Abstract
Objectives
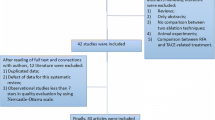
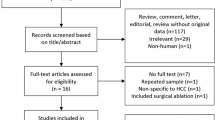
Reported rates of major complications and mortality of radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA) and percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) for the treatment of liver tumours were substantially heterogeneous among studies. The aim was to analyse the mortality and major complication rates of percutaneous RFA, PEI and MWA.
Methods
MEDLINE and EMBASE search from January 1982 to August 2010. Randomised clinical trials and observational studies, age >18, more than 50 patients for each technique analysed, studies reporting mortality and major complications were included. Random effects model was performed, with assessment for heterogeneity and publication bias.
Results
Thirty-four studies including 9531, 1185, and 1442 patients for RFA, MWA, and PEI, respectively were included. For all ablative techniques pooled proportion mortality rate was 0.16% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.10–0.24). Pooled mortality rate associated with RFA, PEI and MWA was 0.15% (0.08–0.23), 0.59% (0.14–1.3) and 0.23% (0.0–0.58) respectively. Pooled proportion of major complications was 3.29% (2.43–4.28). Major complication rates associated with RFA, MWA, and PEI was 4.1% (3.3–5.1), 4.6% (0.7–11.8) and 2.7% (0.28–7.4) respectively.
Conclusions
Percutaneous RFA, PEI and MWA can be considered safe techniques for the treatment of liver tumours.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- PEI:
-
Percutaneous ethanol injection
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SIR:
-
Society of interventional radiology
References
Sutherland LM, Williams JA, Padbury RT, Gotley DC, Stokes B, Maddern GJ (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: a systematic review. Arch Surg 141:181–190
Sherman M (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, surveillance, and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis 30:3–16
Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:346–353
Vanagas T, Gulbinas A, Pundzius J, Barauskas G (2010) Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors (I): biological background. Medicina 46:13–17
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma—The Japan Society of Hepatology 2009 update. Hepatol Res 40(Suppl 1):2–144
Bruix J, Sherman M (2010) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology (American Association for Study of Liver Disease website. Available at http://www.aasld.org/practiceguidelines/Documents/Bookmarked%20Practice%20Guidelines/HCCUpdate2010.pdf (Accessed December 28 2010))
Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R et al (2010) Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 4:439–474
Lencioni R (2010) Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 52:762–773
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, De Simone P, Filipponi F (2010) Loco-regional interventional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: techniques, outcomes, and future prospects. Transpl Int 23:698–703
Curley SA, Marra P, Beaty K et al (2004) Early and late complications after radiofrequency ablation of malignant liver tumors in 608 patients. Ann Surg 239:450–458
de Baere T, Risse O, Kuoch V et al (2003) Adverse events during radiofrequency treatment of 582 hepatic tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:695–700
Kasugai H, Osaki Y, Oka H, Kudo M, Seki T (2007) Severe complications of radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: an analysis of 3,891 ablations in 2,614 patients. Oncology 72(Suppl 1):72–75
Tateishi R, Shiina S, Teratani T et al (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer 103:1201–1209
Crocetti L, de Baere T, Lencioni R (2010) Quality improvement guidelines for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:11–17
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235:728–739
Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF et al (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for the reporting and archiving of interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S293–S295
Chou R, Helfand M (2005) Challenges in systematic reviews that assess treatment harms. Ann Intern Med 142:1090–1099
Ioannidis JPA, Evans SJW, Gotzsche PC et al (2004) Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: an extension of the CONSORT statement. Ann Intern Med 141:781–788
Loke YK, Price D, Herxheimer A, Caem G (2007) Systematic reviews of adverse effects: framework for a structured approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 7:32
Dersimonian R, Laird N (1986) Metaanalysis in clinical-trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Higgins JPT GS Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.0.0 [updated February 2008]: The Cochrane Collaboration; . Available from: www.cochrane-handbook.org (Accessed August 28 2010)
Brunello F, Veltri A, Carucci P et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation versus ethanol injection for early hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Scand J Gastroenterol 43:727–735
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Hsu CW, Chen YC (2005) Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut 54:1151–1156
Shibata T, Maetani Y, Isoda H, Hiraoka M (2006) Radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: prospective comparison of internally cooled electrode and expandable electrode. Radiology 238:346–353
Shiina S, Tagawa K, Niwa Y et al (1993) Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: results in 146 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 160:1023–1028
Livraghi T, Giorgio A, Marin G et al (1995) Hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis in 746 patients: long-term results of percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 197:101–108
Giorgio A, Tarantino L, de Stefano G et al (2000) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous ethanol injection under general anesthesia for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis: long-term results in 268 patients. Eur J Ultrasound 12:145–154
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S et al (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
Ikeda M, Okada S, Ueno H, Okusaka T, Kuriyama H (2001) Radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous ethanol injection in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study. Jpn J Clin Oncol 31:322–326
Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M, Vallisa D, Quaretti P, Rocca A (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol 11:914–921
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF et al (2003) Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology 226:441–451
Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Battocchia A, Tonon A, Fracastoro G, Cordiano C (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. Hepatogastroenterology 50:480–484
Buscarini E, Buscarini L (2004) Radiofrequency thermal ablation with expandable needle of focal liver malignancies: complication report. Eur Radiol 14:31–37
Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM et al (2003) Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics 23:123–134
