Abstract
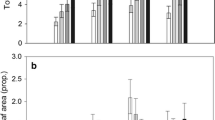
According to available evidence, leaf gallers have only minor impacts on their plant hosts. We hypothesised that the relatively large leaf gallers formed by Eupontania sawflies on small, creeping arctic-alpine willows have a strong influence on their host plants. In this study, we specifically tested the effects of leaf galler (Eupontania aquilonis) on the survival and growth of dwarf willow (Salix herbacea) in a mountain snow-bed in northern Finland. We marked galled, leaves-removed and untreated ramets in experimental blocks. In the following year, we measured the growth and survival of the ramets. The mortality of galled shoots was approx. 40% higher, and the mortality of galled ramets approx. 25% higher than in the control ramets and in the leaf-removal treatment. The leaf biomass of galled ramets and the number of leaves were significantly less in galled ramets than in untreated or leaves-removed ramets. It is possible that galling causes fatal resource depletion of shoots in its host plant. The results show that leaf gallers are ecologically more influential than previously thought.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beerling DJ (1998) Salix herbacea L. J Ecol 86:872–895
Billings WD (1987) Constraints to plant growth, reproduction, and establishment in arctic environments. Arct Alp Res 19:357–365
Craig TP, Price PW, Itami JK (1986) Resource regulation by a steam-galling sawfly on the arroyo willow. Ecology 67:419–425
DeClerck-Floate R, Price PW (1994) Impact of bud-galling midge on bud populations of Salix exigua. Oikos 70:253–260
Dennill GB, Donelly D (1991) Biological control of Acacia longifolia and related weed species (Fabaceae) in South Africa. Agric Ecosyst Environ 37:115–135
Fay PA, Hartnett DC, Knapp AK (1996) Plant tolerance of gall-insect attack and gall-insect performance. Ecology 77:521–534
Hartley SE (1998) The chemical composition of plant galls: are levels of nutrients and secondary compounds controlled by the gall-former? Oecologia 113:492–501
Hartnett DC, Abrahamson WG (1979) The effects of stem gall insects on life history patterns in Solidago canadensis. Ecology 60:910–917
Hoffman JH, Impson FAC, Moran VC, Donelly D (2002) Biological control of invasive golden wattle trees (Acacia pycnantha) by a gall wasp, Trichilogaster sp. (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), in South Africa. Biol Control 25:64–73
Larson KC, Whitham TG (1991) Manipulation of food resources by a gall-forming aphid: the physiology of sink-source interactions. Oecologia 88:15–21
Larson KC, Whitham TG (1997) Competition between gall aphids and natural plant sinks: plant architecture affects resistance to galling. Oecologia 109:575–582
Nyman T (2000) Phylogeny and ecological evolution of gall-inducing sawflies (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae). PhD Dissertation, University of Joensuu, Joensuu
Preus LE, Morrow PA (1999) Direct and indirect effects of two herbivore species on resource allocation in their shared host plant: the rhizome galler Eurosta comma, the folivore Trirhabda canadensis and Solidago missouriensis. Oecologia 119:219–226
Price PW (2003) Macroevolutionary theory on macroecological patterns. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Price PW, Ohgushi T, Roininen H, Ishihara M, Craig TP, Tahvanainen J, Ferrier SM (2004) Release of phylogenetic constraints through low resource heterogeneity: the case of gall-inducing sawflies. Ecol Entomol 29:467–481
Roininen H, Danell K, Zirnovjev A, Vikberg V, Virtanen R (2002) Community structure, survival and mortality factors in arctic populations of Eupontania leaf gallers. Polar Biol 25:605–611
Sacchi CF, Price PW, Craig TP, Itami JK (1988) Impact of shoot galler attact on sexual reproduction in the arroyo willow. Ecology 69:2021–2030
Silva IM, Andrade GI, Fernandes GW, Filho JPL (1996) Parasitic relationship between a gall-forming insect Tomoplagia rudolphi (Diptera: Tephritidae) and its host plant (Veronia polyanthes, Asteraceae). Ann Bot 78:45–48
Vikberg V (2003) Taxonomy of species of Eupontania crassipes- and aquilonis-groups (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae: Nematinae). Entomol Fennica 14:129–172
Acknowledgements
Kilpisjärvi Biological Station provided facilities and accommodation for fieldwork. We thank Jani Honkanen for field assistance and comments on the manuscript, Jyrki Pusenius for statistical consultation, and Peter Price for critical comments on the manuscript. The study was funded by the Finnish Cultural Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakkarainen, H., Roininen, H. & Virtanen, R. Negative impact of leaf gallers on arctic-alpine dwarf willow, Salix herbacea. Polar Biol 28, 647–651 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-005-0714-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-005-0714-9