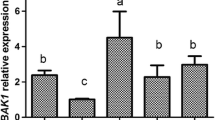
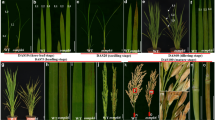
Abstract
Key message
OsMKK1, a MAPK gene, positively regulates rice Xa21-mediated resistance response and also plays roles in normal growth and development process of rice.
Abstract
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade was highly conserved among eukaryotes, which played crucial roles in plant responses to pathogen infection. Bacterial blight is the most devastating bacterial disease. Xa21 confers broad-spectrum resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo). This study identified that the transcription level of OsMKK1 was up-regulated in resistant response against Xoo, thus overexpression (OsMKK1-OX) and RNA interference (OsMKK1-RNAi) transgenic rice lines under the background of Xa21 was constructed. Compared with recipient control plants 4021, the OsMKK1-OX lines significantly enhanced disease resistance to Xoo, on the contrary, the resistance of OsMKK1-RNAi lines was weakened, demonstrated that OsMKK1 played a positive role in Xa21-mediated disease resistance pathway. A number of pathogenesis-related proteins, including PR1A, PR2 and PR10A showed enhanced expression in OsMKK1-OX lines, supported that these PR genes may be regulated by OsMKK1 to participate in the defense responses. In addition, the agronomic traits of OsMKK1 transgenic plants were affected. Overall, these results revealed the role of OsMKK1 in Xa21-mediated resistance against Xoo and in the normal growth and development process in rice.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Files.
References
Bai H, Li LY, Liu GZ et al (2006) Advances of rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene Xa21. Hereditas 28(6):745–753
Bai H, Lan JP, Gan Q et al (2012) Identification and expression analysis of components involved in rice Xa21-mediated disease resistance signalling. Plant Biol (stuttg) 14(6):914–922. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2012.00585.x
Bigeard J, Hirt H (2018) Nuclear signaling of plant MAPKs. Front Plant Sci 9:469. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00469
Brown JK (2002) Yield penalties of disease resistance in crops. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5(4):339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00270-4
Chen X, Chern M, Canlas PE et al (2010) An ATPase promotes autophosphorylation of the pattern recognition receptor XA21 and inhibits XA21-mediated immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8029–8034. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912311107
Chen J, Wang L, Yang Z et al (2021a) The rice Raf-like MAPKKK OsILA1 confers broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight by suppressing the OsMAPKK4-OsMAPK6 cascade. J Integr Plant Biol 63(10):1815–1842. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13150
Chen J, Wang L, Yuan M (2021b) Update on the roles of rice MAPK cascades. Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041679
Chen M, Ni L, Chen J et al (2021c) Rice calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase directly phosphorylates a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase to regulate abscisic acid responses. Plant Cell 33(5):1790–1812. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab071
Chen X, Zuo S, Schwessinger B et al (2014) An XA21-Associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors. Mol Plant 7(5):874–892. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu003
Dou SJ, Guan M, Li LY et al (2014) Pathogenesis-related genes in rice. Chin Sci Bull (chin Ver) 59:245–258
Duan Y, Zhai C, Li H et al (2012) An efficient and high-throughput protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation based on phosphomannose isomerase positive selection in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 31(9):1611–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1275-3
Ercoli MF, Luu DD, Rim EY et al (2022) Plant immunity: rice XA21-mediated resistance to bacterial infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119(8):e2121568119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2121568119
Guo M, Lan J, Shi J et al (2015) Western blot detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. J Plant Pathol Microbiol S4:005
Hamel LP, Nicole MC, Sritubtim S et al (2006) Ancient signals: comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci 11(4):192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2006.02.007
Hong Y, Liu Q, Cao Y et al (2019) The OsMPK15 negatively regulates Magnaporthe oryza and Xoo disease resistance via SA and JA signaling pathway in rice. Front Plant Sci 10:752. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00752
Hou M, Xu W, Bai H et al (2012) Characteristic expression of rice pathogenesis-related proteins in rice leaves during interactions with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Cell Rep 31:895–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1210-z