Ruzzenente A, Manzoni GD, Molfetta M et al (2004) Rapid progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation. World J Gastroenterol 10:1137–1140
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2004) Radio-frequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases in 167 patients. Eur Radiol 14:2261–2267
Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K et al (2004) Large liver tumors: protocol for radiofrequency ablation and its clinical application in 110 patients–mathematic model, overlapping mode, and electrode placement process. Radiology 232:260–271
Lu DS, Yu NC, Raman SS et al (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as a bridge to liver transplantation. Hepatology 41:1130–1137
Lu MD, Xu HX, Xie XY et al (2005) Percutaneous microwave and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective comparative study. J Gastroenterol 40:1054–1060
Raut CP, Izzo F, Marra P et al (2005) Significant long-term survival after radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg Oncol 12:616–628
Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K et al (2005) Treatment efficacy of radiofrequency ablation of 338 patients with hepatic malignant tumor and the relevant complications. World J Gastroenterol 11:6395–6401
Cabassa P, Donato F, Simeone F, Grazioli L, Romanini L (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term experience with expandable needle electrodes. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:S316–S321
Solmi L, Nigro G, Roda E (2006) Therapeutic effectiveness of echo-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy with a LeVeen needle electrode in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 12:1098–1104
Choi D, Lim HK, Rhim H et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma as a first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in a large single-institution series. Eur Radiol 17:684–692
Choi D, Lim HK, Rhim H et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: long-term results and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol 14:2319–2329
Poggi G, Riccardi A, Quaretti P et al (2007) Complications of percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation of primary and secondary lesions of the liver. Anticancer Res 27:2911–2916
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M et al (2008) Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology 47:82–89
Kondo Y, Yoshida H, Tateishi R, Shiina S, Kawabe T, Omata M (2008) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver cancer in the hepatic dome using the intrapleural fluid infusion technique. Br J Surg 95:996–1004
Tsai WL, Cheng JS, Lai KH et al (2008) Clinical trial: percutaneous acetic acid injection vs. percutaneous ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma—a long-term follow-up study. Aliment Pharm Therapy 28:304–311
Zavaglia C, Corso R, Rampoldi A et al (2008) Is percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma a safe procedure? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:196–201
Chen TM, Huang PT, Lin LF, Tung JN (2008) Major complications of ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablations for liver malignancies: single center experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:e445–e450
Casaril A, Abu Hilal M, Harb A, Campagnaro T, Mansueto G, Nicoli N (2008) The safety of radiofrequency thermal ablation in the treatment of liver malignancies. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:668–672
Sartori S, Tombesi P, Macario F et al (2008) Subcapsular liver tumors treated with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: a prospective comparison with nonsubcapsular liver tumors for safety and effectiveness. Radiology 248:670–679
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2009) Five-year survival in 309 patients with colorectal liver metastases treated with radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol 19:1206–1213
Liang P, Wang Y, Yu X, Dong B (2009) Malignant liver tumors: treatment with percutaneous microwave ablation–complications among cohort of 1136 patients. Radiology 251:933–940
Bouza C, Lopez-Cuadrado T, Alcazar R, Saz-Parkinson Z, Amate JM (2009) Meta-analysis of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus ethanol injection in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol 9:31
Ong SL, Gravante G, Metcalfe MS, Strickland AD, Dennison AR, Lloyd DM (2009) Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation for primary and secondary liver malignancies: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:599–605
Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y et al (2002) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223:331–337
Llovet JM, Vilana R, Bru C et al (2001) Increased risk of tumor seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 33:1124–1129
Livraghi T, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L (2005) Risk of tumour seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg 92:856–858
Stigliano R, Marelli L, Yu D, Davies N, Patch D, Burroughs A (2007) Seeding risk following percutaneous approach to hepatocellular carcinoma—seeding following percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. What is the risk and the outcome? Seeding risk for percutaneous approach of HCC. Liver Transplant 13:1603–1603
Imamura J, Tateishi R, Shiina S et al (2008) Neoplastic seeding after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 103:3057–3062
Latteri F, Sandonato L, Di Marco V et al (2008) Seeding after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a prospective study. Dig Liver Dis 40:684–689
Poon RT, Ng KK, Lam CM, Ai V, Yuen J, Fan ST (2004) Radiofrequency ablation for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 11:281–289
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by Health Sciences Research Grants of The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (Research on Hepatitis).The supporters had no role in study design; collection, analysis, interpretation of data; writing of the report or decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Search terms for databases.
For PubMed,
“Liver Neoplasms”[majr] AND (“Ethanol Injection”[TIAB] OR “Ablation”[TIAB] OR “Ablative therapy”[TIAB] OR “Thermal Ablation”[TIAB] OR “radiofrequency”[TIAB] OR “RFA”[TIAB] OR “PEI”[TIAB] OR “PEIT”[TIAB] OR “Ethanol/administration and dosage”[MH] OR “Injections, Intralesional”[MH] OR “microwave”[TIAB]) AND 1982/1: 2010/8[dp]) NOT Review[pt] NOT Case reports[pt]
For EMBASE
(ethanol:ab AND injection:ab) OR ablation:ab OR (ablative:ab AND therapy:ab) OR (thermal:ab AND ablation:ab) OR radiofrequency:ab OR rfa:ab OR pei:ab OR peit:ab OR microwave:ab OR (ethanol:ti AND injection:ti) OR ablation:ti OR (ablative:ti AND therapy:ti) OR (thermal:ti AND ablation:ti) OR radiofrequency:ti OR rfa:ti OR pei:ti OR peit:ti AND ‘liver tumor’/exp/mj AND [english]/lim AND [1-1-1982]/sd NOT [1-8-2010]/sd NOT [review]/lim NOT [medline]/lim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertot, L.C., Sato, M., Tateishi, R. et al. Mortality and complication rates of percutaneous ablative techniques for the treatment of liver tumors: a systematic review. Eur Radiol 21, 2584–2596 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2222-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2222-3