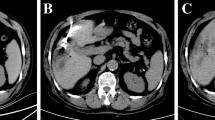
Abstract
The aim of this study was to establish whether using a percutaneously inserted metallic coil as a target facilitates the radiofrequency (RF) ablation of tumors poorly seen on unenhanced computed tomography (CT) or ultrasound (US) studies. We inserted a metallic coil percutaneously via a 21-gauge needle under CT guidance into five tumors during the phase of contrast enhancement in five patients. The coil was subsequently used as a target to guide placement of the RF electrode under fluoroscopic guidance. The precision of position was then checked with CT or US. We also carried out a small experimental study to establish the effect of metallic coils on the pattern of coagulation induced by RF. Placement of a metallic coil into the tumor enabled rapid and accurate placement of the RF electrode. The tumors were ablated with no adverse effects. The experimental study showed that the area of coagulation extends predictably along the coil. The application of the above technique is useful when using RF to ablate tumors poorly visualized on US and unenhanced CT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Solbiati L, Ierace T, Tonolini M et al (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic metastases. Eur J Ultrasound 13:149–158
Livraghi T, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Ultrasound 13:159–166
Wood TF, Rose M, Chung M et al (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of 231 unresectable hepatic tumors: indications, limitations, and complications. Ann Surg Oncol 7:593–600
Wong SL, Edwards MJ, Chao C et al (2001) Radiofrequency ablation for unresectable hepatic tumors. Am J Surg 182:552–557
Buscarini E, Buscarini L (2003) Radiofrequency thermal ablation with expandable needle of focal liver malignancies. Eur Radiol 14:31–37
Sica GT, Ji H, Ros PR (2002) Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic metastases. Clin Liver Dis 6:165–179
Pedro MS, Semelka RC, Braga L (2002) MR imaging of hepatic metastases. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 10:15–29
Skjoldbye B, Pedersen MH, Struckmann J et al (2002) Improved detection and biopsy of solid liver lesions using pulse-inversion ultrasound scanning and contrast agent infusion. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:439–444
de Baere T, Bessoud B, Dromain C et al (2002) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors during temporary venous occlusion. Am J Roentgenol 178:53–59
Hohmann J, Skrok J, Puls R et al (2003) Characterization of focal liver lesions with contrast-enhanced low MI real time ultrasound and SonoVue. RoFo 175:835–843
Boll DT, Lewin JS, Duerk JL, Merkle EM (2003) Do surgical clips interfere with radiofrequency thermal ablation? Am J Roentgenol 180:1557–1560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adam, A., Hatzidakis, A., Hamady, M. et al. Percutaneous coil placement prior to radiofrequency ablation of poorly visible hepatic tumors. Eur Radiol 14, 1688–1691 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2294-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2294-4