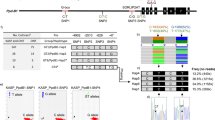
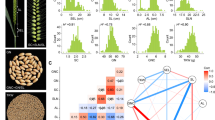
Abstract
Key message
This study provides important information on the genetic basis of GCaC in wheat, thus contributing to breeding efforts to improve the nutrient quality of wheat.
Abstract
Calcium (Ca) plays important roles in the human body. Wheat grain provides the main diet for billions of people worldwide but is low in Ca content. Here, grain Ca content (GCaC) of 471 wheat accessions was determined in four field environments. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed to reveal the genetic basis of GCaC using the phenotypic data form four environments and a wheat 660 K single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array. Twelve quantitative trait locus (QTLs) for GCaC were identified on chromosomes 1A, 1D, 2A, 3B, 6A, 6D, 7A, and 7D, which was significant in at least two environments. Haplotype analysis revealed that the phenotypic difference between the haplotypes of TraesCS6D01G399100 was significant (P ≤ 0.05) across four environments, suggesting it as an important candidate gene for GCaC. This research enhances our understanding of the genetic architecture of GCaC for further improving the nutrient quality of wheat.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data for the study is available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Aciksoz SB, Yazici A, Ozturk L, Cakmak I (2011) Biofortification of wheat with iron through soil and foliar application of nitrogen and iron fertilizers. Plant Soil 349:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0863-2
Alomari DZ, Eggert K, von Wirén N, Pillen K, Röder MS (2017) Genome-wide association study of calcium accumulation in grains of European wheat cultivars. Front Plant Sci 8:1797. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01797
Alomari DZ, Alqudah AM, Pillen K, von Wirén N, Röder MS (2021) Toward identification of a putative candidate gene for nutrient mineral accumulation in wheat grains for human nutrition purposes. J Exp Bot 72(18):6305–6318. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab297
Amiri R, Bahraminejad S, Sasani S, Jalali-Honarmand FR (2015) Bread wheat genetic variation for grain’s protein, iron and zinc concentrations as uptake by their genetic ability. Eur J Agron 67:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.03.004
Bhatta M, Baenziger PS, Waters BM, Poudel R, Belamkar V, Poland J, Morgounov A (2018) Genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions associated with 10 grain minerals in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Int J Mol Sci 19(10):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103237
Centeno V, Díaz de Barboza G, Marchionatti A, Rodríguez V, Tolosa de Talamoni N (2009) Molecular mechanisms triggered by low-calcium diets. Nutr Res Rev 22(2):163–174. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422409990126
Earl DA, VonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Erdogmus S, Ates D, Nemli S, Yagmur B, Asciogul TK, Ozkuru E, Karaca N, Yilmaz H, Esiyok D, Tanyolac MB (2020) Genome-wide association studies of Ca and Mn in the seeds of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Genomics 112(6):4536–4546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.03.030
Fedorowicz-Strońska O, Koczyk G, Kaczmarek M, Krajewski P, Sadowski J (2017) Genome-wide identification, characterisation and expression profiles of calcium-dependent protein kinase genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Appl Genet 58:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-016-0357-2
Goel A, Taj G, Pandey D, Gupta S, Kumar A (2011) Genome-wide comparative in silico analysis of calcium transporters of rice and sorghum. Genom Proteom Bioinform 9(4–5):138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60017-X
Gunjača J, Carović-Stanko K, Lazarević B, Vidak M, Petek M, Liber Z, Šatović Z (2021) Genome-wide association studies of mineral cont ent in common bean. Front Plant Sci 12:636484. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.636484
Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3735–3740. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.7.3735
Han JC, Yang XD, Zhang T, Li H, Li WL, Zhang ZY, Yao JH (2009) Effects of 1alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol on growth performance, parameters of tibia and plasma, meat quality, and type IIb sodium phosphate cotransporter gene expression of one- to twenty-one-day-old broilers. Poult Sci 88(2):323–329. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2008-00252
(IWGSC) International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361:eaar7191
Kranz S, Lin PJ, Wagstaff DA (2007) Children’s dairy intake in the United States: too little, too fat? J Pediatr 151(6):642–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.04.067
Kumssa DB, Joy EJ, Ander EL, Watts MJ, Young SD, Walker S, Broadley MR (2015) Dietary calcium and zinc deficiency risks are decreasing but remain prevalent. Sci Rep 5:10974. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10974
