Abstract
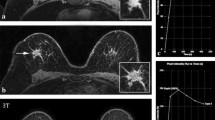
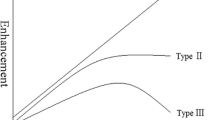
We compared the detection of malignant lesions in two different methods of parametric-guided analysis to the widely used early subtraction images. The parametric colour-coded overlays were defined by the increase of signal intensity after contrast injection and the course of the time signal intensity curve. Exams of 30 patients with histopathological evidence of 32 invasive breast carcinomas were evaluated. Five hundred five areas of additional enhancing tissue were found in the early subtraction images. The sensitivity was 100 in the subtraction images and 100 and 93.8 in the parametric images, respectively, the specificity 67.5, 84.2 and 88.7, respectively. On average 4.4 ROI-measurements were needed to find the highest increase of signal intensity in the subtraction series compared to 1.9 in the parametric images. Properly selected thresholds in parametric imaging may be helpful in the differentiation of enhancing tissue. Furthermore the parametric image-guided ROI selection significantly speeds up the analysis and makes it safer as a lower rate of ROI-measurements is needed to find the strongest enhancement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sardanelli F, Iozzelli A, Fausto A (2003) MR imaging of the breast: indications, established technique, and new directions. Eur Radiol 13(Suppl 3):N28–N36
Kuhl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S, Leutner C, Wardelmann E, Gieseke J, Schild HH (1999) Dynamic breast MR imaging: are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211:101–110
Helbich TH (2000) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. Eur J Radiol 34:208–219
Szabo BK, Aspelin P, Kristoffersen Wiberg M, Tot T, Bone B (2003) Invasive breast cancer: correlation of dynamic MR features with prognostic factors. Eur Radiol 13:2425–2435
Schnall MD, Blume J, Bluemke DA, DeAngelis GA, DeBruhl N, Harms S, Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Hylton N, Kuhl CK, Pisano ED, Causer P, Schnitt SJ, Thickman D, Stelling CB, Weatherall PT, Lehman C, Gatsonis CA (2006) Diagnostic architectural and dynamic features at breast MR imaging: multicenter study. Radiology 238:42–53
Agoston AT, Daniel BL, Herfkens RJ, Ikeda DM, Birdwell RL, Heiss SG, Sawyer-Glover AM (2001) Intensity-modulated parametric mapping for simultaneous display of rapid dynamic and high-spatial-resolution breast MR imaging data. Radiographics 21:217–226
Kelcz F, Furman-Haran E, Grobgeld D, Degani H (2002) Clinical testing of high-spatial-resolution parametric contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1485–1492
Hauth EA, Jaeger H, Maderwald S, Stockamp C, Muhler A, Kimmig R, Forsting M (2006) Evaluation of quantitative parametric analysis for characterization of breast lesions in contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Eur Radiol 16(12):2834–2841
Hoffmann U, Brix G, Knopp MV, Hess T, Lorenz WJ (1995) Pharmacokinetic mapping of the breast: a new method for dynamic MR mammography. Magn Reson Med 33:506–514
Parker GJ, Suckling J, Tanner SF, Padhani AR, Revell PB, Husband JE, Leach MO (1997) Probing tumor microvascularity by measurement, analysis and display of contrast agent uptake kinetics. J Magn Reson Imaging 7:564–574
Jacobs MA, Barker PB, Bluemke DA, Maranto C, Arnold C, Herskovits EH, Bhujwalla Z (2003) Benign and malignant breast lesions: diagnosis with multiparametric MR imaging. Radiology 229:225–232
Degani H, Gusis V, Weinstein D, Fields S, Strano S (1997) Mapping pathophysiological features of breast tumors by MRI at high spatial resolution. Nat Med 3:780–782
Furman-Haran E, Schechtman E, Kelcz F, Kirshenbaum K, Degani H (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging reveals functional diversity of the vasculature in benign and malignant breast lesions. Cancer 104:708–718
Turkat TJ, Klein BD, Polan RL, Richman RH (1994) Dynamic MR mammography: a technique for potentially reducing the biopsy rate for benign breast disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 4:563–568
Szabo BK, Aspelin P, Wiberg MK (2004) Neural network approach to the segmentation and classification of dynamic magnetic resonance images of the breast: comparison with empiric and quantitative kinetic parameters. Acad Radiol 11:1344–1354
Baum F, Fischer U, Vosshenrich R, Grabbe E (2002) Classification of hypervascularized lesions in CE MR imaging of the breast. Eur Radiol 12:1087–1092
Brinck U, Fischer U, Korabiowska M, Jutrowski M, Schauer A, Grabbe E (1997) The variability of fibroadenoma in contrast-enhanced dynamic MR mammography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:1331–1334
