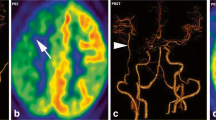
Abstract
Assessment was made of the cerebral vascular haemodynamic parameters in patients with a high-flow extra-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass performed for therapeutic occlusion of the internal carotid artery (ICA). Sixteen patients with ICA occlusion and EC-IC bypass (time interval from surgery 1–6 years) underwent MRI. Perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (PW-MRI) sequences were performed without the use of an arterial input function. The relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV), mean transit time (MTT) and relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF) were evaluated in all patients at the level of the basal ganglia, centrum semiovale and cortex in both hemispheres. Statistically significant differences (P<0.005) were observed in the haemodynamic parameters, indicating increased rCBV in the basal ganglia and decreased rCBF and rCBV in the cortex of the hemisphere supplied by the graft with respect to the contralateral. Patients with occlusion of the ICA and high flow EC-IC bypass do have altered vascular haemodynamic status between the hemispheres. In particular, rCBF is impaired in the surgical hemisphere at the level of the cortex. These patients should be followed-up to rule out chronic ischemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fox AJ, Vinuela F, Peltz DK et al (1987) Use of detachable balloonsfor proximal artery occlusion in the treatment of unclippable cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 66:40–44
Spetzler RF, Fukushima T, Martin N, Zabramski J (1990) Petrous carotid-to-intradural carotid saphenous vein graft for intracavernous giant aneurysm, tumor and occlusive cerebrovasculardisease. J Neurosurg 73:496–501
Liu JK, Couldwell WT (2003) Interpositional carotid artery bypass strategies in the surgical management of aneurysms and tumors of the skull base. Neurosurg Focus 14:e2
Caramia F, Santoro F, Pantano P, Passacantilli E, Guidetti G, Pierallini A, Fantozzi LM, Cantore GP, Bozzao L (2001) Cerebral hemodynamics on MR perfusion images before and after bypass surgery in patients with giant intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1704–1710
Iwama T, Hashimoto N, Hayashida K (2001) Cerebral hemodynamic parameters for patients with neurological improvements after extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass surgery: evaluation using positron emission tomography. Neurosurgery 48:504–510
Anderson DE, McLane MP, Reichman OH, Origitano TC (1992) Improved cerebral blood flow and CO2 reactivity after microvascular anastomosis in patients at high risk for recurrent stroke. Neurosurgery 31:26–34
Baron JC, Bousser MG, Rey A, Guillard A, Comer D, Castaigne P (1981) Reversal of focal “misery-perfusion syndrome” by extraintracranial arterial bypass in hemodynamic cerebral ischemia: A case study with 15-O positron emission tomography. Stroke 12:454–459
Batjer HH, Devous MD Sr, Purdy PD, Mickey B, Bonte FJ, Samson D (1988) Improvement in regional cerebral blood flow and cerebral vasoreactivity after extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass. Neurosurgery 22:913–919
Samson Y, Baron JC, Bousser MG, Rey A, Derlon JM, David P, Comoy J (1985) Effects of extra-intracranial arterial bypass on cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in humans. Stroke 16:609–616
Schmiedek P, Piepgras A, Leinsinger G, Kirsh CM, Einhäupl K (1994) Improvement of cerebrovascular reserve capacity by EC-IC arterial bypass surgery in patients with ICA occlusion and hemodynamic cerebral ischemia. J Neurosurg 81:236–244
Neff KW, Horn P, Dinter D, Vajkoczy P, Schmiedek P, Duber C (2004) Extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass surgery improves total brain blood supply in selected symptomatic patients with unilateral internal carotid artery occlusion and insufficient collateralization. Neuroradiology 46:730–737
Murata Y, Katayama Y, Sakatani K, Fukaya C, Kano T (2003) Evaluation of extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass function by using near-infrared spectroscopy. J Neurosurg 99:304–310
Hendrikse J, van der Zwan A, Ramos LM, van Osch MJ, Golay X, Tulleken CA, van der Grond J (2005) Altered flow territories after extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery. Neurosurgery 57:486–494
Leblanc R, Tyler JL, Mohr G, Meyer E, Diksic M, Yamamoto L, Taylor L, Gauthier S, Hakim A (1987) Hemodynamic and metabolic effects of cerebral revascularization. J Neurosurg 66:529–535
Nielsen H, Hojer-Pedersen E, Gulliksen G, Haase J, Enevoldosen E (1986) Reversible ischemic neurological deficit and minor strokes before and after EC/IC bypass surgery: a neuropsychological study. Acta Neurol Scand 73:615–618
Takagi Y, Hashimoto N, Iwama T, Hayashida K (1997) Improvement of oxygen metabolic reserve after extracranial-intracranial bypass surgery in patients with severe haemodynamic insufficiency. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 139:52–56; 56–57
Petrella JR, DeCarli C, Dagli M, Grandin CB, Duyn JH, Frank JA, Hoffman EA, Theodore WH (1998) Age-related vasodilatory response to acetazolamide challenge in healthy adults: a dynamic contrast-enhanced MR study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:39–44
Kim JH, Lee SJ, Shin T, Kang KH, Choi PY, Kim JH, Gong JC, Choi NC, Lim BH (2000) Correlative assessment of hemodynamic parameters obtained with T2*-weighted perfusion MR imaging and SPECT in symptomatic carotid artery occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1450–1456
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozzao, A., Fasoli, F., Finocchi, V. et al. Long term evaluation of brain perfusion with magnetic resonance in high flow extracranial-intracranial saphenous graft bypass. Eur Radiol 17, 33–38 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0293-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0293-3