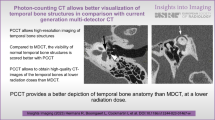
Abstract
Objectives
To prospectively evaluate radiation dose and image quality of a third generation dual-source CT (DSCT) without z-axis filter behind the patient for temporal bone CT.
Methods
Forty-five patients were either examined on a first, second, or third generation DSCT in an ultra-high-resolution (UHR) temporal bone-imaging mode. On the third generation DSCT system, the tighter focal spot of 0.2 mm2 removesthe necessity for an additional z-axis-filter, leading to an improved z-axis radiation dose efficiency. Images of 0.4 mm were reconstructed using standard filtered-back-projection or iterative reconstruction (IR) technique for previous generations of DSCT and a novel IR algorithm for the third generation DSCT. Radiation dose and image quality were compared between the three DSCT systems.
Results
The statistically significantly highest subjective and objective image quality was evaluated for the third generation DSCT when compared to the first or second generation DSCT systems (all p < 0.05). Total effective dose was 63 %/39 % lower for the third generation examination as compared to the first and second generation DSCT.
Conclusions
Temporal bone imaging without z-axis-UHR-filter and a novel third generation IR algorithm allows for significantly higher image quality while lowering effective dose when compared to the first two generations of DSCTs.
Key Points
• Omitting the z-axis-filter allows a reduction in radiation dose of 50 %
• A smaller focal spot of 0.2 mm 2 significantly improves spatial resolution
• Ultra-high-resolution temporal-bone-CT helps to gain diagnostic information of the middle/inner ear



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTDIvol :
-
CT dose index
- DLP:
-
dose length product
- DSCT:
-
dual source CT
- HU:
-
Hounsfield units
- IR:
-
iterative reconstruction
- ROI:
-
regions-of-interest
- SNR:
-
signal-to-noise ratio
- UHR:
-
ultra-high-resolution
References
Lane JI, Lindell EP, Witte RJ, DeLone DR, Driscoll CL (2006) Middle and inner ear: improved depiction with multiplanar reconstruction of volumetric CT data. Radiographics 26:115–124
McCollough CH, Leng S, Sunnegardh J et al (2013) Spatial resolution improvement and dose reduction potential for inner ear CT imaging using a z-axis deconvolution technique. Med Phys 40:061904
Venema HW, Phoa SS, Mirck PG, Hulsmans FJ, Majoie CB, Verbeeten B Jr (1999) Petrosal bone: coronal reconstructions from axial spiral CT data obtained with 0.5-mm collimation can replace direct coronal sequential CT scans. Radiology 213:375–382
Flohr TG, Stierstorfer K, Suss C, Schmidt B, Primak AN, McCollough CH (2007) Novel ultrahigh resolution data acquisition and image reconstruction for multi-detector row CT. Med Phys 34:1712–1723
Korn A, Bender B, Fenchel M et al (2013) Sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction in head CT: improvement of objective and subjective image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction. Eur J Radiol 82:1431–1435
Danish Society of Radiology (1998) European guidelines on quality criteria for computed tomography
The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP 37(2-4):1-332
Moore WH, Bonvento M, Olivieri-Fitt R (2006) Comparison of MDCT radiation dose: a phantom study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:W498–W502
Niu Y, Wang Z, Liu Y, Liu Z, Yao V (2010) Radiation dose to the lens using different temporal bone CT scanning protocols. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:226–229
Tan JS, Tan KL, Lee JC, Wan CM, Leong JL, Chan LL (2009) Comparison of eye lens dose on neuroimaging protocols between 16- and 64-section multidetector CT: achieving the lowest possible dose. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:373–377
Bauknecht HC, Siebert E, Dannenberg A et al (2010) Image quality and radiation exposure in 320-row temporal bone computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 39:199–206
Niu YT, Mehta D, Zhang ZR et al (2012) Radiation dose reduction in temporal bone CT with iterative reconstruction technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1020–1026
Schwab SA, Eberle S, Adamietz B et al (2012) Comparison of 128-section single-shot technique with conventional spiral multisection CT for imaging of the temporal bone. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:E55–E60
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Thomas Henzler. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: C.L., T.A., R.R., B.S., and T.F. are employees of Siemens Healthcare, Forchheim, Germany. All other authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors with no relationship to Siemens Healthcare were in control of this study. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, case-control, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, M., Haubenreisser, H., Raupach, R. et al. Initial results of a new generation dual source CT system using only an in-plane comb filter for ultra-high resolution temporal bone imaging. Eur Radiol 25, 178–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3406-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3406-4