Abstract
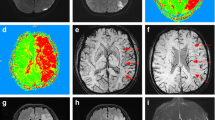
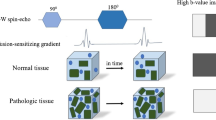
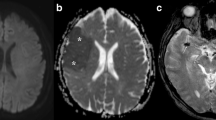
The aim of our study was to investigate the usefulness of high-b-value diffusion-weighted (DW) MR imaging in patients with acute cerebral infarction. DW images at b-values of 1,000, 2,000, and 3,000 s/mm2 were performed for 32 patients 48 h after the onset of stroke using a 1.5 T clinical imager. The area of restricted diffusion became more distinct and extensive with increasing b-value in 19 of 32 patients, especially in patients with the atherothrombotic-type cerebral infarction. The visualized extent of infarction was almost the same among the area of restricted diffusion on the b=3,000 ADC map, b=3,000 DWI and final infarction in 12 of 15 patients. High-b-value DWI provided better identification of lesion extension in the cerebral ischemia. It is suggested that the size of the final infarction or irreversible cytotoxic edema is more predictable on high-b-value DWIs than on the usual b=1,000 DWI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauchamp NJ, Barker PB, Wang PY, vanZijl PC (1999) Imaging of acute cerebral ischemia. Radiology 212:307–324
Yoshiura T, Wu O, Zaheer A, Reese TG, Sorensen AG (2001) High-diffusion-sensitized MRI of brain: dissociation of gray and white matter. Magn Reson Med 45:734–740
Meyer JR, Gutierrez A, Mock B et al (2000) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of suspected brain infarction. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1821–1829
Burdette JH, Elster AD (2002) Diffusion-weighted imaging of cerebral infarctions: are higher B-values better? J Comut Assist Tomogr 26:622–627
Toyoda K, Ida M, Tozaki M, Ojiri H, Ujita M, Fukuda K (2002) Clinical application of high-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cases with infarction and tumorous condition. Proceedings of 40th annual meeting American Society of Neuroradiology, Vancouver, British Colombia, Canada 244
Thurnher MM, Castillo M (2005) Imaging in acute stroke. Eur Radiol 15:408-415 DOI 10.1007/s00330-004-2630-8
Lovblad KO, Baird AE (2005) Actual diagnostic approach to the acute stroke patient. Eur Radiol 15:1–17 DOI 10.1007/s00330-005-0130-3
Baird AE, Benfield A, Schlaug G et al (1997) Enlargement of human cerebral ischemic lesion volumes measured by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 41:581–589
Lovblad KO, Baird AE, Schlaug G et al (1997) Ischemic lesion volumes in acute stroke by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging correlate with clinical outcome. Ann Neurol 42:164–170
Sorensen AG, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG et al (1996) Hyperacute stroke: evaluation with combined multisection diffusion weighted and hemodynamically weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 199:391–401
Soher BJ, Gillard JH, Bryan RN et al (1998) MR perfusion imaging in acute middle cerebral artery stroke: comparison of blood volume and bolus arrival time. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 7:17–23
Schaefer PW, Hunter GJ, He J et al (2002) Predicting cerebral ischemic infarct volume with diffusion and perfusion MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1785–1794
Rovira A, Grive E, Rovira A, Alvarez-Sabin J (2005) Distribution territories and causative mechanisms of ischemic stroke. Eur Radiol 15:416–426 DOI 10.1007/s00330-004-2633-5
Benfield A, Griswald M, Jakob P, Edelman R, Warach S (1997) Optimisation of diffusion weighted imaging: a theoretical approach to sequence programming. Proceedings of the 6th annual meeting of ISMRM, Vancouver, British Colombia, Canada, 1747
DeLano MC, Cooper TG, Siebert JE, Potchen MJ, Kuppusamy K (2000) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of adult brain: image contrast and apparent diffusion coefficient map features. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1830–1836
Burdette JH, Elster AD, Ricci PE (1999) Acute cerebral infarction: quantification of spin-density and T2 shine-through phenomena on diffusion-weighted MR images. Radiology 212:333–339
Kim HJ, Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Suh DC (2005) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of hyperacute ischemic stroke at 1.5T. Am J Neuroradiol 26:208–215
Lev MH, Farkas J, Gemmete JJ et al (1999) Acute stroke: improved nonenhanced CT detection: benefits of soft-copy interpretation by using variable window width and center level settings. Radiology 213:150–155
Watanabe Y, Yoshiura T, Mihara F, Tanaka A, Sorensen AG, Masuda K (1999) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging: mapping of fast and slow diffusion components. JJMRM 22:22–25
Benfield A, Prasad PV, Edelman RR, Warach S (1996) On the optimal b-value for measurement of lesion volumes in acute human stroke by diffusion-weighted imaging. Proceedings of the 4th annual meeting of ISMRM, New York, USA 1344
Kuhl CK, Gieseke J, von Falkenhausen M et al (2005) Sensitivity encoding for diffusion-weighted MR imaging at 3.0T: intraindividual comparative study. Radiology 234:517–526
Wardlaw JM, Keir SL, Bastin ME, Armitage PA, Rana AK (2002) Is diffusion imaging appearance an independent predictor of outcome after ischemic stroke? Neurology 59:1381–1387
Dávalos A, Blanco M, Pedraza S et al (2004) The clinical-DWI mismatch: a new diagnostic approach to the brain tissue at risk of infarction. Neurology 62:2187–2192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toyoda, K., Kitai, S., Ida, M. et al. Usefulness of high-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging in acute cerebral infarction. Eur Radiol 17, 1212–1220 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0397-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0397-9