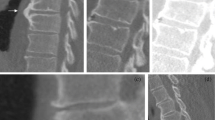
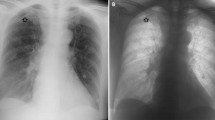
Abstract
Purpose
To determine inter-rater reliability of sarcoidosis-related computed tomography (CT) findings that can be used for scoring of thoracic sarcoidosis.
Materials and methods
CT images of 51 patients with sarcoidosis were scored by five chest radiologists for various abnormal CT findings (22 in total) encountered in thoracic sarcoidosis. Using intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) analysis, inter-rater reliability was analysed and reported according to the Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) criteria. A pre-specified sub-analysis was performed to investigate the effect of training. Scoring was trained in a distinct set of 15 scans in which all abnormal CT findings were represented.
Results
Median age of the 51 patients (36 men, 70 %) was 43 years (range 26 – 64 years). All radiographic stages were present in this group. ICC ranged from 0.91 for honeycombing to 0.11 for nodular margin (sharp versus ill-defined). The ICC was above 0.60 in 13 of the 22 abnormal findings. Sub-analysis for the best-trained observers demonstrated an ICC improvement for all abnormal findings and values above 0.60 for 16 of the 22 abnormalities.
Conclusions
In our cohort, reliability between raters was acceptable for 16 thoracic sarcoidosis-related abnormal CT findings.
Key Points
• Thoracic sarcoidosis is common; knowledge on reliability of CT scoring is limited.
• Scoring CT abnormalities in pulmonary sarcoidosis can achieve good inter-rater agreement.
• CT scoring validation in thoracic sarcoidosis is important for diagnostic and prognostic studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- ICC:
-
Intra-class correlation coefficient
- GRRAS:
-
Guidelines for Reporting reliability and Agreement Studies
- PACS:
-
Picture Archiving and Communication System
- WASOG:
-
World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous disorders
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Chiles C (2002) Imaging features of thoracic sarcoidosis. Semin Roentgenol 37:82–93
Hennebicque AS, Nunes H, Brillet PY, Moulahi H, Valeyre D, Brauner MW (2005) CT findings in severe thoracic sarcoidosis. Eur Radiol 15(1):23–30
Criado E, Sanchez M, Ramirez J et al (2010) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: Typical and atypical manifestations at high-resolution CT with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 30:1567–1586
Spagnolo P, Sverzellati N, Wells AU, Hansell D (2014) Imaging aspects of the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Eur Radiol 24(4):807–816
Naccache JM, Lavole A, Nunes H et al (2008) High-resolution computed tomographic imaging of airways in sarcoidosis patients with airflow obstruction. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32:905–912
Drent M, De Vries J, Lenters M et al (2003) Sarcoidosis: Assessment of disease severity using HRCT. Eur Radiol 13:2462–2471
Abehsera M, Valeyre D, Grenier P, Jaillet H, Battesti JP, Brauner MW (2000) Sarcoidosis with pulmonary fibrosis: CT patterns and correlation with pulmonary function. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:1751–1757
Bergin CJ, Bell DY, Coblentz CL et al (1989) Sarcoidosis: Correlation of pulmonary parenchymal pattern at CT with results of pulmonary function tests. Radiology 171:619–624
Hansell DM, Milne DG, Wilsher ML, Wells AU (1998) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: Morphologic associations of airflow obstruction at thin-section CT. Radiology 209:697–704
Murdoch J, Muller NL (1992) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: Changes on follow-up CT examination. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159:473–477
Brauner MW, Lenoir S, Grenier P, Cluzel P, Battesti JP, Valeyre D (1992) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: CT assessment of lesion reversibility. Radiology 182:349–354
Fazzi P, Sbragia P, Solfanelli S, Troilo S, Giuntini C (2001) Functional significance of the decreased attenuation sign on expiratory CT in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 119:1270–1274
Akira M, Kozuka T, Inoue Y, Sakatani M (2005) Long-term follow-up CT scan evaluation in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 127:185–191
Zappala CJ, Desai SR, Copley SJ et al (2014) Accuracy of individual variables in the monitoring of long-term change in pulmonary sarcoidosis as judged by serial high- resolution CT scan data. Chest 145:101–107
Scadding JG (1961) Prognosis of intrathoracic sarcoidosis in england. A review of 136 cases after five years' observation. Br Med J 2:1165–1172
Costabel U, Hunninghake GW (1999) ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. sarcoidosis statement committee. american thoracic society. european respiratory society. world association for sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders. Eur Respir J 14:735–737
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner society: Glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246:697–722
Sverzellati N, Devaraj A, Desai SR, Quigley M, Wells AU, Hansell DM (2011) Method for minimizing observer variation for the quantitation of high-resolution computed tomographic signs of lung disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:596–601
Kottner J, Audige L, Brorson S et al (2011) Guidelines for reporting reliability and agreement studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J Clin Epidemiol 64:96–106
Rosner B (2010) Fundamentals in biostatisctics 7th, edn. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove California United States
Rankin G, Stokes M (1998) Reliability of assessment tools in rehabilitation: An illustration of appropriate statistical analyses. Clin Rehabil 12:187–199
Mostard RL, Verschakelen JA, van Kroonenburgh MJ (2013) Severity of pulmonary involvement and (18)F-FDG PET activity in sarcoidosis. Respir Med 107(3):439–447
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Barreto MM, de Andrade FT, Rodrigues RS (2011) Atypical distribution of small nodules on high resolution CT studies: patterns and differentials. Respir Med 105(9):1263–1267
Walsh SL, Wells AU, Sverzellati N et al (2014) An integrated clinicoradiological staging system for pulmonary sarcoidosis: a case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2(2):123–130
Oberstein A, von Zitzewitz H, Schweden F, Muller-Quernheim J (1997) Non invasive evaluation of the inflammatory activity in sarcoidosis with high-resolution computed tomography. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 14:65–72
Baughman RP, Shipley R, Desai S et al (2009) Changes in chest roentgenogram of sarcoidosis patients during a clinical trial of infliximab therapy: comparison of different methods of evaluation. Chest 136(2):526–535
Zappala CJ, Desai SR, Copley SJ et al (2011) Optimal scoring of serial change on chest radiography in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 28(2):130–138
Muers MF, Middleton WG, Gibson GJ et al (1997) A simple radiographic scoring method for monitoring pulmonary sarcoidosis: relations between radiographic scores, dyspnoea grade and respiratory function in the British Thoracic Society Study of Long-Term Corticosteroid Treatment. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 14(1):46–56
Johkoh T, Sakai F, Noma S et al (2014) Honeycombing on CT; its definition, pathologic correlation, and future direction of its diagnosis. Eur J Radiol 83:27–31
Ng CS, Desai SR, Rubens MB, Padley SP, Wells AU, Hansell DM (1999) Visual quantitation and observer variation of signs of small airways disease at inspiratory and expiratory CT. J Thorac Imaging 14:279–285
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is prof. J.C. Grutters. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. None of the study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported. Methodology: retrospective, cross sectional study, multicenter study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van den Heuvel, D.A., de Jong, P.A., Zanen, P. et al. Chest Computed Tomography-Based Scoring of Thoracic Sarcoidosis: Inter-rater Reliability of CT Abnormalities. Eur Radiol 25, 2558–2566 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3685-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3685-4