in patients with aural atresia. Biomed Res Int 2014:761579
Plontke SK, Radetzki F, Seiwerth I, Herzog M, Brandt S, Delank KS, Rahne T (2014) Individual computer-assisted 3D planning for surgical placement of a new bone conduction hearing device. Otol Neurotol 35:1251–1257
Tsang WS, Yu JK, Bhatia KS, Wong TK, Tong MC (2013) The Bonebridge semi-implantable bone conduction hearing device: experience in an Asian patient. J Laryngol Otol 127:1214–1221
Güldner C, Heinrichs J, Weiß R, Zimmermann AP, Dassinger B, Bien S, Werner JA, Diogo I (2013) Visualisation of the Bonebridge by means of CT and CBCT. Eur J Med Res 18:30
Lassaletta L, Sanchez-Cuadrado I, Muñoz E, Gavilan J (2014) Retrosigmoid implantation of an active bone conduction stimulator in a patient with chronic otitis media. Auris Nasus Larynx 1-4
Lin S, Wang D, Lok KH, Li L, Bhatia KS, Tong MC (2014) Computer-assisted Surgical Planning for Bonebridge Implantation. 4th East Asian Symposium on Otology, Shanghai, China
Wimmer W, Gerber N, Guignard J, Dubach P, Kompis M, Weber S, Caversaccio M (2015) Topographic bone thickness maps for Bonebridge implantations. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Off J Eur Fed Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Soc 272:1651–1658
Takumi Y, Matsumoto N, Cho B, Ono H, Mori K, Tsukada K, Ichinose A, Yoshimura H, Iwasaki S, Komune S, Usami S (2014) A clinical experience of 'STAMP' plate-guided Bonebridge implantation. Acta Otolaryngol 134:1042–1046
Hassepass F, Bulla S, Aschendorff A, Maier W, Traser L, Steinmetz C, Wesarg T, Arndt S (2014) The Bonebridge as a transcutaneous bone conduction hearing system: preliminary surgical and audiological results in children and adolescents. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(9):2235-41
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ms. Li Lening for her assistance in Bonebridge device planning. This paper was presented as an abstract at ECR 2015. The scientific guarantor of this publication is Associate Professor Kunwar Bhatia. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study was partly funded by Med-El Hong Kong Asia Pacific Headquarters and a grant from the Innovation and Technology Commission (Project No: ITS/225/12). No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was waived by the institution because of its retrospective study design. Written informed consent was waived by the institutional review board. Some study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in Tsang et al. The Bonebridge semi-implantable bone conduction hearing device: experience in an Asian patient. 2013 The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, doi: 10.1017/S0022215113002144. This paper was a short communication describing the surgical techniques and audiology outcome in the first patient in Asia to receive the Bonebridge device. It does not focus on the radiological aspect during pre-operative assessment, which is the focus of this study. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Law, E.K.C., Bhatia, K.S.S., Tsang, W.S.S. et al. CT pre-operative planning of a new semi-implantable bone conduction hearing device. Eur Radiol 26, 1686–1695 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3983-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3983-x