Abstract
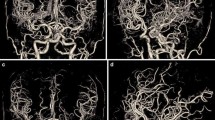
The aim of this prospective, multireader trial was to investigate image quality and vascular delineation of cranial multislice CT angiography (MSCTA) to identify strengths and weaknesses of the method. Sixty consecutive patients underwent standardized cranial MSCTA. The mean estimated effective dose was 0.96±0.11 mSv. Three masked readers independently graded image quality parameters and vascular delineation on a 5-point scale. Vascular attenuation values and dose-length products were assessed quantitatively. Quantitative parameters were evaluated with a proportional odds regression model with bootstrapped standard errors to adjust the relevant standard errors for correlation within subjects and across readers. The non-parametric Wilcoxon sign-rank test was applied for quantitative measurements. Good to excellent ratings were observed regarding image quality parameters and vascular delineation. The delineation of veins was rated higher than that of arteries (OR 2.00). Smaller arterial segments were rated significantly less favorably than larger segments (OR up to 26.98). Moreover, the cavernous sinus, the C2 segment of the ICA and the communicating arteries demonstrated lower scores. Attenuation values were >240 HU and vessel-to-parenchyma ratios >7 in all vessels. Cranial MSCTA achieved high ratings regarding image quality and vascular delineation. Relative weaknesses were found in small arterial subsegments and in vessels in close topographical proximity to bone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubin GD, Shiau MC, Schmidt AJ et al. (1999) Computed tomographic angiography: historical perspective and new state-of-the-art using multi detector-row helical computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23(Suppl 1):S83–S90
Kalender WA, Seissler W, Klotz E, Vock P (1990) Spiral volumetric CT with single-breath-hold technique, continuous transport, and continuous scanner rotation. Radiology 176:181–183
Klingenbeck-Regn K, Schaller S, Flohr T, Ohnesorge B, Kopp AF, Baum U (1999) Subsecond multi-slice computed tomography: basics and applications. Eur J Radiol 31:110–124
Polacin A, Kalender WA, Marchal G (1992) Evaluation of section sensitivity profiles and image noise in spiral CT. Radiology 185:29–35
White PM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V (2000) Can noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review. Radiology 217:361–370
Kato Y, Nair S, Sano H et al. (2002) Multi-slice 3D-CTA—an improvement over single slice helical CTA for cerebral aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:715–722
Tomandl BF, Klotz E, Handschu R et al. (2003) Comprehensive imaging of ischemic stroke with multisection CT. Radiographics 23:565–592
Klingebiel R, Zimmer C, Rogalla P et al. (2001) Assessment of the arteriovenous cerebrovascular system by multi-slice CT. A single-bolus, monophasic protocol. Acta Radiol 42:560–562
Klingebiel R, Busch M, Bohner G, Zimmer C, Hoffmann O, Masuhr F (2002) Multi-slice CT angiography in the evaluation of patients with acute cerebrovascular disease—a promising new diagnostic tool. J Neurol 249:43–49
Jones TR, Kaplan RT, Lane B, Atlas SW, Rubin GD (2001) Single- versus multi-detector row CT of the brain: quality assessment. Radiology 219:750–755
Ghaye B, Szapiro D, Mastora I et al. (2001) Peripheral pulmonary arteries: how far in the lung does multi-detector row spiral CT allow analysis? Radiology 219:629–636
Kudo K, Terae S, Asano T et al. (2003) Anterior spinal artery and artery of Adamkiewicz detected by using multi-detector row CT. Am J Neuroradiol 24:13–17
Hidajat N, Maurer J, Schroder RJ et al. (1999) Relationships between physical dose quantities and patient dose in CT. Br J Radiol 72:556–561
Efron B, Halloran E, Holmes S (1996) Bootstrap confidence levels for phylogenetic trees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13429–13434
Carmelo A, Ficola A, Fravolini ML, La Cava M, Maira G, Mangiola A (2002) ICP and CBF regulation: a new hypothesis to explain the “windkessel” phenomenon. Acta Neurochir Suppl 81:112–116
Acuff CG, Hoskins G, Moore NA, Rockhold RW (1996) Acute cerebral artery constriction in the spontaneously hypertensive rat following blood and plasma administration into the subarachnoid space. J Biomed Sci 3:117–125
Fukuhara T, Duoville CM, Eliott JP, Newell DW, Winn HR (1998) Relationship between intracranial pressure and the development of vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir 38:710–715
Ertl-Wagner BB, Hoffmann RT, Bruening R, Herrmann K, Dichgans M, Reiser MF (2004) Blurring of the vessels of the interhemispheric fissure in multislice CT angiography: a sign of meningeal carcinomatosis. Eur Radiol 14:673–678
van der Lugt A, Buter TC, Govaere F, Siepman DA, Tanghe HL, Dippel DW (2004) Accuracy of CT angiography in the assessment of a fetal origin of the posterior cerebral artery. Eur Radiol 14:1627–1633
van Straten M, Venema HW, Streekstra GJ, Majoie CB, den Heeten GJ, Grimbergen CA (2004) Removal of bone in CT angiography of the cervical arteries by piecewise matched mask bone elimination. Med Phys 31:2924–2933
Venema HW, den Heeten GJ (2003) Subtraction helical CT angiography of intra- and extracranial vessels: technical considerations and preliminary experience-rediscovery of matched mask bone elimination? Am J Neuroradiol 24:1491 (author reply 1491–1492)
Venema HW, Hulsmans FJ, den Heeten GJ (2001) CT angiography of the circle of Willis and intracranial internal carotid arteries: maximum intensity projection with matched mask bone elimination-feasibility study. Radiology 218:893–898
Luboldt W, Weber R, Seemann M, Desantis M, Reiser M (1999) Influence of helical CT parameters on spatial resolution in CT angiography performed with a subsecond scanner. Invest Radiol 34:421–426
Polacin A, Kalender WA, Brink J, Vannier MA (1994) Measurement of slice sensitivity profiles in spiral CT. Med Phys 21:133–140
Imanishi Y, Fukui A, Niimi H et al. Radiation-induced temporary hair loss as a radiation damage only occurring in patients who had the combination of MDCT and DSA. Eur Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00330-004-2459-1
Huda W, Chamberlain CC, Rosenbaum AE, Garrisi W (2001) Radiation doses to infants and adults undergoing head CT examinations. Med Phys 28:393–399
Hamberg L, Rhea JT, Hunter GJ, Thrall JH (2003) Multi-detector row CT: radiation dose characteristics. Radiology 226:762–772
Ertl-Wagner BB, Hoffmann RT, Bruning R et al. (2004) Multi-detector row CT angiography of the brain at various kilovoltage settings. Radiology 231:528–535
Sohaib SA, Peppercorn PD, Horrocks JA, Keene MH, Kenyon GS, Reznek RH (2001) The effect of decreasing mAs on image quality and patient dose in sinus CT. Br J Radiol 74:157–161
Prasad SRWC, Shepard JA, McLoud T, Rhea J (2002) Standard-dose and 50%-reduced dose chest CT: comparing the effect on image quality. Am J Roentgenol 179:461–465
Garg K, Keith RL, Byers T, Kelly K, Kerzner AL, Lynch DA, Miller YE (2002) Randomized controlled trial with low-dose spiral CT for lung cancer screening: feasibility study and first results. Radiology 225:506–510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ertl-Wagner, B.B., Bruening, R., Blume, J. et al. Prospective, multireader evaluation of image quality and vascular delineation of multislice CT angiography of the brain. Eur Radiol 15, 1051–1059 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2689-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2689-x