Jalmi SK, Sinha AK (2016) Functional involvement of a mitogen activated protein kinase module, OsMKK3-OsMPK7-OsWRK30 in mediating resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Sci Rep 6:37974. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37974
Jiang Y, Chen X, Ding X et al (2013) The XA21 binding protein XB25 is required for maintaining XA21-mediated disease resistance. Plant J 73:814–823. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12076
Kou Y, Wang S (2013) Bacterial blight resistance in rice. In: Varshney R, Tuberosa R (eds) Genomics applications in plant breeding. Wiley-Blackwell Press, Hoboken, NJ, pp 11–30
Kumar K, Rao KP, Sharma P et al (2008) Differential regulation of rice mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (MKK) by abiotic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 46(10):891–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.05.014
Lee BM, Park YJ, Park DS et al (2005) The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Nucleic Acids Res 33(2):577–586. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki206
Li X, Bai H, Wang X et al (2011) Identification and validation of rice reference proteins for western blotting. J Exp Bot 62:4763–4772. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err084
Li W, Deng Y, Ning Y et al (2020) Exploiting broad-spectrum disease resistance in crops: from molecular dissection to breeding. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71:575–603. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-010720-022215
Li N, Yang Z, Li J et al (2021) Two VQ proteins are substrates of the OsMPKK6-OsMPK4 cascade in rice defense against bacterial blight. Rice (NY) 14(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-021-00483-y
Liu G, Liu S, Wu L et al (2011) Antibody-based rice proteomics-the beginning and perspectives. Scientia Sin Vitae 41:173–177
Liu Y, Yan G, Zhang T et al (2021) Overexpression of OsPR1A enhanced Xa21-mediated resistance to rice bacterial blight. Sci Agric Sin 54:4933–4942
Ma J, Zhang T, Lan J et al (2019) Overexpression of OsMPK17 protein enhances drought tolerance of rice. Acta Agron Sin 46:20–30
Ma H, Li J, Ma L et al (2021) Pathogen-inducible OsMPKK10.2-OsMPK6 cascade phosphorylates the Raf-like kinase OsEDR1 and inhibits its scaffold function to promote rice disease resistance. Mol Plant 14(4):620–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.01.008
Ning Y, Liu W, Wang GL (2017) Balancing immunity and yield in crop plants. Trends Plant Sci 22(12):1069–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.010
Nishimura A, Aichi I, Matsuoka M (2006) A protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in rice. Nat Protoc 1(6):2796–2802. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.469
Park CJ, Peng Y, Chen X et al (2008) Rice XB15, a protein phosphatase 2C, negatively regulates cell death and XA21-mediated innate immunity. Plos Biol 6:e282. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060231
Park CJ, Bart R, Chern M et al (2010a) Overexpression of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP3 regulates XA21-mediated innate immunity in rice. PLoS ONE 5:e9262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009262
Park CJ, Han SW, Chen X et al (2010b) Elucidation of XA21-mediated innate immunity. Cell Microbiol 12(8):1017–1025. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01489.x
Park CJ, Sharma R, Lefebvre B et al (2013) The endoplasmic reticulum-quality control component SDF2 is essential for XA21-mediated immunity in rice. Plant Sci 210:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.05.003
Park CJ, Wei T, Sharma R et al (2017) Overexpression of rice auxilin-like protein, XB21, induces necrotic lesions, up-regulates endocytosis-related genes, and confers enhanced resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice (NY) 10:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-017-0166-1
Peng Y, Bartley LE, Chen X et al (2008) OsWRKY62 is a negative regulator of basal and Xa21-mediated defense against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Mol Plant 1(3):446–458. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssn024
Pruitt R, Schwessinger B, Joe A et al (2015) The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci Adv 1:e1500245. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1500245
Rao KP, Richa T, Kumar K et al (2010) In silico analysis reveals 75 members of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase gene family in rice. DNA Res 17(3):139–153. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsq011
Reyna N, Yang Y (2006) Molecular analysis of the rice MAP kinase gene family in relation to Magnaporthe grisea infection. Mol Plant 19:530–540. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-19-0530
Seo YS, Chern M, Bartley LE et al (2011) Towards establishment of a rice stress response interactome. PLoS Genet 7(4):e1002020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002020
Shen X, Yuan B, Liu H et al (2010) Opposite functions of a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase during the process of resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant J 64(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04306.x
Shen X, Liu H, Yuan B et al (2011) OsEDR1 negatively regulates rice bacterial resistance via activation of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ 34(2):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02219.x
Singh R, Jwa NS (2013) The rice MAPKK-MAPK interactome: the biological significance of MAPK components in hormone signal transduction. Plant Cell Rep 32(6):923–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1437-y
Singh R, Lee MO, Lee JE et al (2012) Rice mitogen-activated protein kinase interactome analysis using the yeast two-hybrid system. Plant Physiol 160(1):477–487. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.200071
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL et al (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270:1804–1806. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5243.1804
Vo KTX, Kim CY, Hoang TV et al (2018) OsWRKY67 plays a positive role in basal and XA21-mediated resistance in rice. Front Plant Sci 11(8):2220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02220
Wang YS, Pi LY, Chen X et al (2006) Rice XA21 binding protein 3 is a ubiquitin ligase required for full Xa21-mediated disease resistance. Plant Cell 18:3635–3646. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.046730
Wang F, Jing W, Zhang W (2014) The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade MKK1-MPK4 mediates salt signaling in rice. Plant Sci 227:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.08.007
Wang T, Zhu Z, Chen Y et al (2021) Rice OsWRKY42 is a novel element in Xa21-mediated resistance pathway against bacterial leaf blight. Chin Bull Bot 56(6):687–698
Wu Q, Hou M, Li L et al (2011) Induction of pathogenesis-related proteins in rice bacterial resistant gene XA21-mediated interactions with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Plant Pathol 93:455–459
Xiao X, Tang Z, Li X et al (2017) Overexpressing OsMAPK12-1 inhibits plant growth and enhances resistance to bacterial disease in rice. Funct Plant Biol 44(7):694–704. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16397
Xu WH, Wang YS, Liu GZ et al (2006) The autophosphorylated Ser686, Thr688, and Ser689 residues in the intracellular juxtamembrane domain of XA21 are implicated in stability control of rice receptor-like kinase. Plant J 45(5):740–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02638.x
Yan G, Liu Y, Lan J et al (2022) The rapid induction of OsPR1A protein is crucial in Xa21-mediated rice bacterial blight resistance. J Plant Pathol 104(3):969–978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-022-01105-2
Yang Z, Ma H, Hong H et al (2015) Transcriptome-based analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in the rice response to Xanthomonas oryzae infection. Rice (NY) 8:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-014-0038-x
Yang J, Ji L, Liu S et al (2021) The CaM1-associated CCaMK-MKK1/6 cascade positively affects lateral root growth via auxin signaling under salt stress in rice. J Exp Bot 72(18):6611–6627. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab287
Zhu Z, Wang T, Chen Y et al (2021) Rice transcription factor WRKY68 plays a positive role in Xa21-mediated resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Acta Agron Sin 48(5):1129–1140
Zhu Z, Wang T, Lan J et al (2022) Rice MPK17 plays a negative role in the Xa21-mediated resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice (NY) 15(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-022-00590-4
Funding
The research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (C2022204128), Hebei Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Molecular Pathology, Baoding, 071001, China and the Start-up Fund for Introduced Talents of Hebei Agricultural University (YJ201910).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY, ZZ, YG, SC and JL participated in the study design and performed the experiments, collected and analyzed the data. JZ, SD and MY participated in the resources, validation and methodology experiments. ZY, LL and GL wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Woe-Yeon Kim.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Zhu, Z., Guo, Y. et al. OsMKK1 is a novel element that positively regulates the Xa21-mediated resistance response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Rep 43, 31 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03085-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03085-8