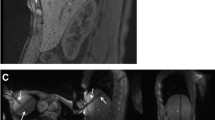
Abstract
Percutaneous radio-frequency (RF) ablation of liver tumors is usually performed under guidance of real-time US, but some tumor nodules in some patients cannot be adequately visualized with this technique. We report our preliminary results with an MR-compatible, internally perfused 17-G RF probe adapted to a standard RF generator for impedance-controlled RF ablation under MR guidance. Following initial testing of the probe for MR compatibility, artifacts and macroscopic effects on an ex vivo pig liver, four patients with eight neoplastic liver nodules (five metastatic and three primary), which could not be properly targeted by US, were treated with the cooled-tip technique under MRI guidance in an open 0.23-T magnet. Metallic artifacts produced by the probe were useful for accurate placement and did not interfere with MRI monitoring at the end of the procedure. Based on imaging findings, the immediate result of RF was considered adequate in all instances. Local recurrence occurred in one instance after 6 months, requiring repeat treatment. No adverse effects were noted. Initial experience suggests that the probe we used allows to perform impedance-controlled cooled-tip RF ablation of liver tumors under open-magnet MR guidance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2000) Survival after percutaneous, image-guided, thermal ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 43:656–661
Livraghi T (2001)Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by interventional methods. Eur Radiol 11:2207–2219
Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Meloni F, Dellanoce M, Cova L, Halpern EF, Gazelle GS (2001) Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients. Radiology 221:159–166
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS (2001) Radio frequency tissue ablation: physical principles and techniques for increasing coagulation necrosis. Hepatogastroenterology 48:359–367
Lewin JS, Connell CF, Duerk JL, Chung YC, Clampitt ME, Spisak J, Gazelle GS, Haaga JR (1998) Interactive MRI-guided radio frequency interstitial thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: clinical trial for evaluation of safety and feasibility. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:40–47
Huppert PE, Trübenbach J, Schick F, Pereira P, König C, Claussen CD (2000) MRI-guided percutaneous radio frequency ablation of hepatic neoplasms: first technical and clinical experiences. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 172:692–700
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Bartolozzi C (2001) Percutaneous radio frequency thermal ablation of liver malignancies: techniques, indications, imaging findings and clinical results. Abdom Imaging 26:345–360
Bartolozzi C, Donati F, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Lencioni R (2000) MnDPDP-enhanced MRI vs dual-phase spiral CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 10:1697–1702
Oudkerk M, Torres CG, Song B, König M, Grimm J, Fernandez–Cuadrado J, de Beck BO, Marquardt M, van Dijk P, de Groot JC (2002) Characterization of liver lesions with mangafodipir trisodium-enhanced MR imaging: multicenter study comparing MR and dual-phase spiral CT. Radiology 223:517–524
Braga HJV, Choti MA, Lee VS, Paulson EK, Siegelman ES, Bluemke DA (2002) Liver lesions: manganese-enhanced MR and dual-phase helical CT for preoperative detection and characterization—comparison with receiver operating characteristic analysis. Radiology 223:525–531
Schlup S, Becker CD, Terrier F, Mentha G, Roth A (2001) Détection de lésions hépatiques en IRM après injection de MN-DPDP: Comparaison à haut (1.5T) et bas (0.23T) champs magnétiques et CT. Swiss Medical Forum (Suppl) 3:27
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Research Foundation (grant no. 3100–057186.99/1); CO-ME: Computer-Aided and Image-Guided Medical Interventions; Celon, Berlin, Germany; the Research Foundation Carlos et Elsie de Reuter, Geneva, Switzerland; the Foundation for Research in Oncology, Geneva, Switzerland; and Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands. The authors also thank T. Andreae, Helsinki, and Dominique Joliat and Marco Giammello, Geneva, for their important technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelekis, A.D., Terraz, S., Roggan, A. et al. Percutaneous treatment of liver tumors with an adapted probe for cooled-tip, impedance-controlled radio-frequency ablation under open-magnet MR guidance: initial results. Eur Radiol 13, 1100–1105 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1847-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1847-2