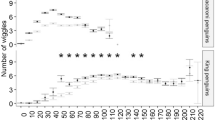
Abstract
Elephant seals are one of the most proficient diving mammals in the world and are also one of the most studied. However, their long periods at sea and pelagic habits make research into their foraging ecology particularly challenging. Most current understanding comes from the use of time-depth recorders (TDRs). We used TDRs that additionally recorded body pitch and roll on four juvenile southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) foraging over the Patagonian Shelf to describe their diving behaviour and compared them with those of adults, using standard descriptions of elephant seal dive profile types provided by the literature. Over 280 days of diving data showed that dive types were similar to those of adults (types: A, B, C, D, Eb and Ef) but that dive types A and C differed slightly, probably because our animals were constrained by bottom topography. Steep dive and return-to-surface angles in all dive types except type B indicate that animals generally attempt to maximize vertical displacement. Horizontal displacement was much greater in type B dives, which indicates a travelling function. Pitching and rolling behaviour lends support to the functions ascribed to the dive types already described for adult elephant seals, although type Eb dives are unusual in that the animals appear to be taking prey by up-ending in the benthos.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailleul F, Charrassin JB, Ezraty R, Girard-Ardhuin F, McMahon CR, Field I, Guinet C (2007) Southern elephant seal from Kerguelen Islands confronted by Antarctic sea ice. Changes in movements and in diving behaviour. Deep-Sea Res II 54:343–355
Bailleul F, Pinaud D, Hindell M, Charrassin JB, Guinet C (2008) Assessment of scale-dependent foraging behaviour in southern elephant seals incorporating the vertical dimension: a development of the First Passage Time method. J Anim Ecol 77:948–957
Bailleul F, Cotté C, Guinet C (2010) Mesoscale eddies as foraging area of a deep-diving predator, the southern elephant seal. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 408:251–264
Bennett KA, McConnell BJ, Fedak MA (2001) Diurnal and seasonal variations in the duration and depth of the longest dives in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) possible physiological and behavioural constraints. J Exp Biol 204:649–662
Biuw M, McConnell B, Bradshaw CJA, Burton H, Fedak M (2003) Blubber and buoyancy: monitoring the body condition of free-ranging seals using simple dive characteristics. J Exp Biol 206:3405–3423
Biuw M, Boehme L, Guinet C, Hindell MA, Costa DP, Charrassin JB, Roquet F, Bailleul F, Meredith M, Thorpe S, Tremblay Y, McDonald BI, Park Y-H, Rintoul SR, Bindoff N, Goebel ME, Crocker DE, Lovell P, Nicholson J, Monks F, Fedak M (2007) Variations in behavior and condition of a Southern Ocean top predator in relation to in situ oceanographic conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13705–13710
Boyd IL (1997) The behavioural and physiological ecology of diving. Trends Ecol Evol 12:213–217
Bradshaw CJA, Higgins J, Michael KJ, Wotherspoon SJ, Hindell MA (2004) At-sea distribution of female southern elephant seals relative to variation in ocean surface properties. ICES J Mar Sci 61:1014–1027
Campagna C, Le Boeuf BJ, Blackwell SB, Crocker DE, Quintana F (1995) Diving behaviour and foraging location of female southern elephant seals from Patagonia. J Zool 236:55–71
Campagna C, Fedak MA, McConnell BJ (1999) Post-breeding distribution and diving behaviour of adult male southern elephant seals from Patagonia. J Mammal 80(4):1341–1352
Campagna C, Rivas AL, Marin MR (2000) Temperature and depth profiles recorded during dives of elephant seals reflect distinct ocean environments. J Mar Syst 24:299–312
Campagna C, Dignani J, Blackwell SB, Marín MR (2001) Detecting bioluminiscence with an irradiance time-depth recorder deployed on southern elephant seals. Mar Mamm Sci 17:402–414
Campagna C, Piola AR, Marín MR, Lewis M, Fernández T (2006) Southern elephant seal trajectories, fronts and eddies in the Brazil/Malvinas confluence. Deep-Sea Res I 53:1907–1924
Campagna C, Piola AR, Marín MR, Lewis M, Zajaczkovski U, Fernández T (2007) Deep divers in shallow seas: Southern elephant seals on the Patagonian shelf. Deep-Sea Res I 54:1792–1814
Crocker DE, Le Boeuf BJ, Naito Y, Asaga T, Costa DP (1994) Swim speed and dive function in a female northern elephant seal. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior and Physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 328–337
Crocker DE, Le Boeuf BJ, Costa DP (1997) Drift diving in female northern elephant seals: implications for food processing. Can J Zool 75:27–39
Davis RW, Weihs D (2007) Locomotion in diving elephant seals: physical and physiological constraints. Phil Trans R Soc B 362:2141–2150
Davis RW, Fuiman LA, Williams TM, Le Boeuf BJ (2001) Three-dimensional movements and swimming activity of a northern elephant seal. Comp Biochem Physiol A 129:759–770
Davis RW, Fuiman LA, Williams TM, Horning M, Hagey W (2003) Classification of Weddell seals dives based on 3-dimensional movements and video-recorded observations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 264:109–122
Gómez Laich A, Wilson RP, Quintana F, Shepard ELC (2008) Identification of imperial cormorant Phalacrocorax atriceps behaviour using accelerometers. Endang Species Res. doi:10.3354/esr00091
Hassrick JL, Crocker DE, Zeno RL, Blackwell SB, Costa DP, Le Boeuf BJ (2007) Swimming speed and foraging strategies of northern elephant seals. Deep-Sea Res II 54:369–383
Hassrick JL, Crocker DE, Teutschel NM, McDonald BI, Robinson PW, Simmons SE, Costa DP (2010) Condition and mass impact oxygen stores and dive duration in adult female northern elephant seals. J Exp Biol 213:585–592
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1991a) The diving behaviour of adult male and female southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina (Pinnipedia: Phocidae). Aust J Zool 39:595–619
Hindell MA, Burton HR, Slip DJ (1991b) Foraging areas of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, as inferred from water temperature data. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 42:115–128
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR, Bryden MM (1992) Physiological implications of continuous, prolonged, and deep dives of the southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina). Can J Zool 70:370–379
Hindell MA, McConnell BJ, Fedak MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR, Reijnders PJH, McMahon CR (1999) Environmental and physiological determinants of successful foraging by naive southern elephant seal pups during their first trip to sea. Can J Zool 77:1807–1821
Hindell MA, Lea M-A, Morrice MG, MacMahon CR (2000) Metabolic limits on dive duration and swimming speed in the Southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina. Physiol Biol Zool 73:790–798
Irvine LG, Hindell MA, van den Hoff J, Burton HR (2000) The influence of body size on dive duration of underyearling southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). J Zool 251:463–471
Kato A, Ropert-Coudert Y, Gremillet D, Cannell B (2006) Locomotion and foraging strategy in foot-propelled and wing-propelled shallow-diving seabirds. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 308:293–301
Kooyman GL (1989) Diverse divers: physiology and behavior. Springer-Verlag, New York
Kooyman GL (2006) Mysteries of adaptation to hypoxia and pressure in marine mammals. Mar Mamm Sci 22:507–526
Kooyman GL, Ponganis PJ (1998) The physiological basis of diving to depth: birds and mammals. Annu Rev Physiol 60:19–32
Kuhn CE, Crocker DE, Tremblay Y, Costa DP (2009) Time to eat: measurements of feeding behaviour in a large marine predator, the northern elephant seal Mirounga angustirostris. J Anim Ecol 78:513–523
Le Boeuf BJ, Costa DP, Huntley AC, Feldkamp SD (1988) Continuous, deep diving in female northern elephant seals, Mirounga angustirostris. Can J Zool 66:446–458
Le Boeuf BJ, Naito Y, Huntley AC, Asaga T (1989) Prolonged, continuous, deep diving by northern elephant seals. Can J Zool 67:2514–2519
Le Boeuf BJ, Naito Y, Asaga T, Crocker DE (1992) Swim speed in a female northern elephant seal: metabolic rate and foraging implications. Can J Zool 70:786–795
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Blackwell SB, Morris PA, Thorson PH (1993) Sex differences in the diving and foraging behaviour of northern elephant seals. Dissertation, Symposium of the zoological society of London
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Blackwell SB, Webb PM, Houser DS (2000) Foraging ecology of northern elephant seals. Ecol Monogr 70:353–382
Liebsch N (2006) Hankering back to ancestral pasts: constraints on two pinnipeds, Phoca vitulina & Leptonychotes weddellii foraging from a central place. Dissertation, Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel
Meir JU, Champagne CD, Costa DP, Williams CL, Ponganis PJ (2009) Extreme hypoxemic tolerance and blood oxygen depletion in diving elephant seals. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R927–R939