Li MX, Yeung JM, Cherny SS, Sham PC (2012) Evaluating the effective numbers of independent tests and significant p-value thresholds in commercial genotyping arrays and public imputation reference datasets. Hum Genet 131(5):747–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-1118-2
Ma J, Qi S, Yuan M, Zhao D, Zhang D, Feng J, Wang J, Li W, Song C, Wang T, Zeng Q, Wu J, Han D, Jiang L (2022) A genome-wide association study revealed the genetic variation and candidate genes for grain copper content in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Food Func 13(9):5177–5188. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo04173h
Murphy KM, Reeves PG, Jones SS (2008) Relationship between yield and mineral nutrient concentrations in historical and modern spring wheat cultivars. Euphytica 163:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9681-x
Park S, Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Yoo KS, Park J, Smith RH, Hirschi KD (2005) Increased calcium levels and prolonged shelf life in tomatoes expressing Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ transporters. Plant Physiol 139(3):1194–1206. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066266
Peleg Z, Cakmak I, Ozturk L, Yazici A, Jun Y, Budak H, Korol AB, Fahima T, Saranga Y (2009) Quantitative trait loci conferring grain mineral nutrient concentrations in durum wheat x wild emmer wheat RIL population. Theor Appl Genet 119(2):353–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1044-z
Poletti S, Gruissem W, Sautter C (2004) The nutritional fortification of cereals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(2):162–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2004.03.002
Poudel R, Bhatta M (2017) Review of nutraceuticals and functional properties of whole wheat. J Nutr Food Sci 7:1. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9600.1000571
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Sharma D, Jamra G, Singh UM, Sood S, Kumar A (2017) Calcium biofortification: three pronged molecular approaches for dissecting complex trait of calcium nutrition in finger millet (Eleusine coracana) for devising strategies of enrichment of food crops. Front Plant Sci 7:2028. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02028
Sharma D, Tiwari A, Sood S, Meher PK, Kumar A (2022) Identification and validation of candidate genes for high calcium content in finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.] through genome-wide association study. J Cereal Sci 107:103517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2022.103517
Shi R, Tong Y, Jing R, Zhang F, Zou C (2013) Characterization of quantitative trait loci for grain minerals in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Integr Agric 12(9):1512–1521. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(13)60559-6
Shi X, Zhou Z, Li W, Qin M, Yang P, Hou J, Huang F, Lei Z, Wu Z, Wang J (2022) Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic architecture for calcium accumulation in grains of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 22(1):229. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03602-z
Singh UM, Metwal M, Singh M, Taj G, Kumar A (2015) Identification and characterization of calcium transporter gene family in finger millet in relation to grain calcium content. Gene 566(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.021
Tong J, Zhao C, Sun M, Fu L, Song J, Liu D, Zhang Y, Zheng J, Pu Z, Liu L, Rasheed A, Li M, Xia X, He Z, Hao Y (2022) High resolution genome wide association studies reveal rich genetic architectures of grain zinc and iron in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Plant Sci 13:840614. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.840614
Vreugdenhil D, Aarts MG, Koornneef M, Nelissen H, Ernst WHO (2004) Natural variation and QTL analysis for cationic mineral content in seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 27(7):828–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01189.x
Welch RM, Graham RD (2004) Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J Exp Bot 55(396):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh064
White PJ, Broadley MR (2005) Biofortifying crops with essential mineral telements. Trends Plant Sci 10(12):586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.001
White PJ, Broadley MR (2009) Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets-iron, zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, selenium and iodine. New Phytol 182(1):49–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02738.x
Wu J, Yu R, Wang H, Zhou C, Huang S, Jiao H, Yu S, Nie X, Wang Q, Liu S, Weining S, Singh RP, Bhavani S, Kang Z, Han D, Zeng Q (2021) A large-scale genomic association analysis identifies the candidate causal genes conferring stripe rust resistance under multiple field environments. Plant Biotechnol J 19(1):177–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13452
Zhou Z, Shi X, Zhao G, Qin M, Ibba MI, Wang Y, Li W, