Abstract
Objective
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhuEpo) is used clinically to treat anaemia. However, rhuEpo-treated cancer patients show decreased survival rates and erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) expression has been found in patient tumour tissue. Thus, rhuEpo application might promote EpoR+ tumour progression. We therefore developed the positron emission tomography (PET)-probe 68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo and evaluated its performance in EpoR+ A549 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) xenografts.
Methods
68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo was generated by coupling DOTA-hydrazide to carbohydrate side-chains of rhuEpo. Biodistribution was determined in tumour-bearing mice 0.5, 3, 6, and 9 h after probe injection. Competition experiments were performed by co-injecting 68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo and rhuEpo in five-fold excess. Probe specificity was further evaluated histologically using Epo-Cy5.5 stainings.
Results
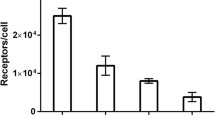
The blood half-life of 68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo was 2.6 h and the unbound fraction was cleared by the liver and kidney. After 6 h, the highest tumour to muscle ratio was reached. The highest 68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo accumulation was found in liver (10.06 ± 6.26%ID/ml), followed by bone marrow (1.87 ± 0.53%ID/ml), kidney (1.58 ± 0.39 %ID/ml), and tumour (0.99 ± 0.16%ID/ml). EpoR presence in these organs was histologically confirmed. Competition experiments showed significantly (p < 0.05) lower PET-signals in tumour and bone marrow at 3 and 6 h.
Conclusion
68Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo shows favourable pharmacokinetic properties and detects EpoR specifically. Therefore, it might become a valuable radiotracer to monitor EpoR status in tumours and support decision-making in anaemia therapy.
Key Points
• PET-probe 68 Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo was administered to assess the EpoR status in vivo
• 68 Ga-DOTA-rhuEpo binds specifically to EpoR positive organs in vivo
• Tumour EpoR status determination might enable decision-making in anaemia therapy with rhuEpo



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BFU-E:
-
burst forming unit erythroid
- CFU-E:
-
colony forming unit erythroid
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- DOTA:
-
1,4,7,10-tetraazo-cyclododecane-tetraacetic acid
- DTPA:
-
diethylene-triamine-pentaacetic acid
- Epo:
-
Erythropoietin
- EpoR:
-
erythropoietin receptor
- FMT:
-
fluorescence-mediated tomography
- NIRF:
-
near infrared fluorescence
- NOTA:
-
1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid
- NSCLC:
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
- OSEM:
-
ordered subset expectation maximization
- PET:
-
positron emission tomography
- rhuEpo:
-
recombinant human erythropoietin
- ROI:
-
region of interest
- SD:
-
Standard Deviation
- SPECT:
-
single photon emission computed tomography
- TLC:
-
Thin Layer Chromatography
References
Spivak JL (2005) The anaemia of cancer: death by a thousand cuts. Nat Rev Cancer 5:543–555
Sato Y, Yanagita M (2013) Renal anemia: from incurable to curable. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F1239–F1248
Henke M, Mattern D, Pepe M et al (2006) Do erythropoietin receptors on cancer cells explain unexpected clinical findings? J Clin Oncol 24:4708–4713
Wright JR, Ung YC, Julian JA et al (2007) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of erythropoietin in non-small-cell lung cancer with disease-related anemia. J Clin Oncol 25:1027–1032
Bohlius J, Schmidlin K, Brillant C et al (2009) Recombinant human erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and mortality in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 373:1532–1542
Bohlius J, Wilson J, Seidenfeld J et al (2006) Recombinant human erythropoietins and cancer patients: updated meta-analysis of 57 studies including 9353 patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:708–714
Bennett CL, Silver SM, Djulbegovic B et al (2008) Venous thromboembolism and mortality associated with recombinant erythropoietin and darbepoetin administration for the treatment of cancer-associated anemia. J Am Med Assoc 299:914–924
Okazaki T, Ebihara S, Asada M, Yamanda S, Niu K, Arai H (2008) Erythropoietin promotes the growth of tumors lacking its receptor and decreases survival of tumor-bearing mice by enhancing angiogenesis. Neoplasia 10:932–939
Belenkov AI, Shenouda G, Rizhevskaya E et al (2004) Erythropoietin induces cancer cell resistance to ionizing radiation and to cisplatin. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1525–1532
Shiozawa Y, McGee S, Pienta MJ et al (2013) Erythropoietin supports the survival of prostate cancer, but not growth and bone metastasis. J Cell Biochem 114:2471–2478
Todaro M, Turdo A, Bartucci M et al (2013) Erythropoietin activates cell survival pathways in breast cancer stem-like cells to protect them from chemotherapy. Cancer Res 73:6393–6400
Rózsás A, Berta J, Rojkó L et al (2013) Erythropoietin receptor expression is a potential prognostic factor in human lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 8:e77459
Baltaziak M, Wincewicz A, Kanczuga-Koda L et al (2013) The relationships between hypoxia-dependent markers: HIF-1alpha, EPO and EPOR in colorectal cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol Pol Acad Sci Pol Histochem Cytochem Soc 51:320–325
