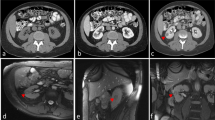
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that when ultrasound (US) guidance is not feasible, abdominal biopsies can be performed safely and accurately under magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance in a low-field environment. MRI-guided abdominal biopsy was performed on 31 consecutive patients, in whom US-guided abdominal biopsy was not possible because the lesion was not visualized in US (n=27) or an US-guided procedure was not considered safe (n=4). The locations of the lesions were liver (n=14), pancreas (n=6), lymph node (n=4), retroperitoneal mass (n=3), adrenal gland (n=3) and spleen (n=1). The average size of the lesion was 2.2 cm (range 1–4 cm) in maximum diameter. All procedures were done by using a 0.23-T open-configuration C-arm-shaped MRI scanner with interventional optical tracking equipment and software. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy was performed on all 31 patients; 18 patients underwent both FNA biopsy and cutting needle core biopsy. Procedures were evaluated for diagnostic sensitivity, specificity and accuracy as well as procedure time and complications. The FNA biopsy specimens were adequate for interpretation in 27 (87%) of 31 cases. Two of these proved to be false-negative findings during follow-up or subsequent biopsy. The final diagnosis was malignant in 15 and benign in 16 patients. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of FNA biopsy were 71, 100 and 81%, respectively. Of the 18 core-needle biopsies, one was determined false-negative owing to nonrepresentativeness. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of histological samples were 90, 100 and 94%, respectively. The needle time was 19 min on average and the mean room time was 1 h 48 min. No immediate or late complications occurred. MRI-guided abdominal biopsy can be performed safely and accurately in a low-field environment in patients for whom an US-guided procedure is not feasible.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gazelle GS, Haaga JR (1991) Imaging-guided percutaneous abdominal biopsy. Oncology 5:27–38
Douglas BR, Charboneau JW, Reading CC (2001) Ultrasound-guided intervention: expanding horizons. Radiol Clin North Am 39:415–428
Brandt KR, Charboneau JW, Stephens DH, Welch TJ, Goellner JR (1993) CT- and US-guided biopsy of the pancreas. Radiology 187:99–104
Welch TJ, Sheedy PF, II, Johnson CD, Johnson CM, Stephens DH (1989) CT-guided biopsy: prospective analysis of 1,000 procedures. Radiology 171:493–496
Sequeiros RB, Hyvonen P, Sequeiros AB et al (2003) MR imaging-guided laser ablation of osteoid osteomas with use of optical instrument guidance at 0.23 T. Eur Radiol 13:2309–2314
Kreitner KF, Loew R, Runkel M, Zollner J, Thelen M (2003) Low-field MR arthrography of the shoulder joint: technique, indications, and clinical results. Eur Radiol 13:320–329
Alanen J, Keski-Nisula L, Blanco-Sequeiros R, Tervonen O (2004) Cost comparison analysis of low-field (0.23 T) MRI- and CT-guided bone biopsies. Eur Radiol 14:123–128
Mueller PR, Stark DD, Simeone JF et al (1986) MR-guided aspiration biopsy: needle design and clinical trials. Radiology 161:605–609
Frahm C, Gehl HB, Weiss HD, Rossberg WA (1996) Technique of MRT-guided core biopsy in the abdomen using an open low-field scanner: feasibility and initial clinical results. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 164:62–67
Mahfouz AE, Rahmouni A, Zylbersztejn C, Mathieu D (1996) MR-guided biopsy using ultrafast T1- and T2-weighted reordered turbo fast low-angle shot sequences: feasibility and preliminary clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167:167–169
vanSonnenberg E, Hajek P, Gylys-Morin V et al (1988) A wire-sheath system for MR-guided biopsy and drainage: laboratory studies and experience in 10 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 151:815–817
Lee MH, Lufkin RB, Borges A et al (1998) MR-guided procedures using contemporaneous imaging frameless stereotaxis in an open-configuration system. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:998–1005
Konig CW, Pereira PL, Trubenbach J et al (2003) MR imaging-guided adrenal biopsy using an open low-field-strength scanner and MR fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1567–1570
Adam G, Neuerburg J, Bucker A et al (1997) Interventional magnetic resonance. Initial clinical experience with a 1.5-tesla magnetic resonance system combined with c-arm fluoroscopy. Invest Radiol 32:191–197
Salomonowitz E (2001) MR imaging-guided biopsy and therapeutic intervention in a closed-configuration magnet: single-center series of 361 punctures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:159–163
Langen HJ, Kugel H, Landwehr P (2002) MR-guided core biopsies using a closed 1.0 T imager. First clinical results. Eur J Radiol 41:19–25
Rofsky NM, Yang BM, Schlossberg P, Goldenberg A, Teperman LW, Weinreb JC (1998) MR-guided needle aspiration biopsies of hepatic masses using a closed bore magnet. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:633–637
Lu DS, Lee H, Farahani K, Sinha S, Lufkin R (1997) Biopsy of hepatic dome lesions: semi-real-time coronal MR guidance technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:737–739
Silverman SG, Collick BD, Figueira MR et al (1995) Interactive MR-guided biopsy in an open-configuration MR imaging system. Radiology 197:175–181
Lewin JS, Petersilge CA, Hatem SF et al (1998) Interactive MR imaging-guided biopsy and aspiration with a modified clinical C-arm system. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:1593–1601
Schmidt AJ, Kee ST, Sze DY et al (1999) Diagnostic yield of MR-guided liver biopsies compared with CT- and US-guided liver biopsies. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:1323–1329
Adam G, Bucker A, Nolte-Ernsting C, Tacke J, Gunther RW (1999) Interventional MR imaging: percutaneous abdominal and skeletal biopsies and drainages of the abdomen. Eur Radiol 9:1471–1478
Lu DS, Silverman SG, Raman SS (1999) MR-guided therapy. Applications in the abdomen. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 7:337–348
Blanco Sequeiros R, Klemola R, Ojala R et al (2002) MRI-guided trephine biopsy and fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of bone lesions in low-field (0.23 T) MRI system using optical instrument tracking. Eur Radiol 12:830–835
Ojala R, Vahala E, Karppinen J et al (2000) Nerve root infiltration of the first sacral root with MRI guidance. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:556–561
Langen HJ, Kugel H, Grewe S, Gindele A, Landwehr P, Fischbach R (2000) MR-guided biopsy using respiratory-triggered high-resolution T2-weighted sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:834–836
Tikkakoski T, Paivansalo M, Siniluoto T et al (1993) Percutaneous ultrasound-guided biopsy. Fine needle biopsy, cutting needle biopsy, or both? Acta Radiol 34:30–34
Klapman JB, Logrono R, Dye CE, Waxman I (2003) Clinical impact of on-site cytopathology interpretation on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1289–1294
Lewin JS, Nour SG, Duerk JL (2000) Magnetic resonance image-guided biopsy and aspiration. Top Magn Reson Imaging 11:173–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kariniemi, J., Blanco Sequeiros, R., Ojala, R. et al. MRI-guided abdominal biopsy in a 0.23-T open-configuration MRI system. Eur Radiol 15, 1256–1262 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2566-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2566-z