Abstract.
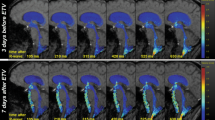
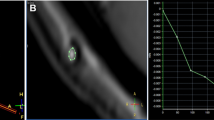
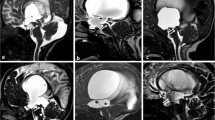
The aim of this study was evaluation of a fast and slow-flow sensitive 2D steady-state free-precession sequence for its capability to prove the patency of endoscopic third ventriculostomy (TVS) in obstructive hydrocephalus, and to exclude communicating third ventricle prior to TVS. We compared gated and ungated variants of this sequence for this purpose. Twenty-three patients with obstructive hydrocephalus underwent 36 MR examinations with a 2D reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession (PSIF) sequence in a retrospectively cardiac gated (cine) and a faster but ungated version beside T1- and T2-weighted sequences in three planes. Thirteen patients were examined both before and after TVS, 4 patients solely before, and 6 patients solely after TVS. Imaging diagnoses were compared with intraoperative findings and clinical findings after TVS. Preoperative diagnosis of non-communicating third ventricle and cisterns was intraoperatively confirmed in 16 of 17 cases. Preoperative MRI was inconclusive in 1 case. Postoperative MRI revealed sufficient TVS in 16 of 19 cases and obstructed TVS in 3 of 19 cases due to several reasons. Findings at MRI were consistent in 19 of 19 cases with the clinical course and intraoperative results. The faster but ungated PSIF sequence was found to be diagnostically equivalent to the cardiac gated cine sequence. The CSF flow imaging with a 2D reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession sequence in conjunction with conventional T1- and T2-weighted images is a fast and reliable tool for pre- and postoperative functional evaluation in third ventriculostomy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulkarni AV, Drake JM, Armstrong DC, Dirks PB (2000) Imaging correlates of successful third ventriculostomy. J Neurosurg 92:915–919
Missir O, Dormont D, Pierot L (1989) MR visualization of CSF flow through a ventriculo-cisternostomy. Neuroradiology 31:93–94
Maeder P, Gudinchet F, Meuli R, Fankhauser H (1998) Dynamic MRI of cerebrospinal fluid flow in endoscopic percutaneous ventriculostomy. Br J Neurosurg 12:18–22
Wilcock DJ, Jaspan T, Worthington BS, Punt J (1997) Neuro-endoscopic third ventriculostomy: evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Radiol 52:50–54
Jack CR Jr, Kelly PJ (1989) Stereotactic third ventriculostomy: assessment of patency with MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 10:512–522
Kim SK, Wang KC, Cho BK (2000) Surgical outcome of pediatric hydrocephalus treated by endoscopic III ventriculostomy: prognostic factors and interpretation of postoperative neuroimaging. Childs Nerv Syst 16:161–169
Lev S, Bhadelia RA, Estin D, Heilman CB, Wolpert SM (1997) Functional analysis of third ventriculostomy patency with phase-contrast MRI velocity measurements. Neuroradiology 39:175–179
Rovira A, Capellades J, Grive E et al. (1999) Spontaneous ventriculostomy: report of three cases revealed by flow-sensitive phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1647–1652
Fukuhara T, Vorster SJ, Ruggieri P, Luciano MG (1999) Third ventriculostomy patency: comparison of findings at cine phase-contrast MR imaging and at direct exploration. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1560–1566
Foroutan M, Mafee MF, Dujovny M (1998) Third ventriculostomy, phase-contrast cine MRI and endoscopic techniques. Neurol Res 20:443–448
Kim MH, Shin KM, Song JH (1998) Cine MR CSF flow study in hydrocephalus: What are the valuable parameters? Acta Neurochir (Suppl) 71:343–346
Goumnerova LC, Frim DM (1997) Treatment of hydrocephalus with third ventriculostomy: outcome and CSF flow patterns. Pediatr Neurosurg 27:149–152
Connor SE, O'Gorman R, Summers P et al. (2001) Spamm, cine phase contrast imaging and fast spin-echo T2-weighted imaging in the study of intracranial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow. Clin Radiol 56:763–772
Laitt RD, Mallucci CL, Jaspan T, McConachie NS, Vloeberghs M, Punt J (1999) Constructive interference in steady-state 3D Fourier-transform MRI in the management of hydrocephalus and third ventriculostomy. Neuroradiology 41:117–123
Hoffmann KT, Hosten N, Meyer BU et al. (2000) CSF flow studies of intracranial cysts and cyst-like lesions achieved using reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession MR sequences. Am J Neuroradiol 21:493–502
Patz S, Hawkes RC (1986) The application of steady-state free precession to the study of very slow fluid flow. Magn Reson Med 3:140–145
Jolesz FA, Patz S, Hawkes RC, Lopez I (1987) Fast imaging of CSF flow/motion patterns using steady-state free precession (SSFP). Invest Radiol 22:761–771
Axel L, Dougherty L (1989) MR imaging of motion with spatial modulation of magnetization. Radiology 171:841–845
Cinalli G, Salazar C, Mallucci C, Yada JZ, Zerah M, Sainte-Rose C (1998) The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of shunt malfunction. Neurosurgery 43:1323–1329
Bruder H, Fischer H, Graumann R, Deimling M (1988) A new steady-state imaging sequence for simultaneous acquisition of two MR images with clearly different contrasts. Magn Reson Med 7:35–42
Schellinger D, Le Bihan D, Rajan SS et al. (1992) MR of slow CSF flow in the spine. Am J Neuroradiol 13:1393–1403
Kelly PJ (1991) Stereotactic third ventriculostomy in patients with nontumoral adolescent/adult onset aqueductal stenosis and symptomatic hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 75:865–873
Quencer RM (1992) Intracranial CSF flow in pediatric hydrocephalus: evaluation with cine-MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 13:601–608
Casselman JW, Kuhweide R, Deimling M, Ampe W, Dehaene I, Meeus L (1993) Constructive interference in steady state-3DFT MR imaging of the inner ear and cerebellopontine angle. Am J Neuroradiol 14:47–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, K.T., Lehmann, T.N., Baumann, C. et al. CSF flow imaging in the management of third ventriculostomy with a reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession sequence. Eur Radiol 13, 1432–1437 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1776-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1776-5