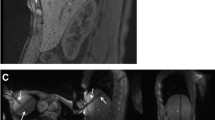
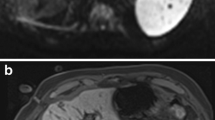
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of magnetic resonance (MR)-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation for small liver tumours with poor conspicuity on both contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (US) and computed tomography (CT), using fast navigation and temperature monitoring.
Methods
Sixteen malignant liver nodules (long-axis diameter, 0.6–2.4 cm) were treated with multipolar RF ablation on a 1.5-T wide-bore MR system in ten patients. Targeting was performed interactively, using a fast steady-state free precession sequence. Real-time MR-based temperature mapping was performed, using gradient echo–echo planar imaging (GRE-EPI) and hardware filtering. MR-specific treatment data were recorded. The mean follow-up time was 19 ± 7 months.
Results
Correct placement of RF electrodes was obtained in all procedures (image update, <500 ms; mean targeting time, 21 ± 11 min). MR thermometry was available for 14 of 16 nodules (88%) with an accuracy of 1.6°C in a non-heated region. No correlation was found between the size of the lethal thermal dose and the ablation zone at follow-up imaging. The primary and secondary effectiveness rates were 100% and 91%, respectively.
Conclusions
RF ablation of small liver tumours can be planned, targeted, monitored and controlled with MR imaging within acceptable procedure times. Temperature mapping is technically feasible, but the clinical benefit remains to be proven.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llovet J, Bruix J (2008) Novel advancements in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in 2008. J Hepatol 48(Suppl 1):20–37. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.022
Lencioni R, Crocetti L (2008) Image-guided thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 66:200–207. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2008.01.003
Mentha G, Majno P, Terraz S et al (2007) Treatment strategies for the management of advanced colorectal liver metastases detected synchronously with the primary tumour. Eur J Surg Oncol 33(Suppl 1):76–83. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2007.09.016
Reuter NP, Woodall CE, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM, Martin RC (2009) Radiofrequency ablation vs resection for hepatic colorectal metastasis: therapeutically equivalent. J Gastrointest Surg 13:486–491. doi:10.1007/s11605-008-0727-0
Willatt JM, Hussain HK, Adusumilli S, Marrero JA (2008) MR Imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: challenges and controversies. Radiology 247:311–330. doi:10.1148/radiol.2472061331
Onishi H, Murakami T, Kim T et al (2006) Hepatic metastases: detection with multi-detector row CT, SPIO-enhanced MR imaging, and both techniques combined. Radiology 239:131–138. doi:10.1148/radiol.2383041825
Bipat S, van Leeuwen M, Comans E et al (2005) Colorectal liver metastases: CT, MR imaging, and PET for diagnosis—meta-analysis. Radiology 237:123–131. doi:10.1148/radiol.2371042060
Quesson B, de Zwart JA, Moonen CT (2000) Magnetic resonance temperature imaging for guidance of thermotherapy. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:525–533
Cernicanu A, Lepetit-Coiffé M, Viallon M, Terraz S, Becker CD (2007) New horizons in MR-controlled and monitored radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours. Cancer imaging 7:160–166. doi:10.1102/1470-7330.2007.0022
de Senneville B, Mougenot C, Quesson B, Dragonu I, Grenier N, Moonen C (2007) MR thermometry for monitoring tumor ablation. Eur Radiol 17:2401–2410. doi:10.1007/s00330-007-0646-6
Kelekis A, Terraz S, Roggan A et al (2003) Percutaneous treatment of liver tumors with an adapted probe for cooled-tip, impedance-controlled radio-frequency ablation under open-magnet MR guidance: initial results. Eur Radiol 13:1100–1105. doi:10.1007/s00330-003-1847-2
Clasen S, Pereira P (2008) Magnetic resonance guidance for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:421–433. doi:10.1002/jmri.21264
Clasen S, Boss A, Schmidt D et al (2007) MR-guided radiofrequency ablation in a 0.2-T open MR system: technical success and technique effectiveness in 100 liver tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:1043–1052. doi:10.1002/jmri.21120
