Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the feasibility of using a single-dose injection protocol in CT angiography (CTA) of the carotid and coronary artery with 320-row multidetector CT.
Methods
A total of 82 consecutive patients with suspected carotid artery disease underwent an original CTA protocol aiming at capturing the extra-cranial carotid arteries and coronary arteries simultaneously using 320-row MDCT. The image quality, attenuation, and CNRs of the carotid and coronary arteries were assessed. The lag time (between two separated volumetric acquisitions) was compared between patients with and without cardiac venous opacification (CVO). The contrast medium volume and radiation dose were recorded.
Results
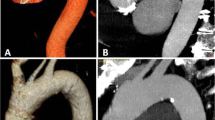
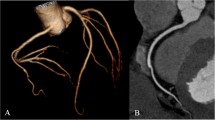
The image quality was 99.4 % diagnostic in carotid and 86.9 % in coronary artery segments. The mean attenuation of carotid and coronary arteries ranged from 462.2 Hu to 533.7 Hu, 415.9 Hu to 454.7 Hu respectively. The mean CNR of the carotid and coronary artery ranged from 15.8 to 18.9 and 17.7 to 20.4 respectively. The lag time in patients with and without CVO was 5.75 ± 1.64 s vs. 4.21 ± 1.14 s (p < 0.05). The mean radiation dose was 6.6 ± 4.1 mSv.The mean contrast media volume was 71.9 ± 9.1 ml.
Conclusions
The carotid and coronary artery can be imaged simultaneously via our original single-dose injection CTA protocol using 320-row CT with adequate image quality.
Key Points
• Carotid and coronary 320-row CTA can be achieved in a single-dose injection.
• Longer coverage was achieved with two or more volumes using 320-row CT.
• The single-dose protocol allows a reduced contrast agent dose of about 72 ml.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector computed tomography
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise ratio
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- CM:
-
Contrast media
References
Lanzer P (2003) Vascular multimorbidity in patients with documented coronary artery disease. Z Kardiol 92:650–659
Di Tullio MR, Sacco RL, Homma S (1996) Atherosclerotic disease of the aortic arch as a risk factor for recurrent ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 335:1464, author reply 1464–1465
Azen SP, Mack WJ, Cashin-Hemphill L et al (1996) Progression of coronary artery disease predicts clinical coronary events. Long-term follow-up from the Cholesterol Lowering Atherosclerosis Study. Circulation 93:34–41
Graner M, Varpula M, Kahri J et al (2006) Association of carotid intima-media thickness with angiographic severity and extent of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 97:624–629
Kablak-Ziembicka A, Tracz W, Przewlocki T et al (2004) Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease. Heart 90:1286–1290
Rohani M, Jogestrand T, Ekberg M et al (2005) Interrelation between the extent of atherosclerosis in the thoracic aorta, carotid intima-media thickness and the extent of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 179:311–316
Wintermark M, Jawadi SS, Rapp JH et al (2008) High-resolution CT imaging of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:875–882
Kuettner A, Beck T, Drosch T et al (2005) Image quality and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive coronary imaging with 16 detector slice spiral computed tomography with 188 ms temporal resolution. Heart 91:938–941
Ferencik M, Lisauskas JB, Cury RC et al (2006) Improved vessel morphology measurements in contrast-enhanced multi-detector computed tomography coronary angiography with non-linear post-processing. Eur J Radiol 57:380–383
Vanhoenacker PK, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Van Heste R et al (2007) Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT angiography for assessment of coronary artery disease: meta-analysis. Radiology 244:419–428
Hein PA, May J, Rogalla P et al (2010) Feasibility of contrast material volume reduction in coronary artery imaging using 320-slice volume CT. Eur Radiol 20:1337–1343
Durmus T, Rogalla P, Lembcke A et al (2011) Low-dose triple-rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT—less contrast medium and lower radiation exposure. Eur Radiol 21:1416–1423
Li Y, Fan Z, Lei X et al (2012) Prospective ECG-gated 320-row CT angiography of the whole aorta and coronary arteries. Eur Radiol 22:2432–2440
Austen WG, Edwards JE, Frye RL et al (1975) A reporting system on patients evaluated for coronary artery disease. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee for Grading of Coronary Artery Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery, American Heart Association. Circulation 51:5–40
Lembcke A, Wiese TH, Schnorr J (2004) Image quality of noninvasive coronary angiography using multislice spiral computed tomography and electron-beam computed tomography: intraindividual comparison in an animal model. InvestRadiol 39:357–364
Leschka S, Stolzmann P, Schmid FT et al (2008) Low kilovoltage cardiac dual-source CT: attenuation, noise, and radiation dose. Eur Radiol 18:1809–1817
Halliburton SS, Abbara S, Chen MY et al (2011) SCCT guidelines on radiation dose and dose-optimization strategies in cardiovascular CT. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 5:198–224
Mnyusiwalla A, Aviv RI, Symons SP (2009) Radiation dose from multidetector row CT imaging for acute stroke. Neuroradiology 51:635–640
Macari M, Israel GM, Hou S (2001) Infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms at multi-detector row CT angiography: intravascular enhancement without a timing acquisition. Radiology 220:519–523
Furtado AD, Adraktas DD, Brasic N et al (2010) The triple rule-out for acute ischemic stroke: imaging the brain, carotid arteries, aorta, and heart. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1290–1296
Yamamuro M, Tadamura E, Kanao S et al (2007) Coronary angiography by 64-detector row computed tomography using low dose of contrast material with saline chaser: influence of total injection volume on vessel attenuation. J Comput Assist Tomography 31:272–280
Cademartiri F, Mollet NR, van der Lugt A et al (2005) Intravenous contrast material administration at helical 16-detector row CT coronary angiography: effect of iodine concentration on vascular attenuation. Radiology 236:661–665
Bae KT, Seeck BA, Hildeboldt CF et al (2008) Contrast enhancement in cardiovascular MDCT: effect of body weight, height, body surface area, body mass index, and obesity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:777–784
From AM, Bartholmai BJ, Williams AW et al (2008) Mortality associated with nephropathy after radiographic contrast exposure. Mayo Clin Proc 83:1095–1100
Toprak O (2007) Conflicting and new risk factors for contrast induced nephropathy. J Urol 178:2277–2283
Tatsugami F, Matsuki M, Inada Y et al (2010) Feasibility of low volume injections of contrast material with a body weight-adapted iodine-dose protocol in 320-detector row coronary CT angiography. Acad Radiol 17:207–211
Kim JJ, Dillon WP, Glastonbury CM et al (2010) Sixty-four-section multidetector CT-angiography of carotid arteries: a systematic analysis of image quality and artifacts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:91–99
Napoli A, Catalano C, Francone M et al (2009) Imaging coronary and extracoronary atherosclerosis: feasibility and impact of whole-body computed tomography angiography. Eur Radiol 19:1704–1714
Bae HJ, Yoon BW, Kang DW et al (2006) Correlation of coronary and cerebral atherosclerosis: difference between extracranial and intracranial arteries. Cerebrovasc Dis 21:112–119
Tomizawa N, Komatsu S, Akahane M et al (2012) Influence of hemodynamic parameters on coronary artery attenuation with 320-detector coronary CT angiography. Eur J Radiol 81:230–233
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Mengsu Zeng. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this study. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, cross-sectional study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Jin, H., Chen, G. et al. Computed tomography angiography of carotid and coronary artery via a single-bolus injection protocol: a feasibility study using 320-row multidetector CT. Eur Radiol 24, 1628–1635 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3183-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3183-0