Heywang SH, Hahn D, Schmidt H, Krischke I, Eiermann W, Bassermann R, Lissner J (1986) MR imaging of the breast using gadolinium-DTPA. J Comput Assist Tomogr 10:199–204
Weinstein D, Strano S, Cohen P, Fields S, Gomori JM, Degani H (1999) Breast fibroadenoma: mapping of pathophysiologic features with three-time-point, contrast-enhanced MR imaging-pilot study. Radiology 210:233–240
Boetes C, Barentsz JO, Mus RD, van der Sluis RF, van Erning LJ, Hendriks JH, Holland R, Ruys SH (1994) MR characterization of suspicious breast lesions with a gadolinium-enhanced TurboFLASH subtraction technique. Radiology 193:777–781
Gilles R, Guinebretiere JM, Lucidarme O, Cluzel P, Janaud G, Finet JF, Tardivon A, Masselot J, Vanel D (1994) Nonpalpable breast tumors: diagnosis with contrast-enhanced subtraction dynamic MR imaging. Radiology 191:625–631
Harms SE, Flamig DP, Hesley KL, Meiches MD, Jensen RA, Evans WP, Savino DA, Wells RV (1993) MR imaging of the breast with rotating delivery of excitation off resonance: clinical experience with pathologic correlation. Radiology 187:493–501
Heiberg EV, Perman WH, Herrmann VM, Janney CG (1996) Dynamic sequential 3D gadolinium-enhanced MRI of the whole breast. Magn Reson Imaging 14:337–348
Ercolani P, Valeri G, Amici F (1998) Dynamic MRI of the breast. Eur J Radiol 27(Suppl 2):S265–S271
Hauth EA, Stockamp C, Maderwald S, Muhler A, Kimmig R, Jaeger H, Barkhausen J, Forsting M (2006) Evaluation of the three-time-point method for diagnosis of breast lesions in contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Clin Imaging 30:160–165
Kuhl CK, Schild HH, Morakkabati N (2005) Dynamic bilateral contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast: trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution. Radiology 236:789–800
Mussurakis S, Buckley DL, Horsman A (1997) Dynamic MRI of invasive breast cancer: assessment of three region-of-interest analysis methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:431–438
Mussurakis S, Gibbs P, Horsman A (1998) Primary breast abnormalities: selective pixel sampling on dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR images. Radiology 206:465–473
Lehman CD, Peacock S, DeMartini WB, Chen X (2006) A new automated software system to evaluate breast MR examinations: improved specificity without decreased sensitivity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:51–56
Safir J (2005) 3TP and magnetic resonance breast imaging: interview with Dr. Julian Safir. Integr Cancer Ther 4:45–47
Kuhl CK (2000) MRI of breast tumors. Eur Radiol 10:46–58
Mariano MN, van den Bosch MA, Daniel BL, Nowels KW, Birdwell RL, Fong KJ, Desmond PS, Plevritis S, Stables LA, Zakhour M, Herfkens RJ, Ikeda DM (2005) Contrast-enhanced MRI of ductal carcinoma in situ: characteristics of a new intensity-modulated parametric mapping technique correlated with histopathologic findings. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:520–526
Vomweg TW, Teifke A, Kunz RP, Hintze C, Hlawatsch A, Kern A, Kreitner KF, Thelen M (2004) Combination of low and high resolution sequences in two orientations for dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: more than a compromise. Eur Radiol 14:1732–1742
Wedegartner U, Bick U, Wortler K, Rummeny E, Bongartz G (2001) Differentiation between benign and malignant findings on MR-mammography: usefulness of morphological criteria. Eur Radiol 11:1645–1650
Obenauer S, Schorn C, Stelter B, Fischer U, Grabbe E (2002) Contrast-enhanced high in-plane resolution dynamic MRI of the breast. Are there advantages in comparison to standard dynamic MRI? Clin Imaging 26:161–165
Kriege M, Brekelmans CT, Boetes C, Muller SH, Zonderland HM, Obdeijn IM, Manoliu RA, Kok T, Rutgers EJ, de Koning HJ, Klijn JG (2006) Differences between first and subsequent rounds of the MRISC breast cancer screening program for women with a familial or genetic predisposition. Cancer 106:2318–2326
Bazzocchi M, Zuiani C, Panizza P, Del Frate C, Soldano F, Isola M, Sardanelli F, Giuseppetti GM, Simonetti G, Lattanzio V, Del Maschio A (2006) Contrast-enhanced breast MRI in patients with suspicious microcalcifications on mammography: results of a multicenter trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1723–1732
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurz, K.D., Wittsack, HJ., Willers, R. et al. Dynamic breast MR imaging: is parametric mapping superior to image subtraction in lesion detection?. Eur Radiol 17, 3093–3099 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0652-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0652-8