Boss A, Rempp H, Martirosian P et al (2008) Wide-bore 1.5 Tesla MR imagers for guidance and monitoring of radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: initial experience on feasibility. Eur Radiol 18:1449–1455. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-0894-0
Laumonier H, Blanc JF, Quesson B et al (2006) Real-time monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma radiofrequency ablation by quantitative temperature MRI. Semin Liver Dis 26:391–397. doi:10.1055/s-2006-951605
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235:728–739. doi:10.1148/radiol.2353042205
Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42:1208–1236. doi:10.1002/hep.20933
Frericks BB, Ritz JP, Roggan A, Wolf KJ, Albrecht T (2005) Multipolar radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: initial experience. Radiology 237:1056–1062. doi:10.1148/radiol.2373041104
Terraz S, Constantin C, Majno PE, Spahr L, Mentha G, Becker CD (2007) Image-guided multipolar radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours: initial clinical results. Eur Radiol 17:2253–2261. doi:10.1007/s00330-007-0626-x
Rosset A, Spadola L, Pysher L, Ratib O (2006) Informatics in radiology (infoRAD): navigating the fifth dimension: innovative interface for multidimensional multimodality image navigation. Radiographics 26:299–308. doi:10.1148/rg.261055066
Cernicanu A, Lepetit-Coiffe M, Roland J, Becker CD, Terraz S (2008) Validation of fast MR thermometry at 1.5 T with gradient-echo echo planar imaging sequences: phantom and clinical feasibility studies. NMR Biomed 21:849–858. doi:10.1002/nbm.1267
Sapareto SA, Dewey WC (1984) Thermal dose determination in cancer therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 10:787–800
Leoni CJ, Potter JE, Rosen MP, Brophy DP, Lang EV (2001) Classifying complications of interventional procedures: a survey of practicing radiologists. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:55–59
Vigen K, Jarrard J, Rieke V, Frisoli J, Daniel B, Butts Pauly K (2006) In vivo porcine liver radiofrequency ablation with simultaneous MR temperature imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:578–584. doi:10.1002/jmri.20528
Lepetit-Coiffé M, Quesson B, Seror O et al (2006) Real-time monitoring of radiofrequency ablation of rabbit liver by respiratory-gated quantitative temperature MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:152–159. doi:10.1002/jmri.20605
Zhang Q, Chung YC, Lewin JS, Duerk JL (1998) A method for simultaneous RF ablation and MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:110–114. doi:10.1002/jmri.1880080122
Mertyna P, Dewhirst MW, Halpern E, Goldberg W, Goldberg SN (2008) Radiofrequency ablation: the effect of distance and baseline temperature on thermal dose required for coagulation. Int J Hypertherm 4:1–10. doi:10.1080/02656730802035662
Dromain C, de Baere T, Elias D et al (2002) Hepatic tumors treated with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: CT and MR imaging follow-up. Radiology 223:255–262. doi:10.1148/radiol.2231010780
Vigen KK, Daniel BL, Pauly JM, Butts K (2003) Triggered, navigated, multi-baseline method for proton resonance frequency temperature mapping with respiratory motion. Magn Reson Med 50:1003–1010. doi:10.1002/mrm.10608
Rieke V, Vigen KK, Sommer G, Daniel BL, Pauly JM, Butts K (2004) Referenceless PRF shift thermometry. Magn Reson Med 51:1223–1231. doi:10.1002/mrm.20090
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank André Roggan, PhD (Celon AG), Jörg Roland, PhD (Siemens Medical Solutions) and Erik Dumont, PhD (Image Guided Therapy) for valuable assistance and technical support.
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation–National Center for Competence in Research (NCCR), Computer-Aided Medical Interventions (CO-ME) Phase 2 Funding n° 51NF40–111383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terraz, S., Cernicanu, A., Lepetit-Coiffé, M. et al. Radiofrequency ablation of small liver malignancies under magnetic resonance guidance: progress in targeting and preliminary observations with temperature monitoring. Eur Radiol 20, 886–897 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1611-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1611-3