Ferracin M, Bassi C, Pedriali M et al (2013) miR-125b targets erythropoietin and its receptor and their expression correlates with metastatic potential and ERBB2/HER2 expression. Mol Cancer 12:130
Miyake M, Goodison S, Lawton A, Zhang G, Gomes-Giacoia E, Rosser CJ (2013) Erythropoietin is a JAK2 and ERK1/2 effector that can promote renal tumor cell proliferation under hypoxic conditions. J Hematol Oncol 6:65
Elliott S, Sinclair A, Collins H, Rice L, Jelkmann W (2014) Progress in detecting cell-surface protein receptors: the erythropoietin receptor example. Ann Hematol 93:181–192
Doleschel D, Mundigl O, Wessner A et al (2012) Targeted Near-Infrared Imaging of the Erythropoietin Receptor in Human Lung Cancer Xenografts. J Nucl Med 53:304–311
Ntziachristos V, Ripoll J, Wang LV, Weissleder R (2005) Looking and listening to light: the evolution of whole-body photonic imaging. Nat Biotechnol 23:313–320
Yoshioka E, Kato K, Shindo H, Mitsuoka C, S.-I. Kitajima S-I, Ogata H et al: Pharmacokinetic study of darbepoetin alfa (2007) Absorption, distribution, and excretion after a single intravenous and subcutaneous administration to rats. Xenobiotica. 37(1)
dos Clemente GS, Duarte VLS (2011) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 125I-erythropoietin as a potential radiopharmaceutical agent for tumours. Braz J Pharm Sci 47:83–88
Ehrenreich H, Degner D, Meller J et al (2004) Erythropoietin: a candidate compound for neuroprotection in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 9:42–54
Fuge F, Weiler M, Gätjens J, Lammers T, Kiessling F (2013) Comparison and systematic optimization of synthetic protocols for DOTA–hydrazide generation. Tetrahedron Lett 54:918–920
Bauwens M, Chekol R, Vanbilloen H, Bormans G, Verbruggen A (2010) Optimal buffer choice of the radiosynthesis of 68Ga–Dotatoc for clinical application. Nucl Med Commun 31:753–758
Narhi LO, Arakawa T, Aoki KH, Elmore R, Rohde MF, Boone T et al (1991) The effect of carbohydrate on the structure and stability of erythropoietin. J Biol Chem 266:23022–23026
Tsuda E, Kawanishi G, Ueda M, Masuda S, Sasaki R (1990) The role of carbohydrate in recombinant human erythropoietin. Eur J Biochem 188:405–411
Kunjachan S, Gremse F, Theek B et al (2013) Noninvasive optical imaging of nanomedicine biodistribution. ACS Nano 7:252–262
Agoram B, Aoki K, Doshi S, Gegg C, Jang G, Molineux G et al (2009) Investigation of the effects of altered receptor binding activity on the clearance of erythropoiesis-stimulating proteins: Nonerythropoietin receptor-mediated pathways may play a major role. J Pharm Sci 98:2198–2211
Blom E, Velikyan I, Estrada S, Hall H, Muhammad T, Ding C et al (2012) 68Ga-Labeling of RGD peptides and biodistribution. Int J Clin Exp Med 5:165–172
Ranyuk E, Lebel R, Bérubé-Lauzière Y, Klarskov K, Lecomte R, van Lier JE et al (2013) 68Ga/DOTA- and 64Cu/NOTA-Phthalocyanine Conjugates as Fluorescent/PET Bimodal Imaging Probes. Bioconjug Chem 24:1624–1633
Knetsch PA, Petrik M, Griessinger CM, Rangger C, Fani M, Kesenheimer C et al (2011) [68Ga]NODAGA-RGD for imaging αvβ3 integrin expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:1303–1312
Zhang Y, Hong H, Engle JW, Bean J, Yang Y, Leigh BR et al (2011) Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of CD105 Expression with a 64Cu-Labeled Monoclonal Antibody: NOTA Is Superior to DOTA. PLoS ONE 6:e28005
Jelkmann W (2002) The enigma of the metabolic fate of circulating erythropoietin (Epo) in view of the pharmacokinetics of the recombinant drugs rhEpo and NESP. Eur J Haematol 69:265–274
Oxboel J, Brandt-Larsen M, Schjoeth-Eskesen C et al (2014) Comparison of two new angiogenesis PET tracers 68Ga-NODAGA-E[c(RGDyK)]2 and (64)Cu-NODAGA-E[c(RGDyK)]2; in vivo imaging studies in human xenograft tumors. Nucl Med Biol 41:259–267
Kang CM, Kim S-M, Koo H-J et al (2013) In vivo characterization of 68Ga-NOTA-VEGF 121 for the imaging of VEGF receptor expression in U87MG tumor xenograft models. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40:198–206
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Fabian Kiessling. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Roche Diagnostics GmbH; Philips Research. This study received funding from the German Ministry for Education and Research/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) project numbers 0315415C and 0316042 F. Felix Gremse received funding from Philips (Philips Research, Aachen,Germany). Axel Wessner is employee of Roche Diagnostics GmbH. The authors would also like to thank Sebastian Lowins from the organic chemistry department for intensive discussions and help. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was not required because it was not applicable. Approval from the institutional animal care committee was obtained. No study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported. Methodology: prospective, experimental, multicenter study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Felix Fuge and Dennis Doleschel shared first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuge, F., Doleschel, D., Rix, A. et al. In-vivo detection of the erythropoietin receptor in tumours using positron emission tomography. Eur Radiol 25, 472–479 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3413-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3413-5