Mitani Y, Andrews RD, Sato K, Kato A, Naito Y, Costa DP (2010) Three-dimensional resting behaviour of northern elephant seals: drifting like a falling leaf. Biol Lett 6:163–166
R Development Core Team (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, http://www.R-project.org
Ropert-Coudert Y, Grémillet D, Kato A, Ryan PG, Naito Y, Le Maho Y (2004) A fine-scale time budget of Cape gannets provides insights into the foraging strategies of coastal seabirds. Anim Behav 67:985–992
Sato K, Mitani Y, Cameron MF, Siniff DB, Naito Y (2003) Factors affecting stroking patterns and body angle in diving Weddell seals under natural conditions. J Exp Biol 206:1461–1470
Sato K, Watanuki Y, Takahashi A, Miller PJO, Tanaka H, Kawabe R, Ponganis PJ, Handrich Y, Akamatsu Y, Watanabe Y, Mitani Y, Costa DP, Bost CA, Aoki K, Amano M, Trathan P, Shapiro A, Naito Y (2007) Stroke frequency, but not swimming speed, is related to body size in free-ranging seabirds, pinnipeds and cetaceans. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 274:471–477
Schreer JF, Kovacs KM, Hines RJO (2001) Comparative diving patterns of pinnipeds and seabirds. Ecol Monogr 71:137–162
Shepard ELC, Wilson RP, Quintana F, Gómez Laich A, Liebsch N, Albareda DA, Halsey LG, Gleiss A, Morgan DT, Myers AE, Newman C, Macdon DW (2008) Identification of animal movement patterns using tri-axial accelerometry. Endang Species Res. doi:10.3354/esr00084
Thornton SJ, Hochachka PW, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Le Boeuf BJ, Spielman DM, Pelc NJ (2005) Stroke volume and cardiac output in juvenile elephant seals during forced dives. J Exp Biol 208:3637–3643
Thums M, Bradshaw CJA, Hindell M (2008) A validated approach for supervised dive classification in diving vertebrates. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 363:75–83
Watanabe S, Izawa M, Kato A, Ropert-Coudert Y, Naito Y (2005) A new technique for monitoring the detailed behaviour of terrestrial animals: a case study with the domestic cat. Appl Anim Behav Sci 94:117–131
Webb PM, Crocker DE, Blackwell SB, Costa DP, Le Boeuf BJ (1998) Effects of buoyancy on the diving behavior of northern elephant seals. J Exp Biol 201:2349–2358
Williams TM (2001) Intermittent swimming by mammals: a strategy for increasing energetic efficiency during diving. Am Zool 41:166–176
Williams TM, Le Boeuf BJ, Davis RW, Crocker DE, Skrovan R (1996) Integrating behavior and energetics in diving marine mammals: new views using video technology. Dissertation, Fifth European conference on wildlife telemetry, Strasbourg, France
Williams TM, Davis RW, Fuiman LA, Francis J, Le Boeuf BJ, Horning M, Calambokidis J, Croll DA (2000) Sink or swim: strategies for cost-efficient diving by marine mammals. Science 288:133–136
Wilson RP, Hustler K, Ryan PG, Burger AE, Noldeke EC (1992) Diving birds in cold water: do Archimedes and Boyle determine energetic costs? Am Nat 140:179–200
Wilson RP, Shepard ELC, Liebsch N (2008) Prying into the intimate details of animal lives: use of a daily diary on animals. Endang Species Res 4:123–137
Wilson RP, McMahon CR, Quintana F, Frere E, Scolaro JA, Hays GC, Bradshaw CJA (2011) N-dimensional animal energetic niches clarify behavioural options in a variable marine environment. J Exp Biol 214:646–656
Yoda K, Sato K, Niizuma Y, Kurita M, Bost CA, Le Maho Y, Naito Y (1999) Precise monitoring of porpoising behaviour of Adélie penguins determined using acceleration data loggers. J Exp Biol 202:3121–3126
Zeno RL, Crocker DE, Hassrick JL, Allen SG, Costa DP (2008) Development of foraging behavior in juvenile northern elephant seals. J Zool (Lond) 274:180–187
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by grants from Wildlife Conservation Society and Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas de la República Argentina. We thank the National Geographic Society for financial support allowing us to work on elephant seal data. We thank M. Uhart for assistance during the anaesthesia process in the field and R. Vera and J. Rua for logistical support. We also thank the Organismo Provincial de Turismo for the permits to work in Península Valdés.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sala, J.E., Quintana, F., Wilson, R.P. et al. Pitching a new angle on elephant seal dive patterns. Polar Biol 34, 1197–1209 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-011-0981-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-011-0981-6