Abstract
Objectives
Three-dimensional (3-D) selective- and relative-scale texture analysis (TA) was applied to structural magnetic resonance (MR) brain images to quantify the presence of grey-matter (GM) and white-matter (WM) textural abnormalities associated with schizophrenia.
Materials and methods
Brain TA comprised volume filtration using the Laplacian of Gaussian filter to highlight fine, medium and coarse textures within GM and WM, followed by texture quantification. Relative TA (e.g. ratio of fine to medium) was also computed. T1-weighted MR whole-brain images from 32 participants with diagnosis of schizophrenia (n = 10) and healthy controls (n = 22) were examined. Five patients possessed marker alleles (SZ8) associated with schizophrenia on chromosome 8 in the pericentriolar material 1 gene while the remaining five had not inherited any of the alleles (SZ0).
Results
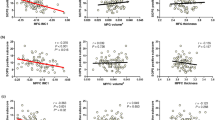
Filtered fine GM texture (mean grey-level intensity; MGI) most significantly differentiated schizophrenic patients from controls (P = 0.0058; area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve = 0.809, sensitivity = 90%, specificity = 70%). WM measurements did not distinguish the two groups. Filtered GM and WM textures (MGI) correlated with total GM and WM volume respectively. Medium-to-coarse GM entropy distinguished SZ0 from controls (P = 0.0069) while measures from SZ8 were intermediate between the two.
Conclusions
3-D TA of brain MR enables detection of subtle distributed morphological features associated with schizophrenia, determined partly by susceptibility genes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woolley J, McGuire P (2005) Neuroimaging in schizophrenia: what does it tell the clinician? Adv Psychiatr Treat 11:195–202
Weinberger DR, Torrey EF, Neophytides AN, Wyatt RJ (1979) Structural abnormalities in the cerebral cortex of chronic schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatr 36:935–939
Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Frith CD et al (1976) Cerebral ventricular size and cognitive impairment in chronic schizophrenia. Lancet 2:924–926
Harvey I, Ron MA, Du Boulay G et al (1993) Reduction of cortical volume in schizophrenia on magnetic resonance imaging. Psychol Med 23:591–604
Lim KO, Tew W, Kushner M et al (1996) Cortical grey matter volume deficit in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatr 153:1548–1553
Wright IC, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff PW et al (2000) Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatr 157:16–25
Nelson MD, Saykin AJ, Flashman LA et al (1998) Hippocampal volume reduction in schizophrenia as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging: a meta-analytic study. Arch Gen Psychiatr 55:433–440
Gur RE, Maany V, Mozley PD et al (1998) Subcortical MRI volumes in neuroleptic-naive and treated patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatr 155:1711–1717
Lawrie SM, McIntosh AM, Hall J et al (2008) Brain structure and function changes during the development of schizophrenia: the evidence from studies of subjects at increased genetic risk. Schizophr Bull 34:330–340
Lawrie SM, Abukmeil SS (1998) Brain abnormality in schizophrenia. A systematic and quantitative review of volumetric magnetic resonance imaging studies. Br J Psychiatr 160:179–186
Liddle PF (1987) Schizophrenic syndromes, cognitive performance and neurological dysfunction. Psychol Med 17:49–57
Lerski R (2006) Clinical applications of texture analysis. In: Hajek M, Dezortova M, Materka A, Lerski R (eds) Texture analysis for magnetic resonance imaging. Med4publishing, Prague, pp 151–187
Kloppel S, Stonnington CM et al (2008) Automatic classification of MR scans in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 131:681–689
Freeborough PA, Fox NC (1998) MR image texture analysis applied to the diagnosis and tracking of Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE Trans Med Imag 17:475–479
Liu Y, Teverovskiy L, Carmichael O et al (2004) Discriminative MR image feature analysis for automatic schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease classification. Technical report CMU-RI-TR-04-15. The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh
Kovalev VA, Petrou M, Suckling J (2003) Detection of structural differences between the brains of schizophrenic patients and controls. Psychiatr Res 124:177–189
Im K, Lee JM et al (2006) Fractal dimension in human cortical surface: multiple regression analysis with cortical thickness, sulcal depth, and folding area. Hum Brain Mapp 27:994–1003
Gurling H, Critchley H, Datta SR et al (2006) Genetic association and brain morphology studies and the chromosome 8p22 pericentriolar material 1 (PCM1) gene in susceptibility to schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatr 63:844–854
Deichmann R, Good CD, Josephs O, Ashburner J, Turner R (2000) Optimization of 3-D MP-RAGE sequences for structural brain imaging. NeuroImage 12:112–127
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry: the methods. NeuroImage 11:805–821
Ganeshan B, Miles KA, Young RCD, Chatwin CR (2008) Three dimensional selective-scale texture analysis of CT pulmonary angiograms. Invest Radiol 43:382–394
Jonsson SA, Luts A, Guldberg-Kjaer N, Ohman R (1999) Pyramidal neuron size in the hippocampus of schizophrenics correlates with total cell count and degree of cell disarray. Eur Arch Psychiatr Clin Neurosci 249:169–173
Casanova MF, Rothberg B (2002) Shape distortion of the hippocampus: a possible explanation of the pyramidal cell disarray reported in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 55:19–24
Roberts RC, Roche JK, Conley RR (2005) Synaptic differences in the postmortem striatum of subjects with schizophrenia: a stereological ultrastructural analysis. Synapse 56:185–197
Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Escámez T et al (2006) Variations in genes regulating neuronal migration predict reduced prefrontal cognition in schizophrenia and bipolar subjects from Mediterranean Spain: a preliminary study. Neuroscience 139:1289–1300
Haroutunian V, Davis KL (2007) Introduction to the special section: myelin and oligodendrocyte abnormalities in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:499–502
Konrad A, Winterer G (2008) Disturbed structural connectivity in schizophrenia sprimary factor in pathology or epiphenomenon? Schizophr Bull 34:72–92
Zilles K (1990) In: Paxinos G (ed) The human nervous system. Academic, San Diego, pp 757–802
Von Economo C (1929) The cytoarchitectonics of the human cerebral cortex. Oxford University Press, London
Moorhead TWJ, Harris JM et al (2006) Automated computation of the gyrification index in prefrontal lobes: methods and comparison with manual implementation. NeuroImage 31:1560–1566
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. PNAS 97:11050–11055
Harris JM, Yates S et al (2004) Gyrification in first-episode schizophrenia: a morphometric study. Biol Psychiatr 55:141–147
Kulynych JJ, Luevano LF et al (1997) Cortical abnormality in schizophrenia: an in vivo application of the gyrification index. Biol Psychiatr 41:995–999
Sallet PC, Elkis H et al (2003) Reduced cortical folding in schizophrenia: an MRI morphometric study. Am J Psychiatr 160:1606–1613
Vogeley K, Tepest R et al (2001) Right frontal hypergyria differentiation in affected and unaffected siblings from families multiply affected with schizophrenia: a morphometric MRI study. Am J Psychiatr 158:494–496
Harris JM, Whalley H et al (2004) Abnormal cortical folding in high risk individuals: a predictor of the development of schizophrenia? Biol Psychiatr 56:182–189
Hariri AR, Weinberger DR (2003) Imaging genomics. Br Med Bull 65:259–270
Kendler KS, Myers JM et al (2000) Clinical features of schizophrenia and linkage to chromosomes 5q, 6p, 8p, and 10p in the Irish study of high density schizophrenia families. Am J Psychiatr 157:402–408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganeshan, B., Miles, K.A., Young, R.C.D. et al. Three-dimensional textural analysis of brain images reveals distributed grey-matter abnormalities in schizophrenia. Eur Radiol 20, 941–948 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1605-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1605-1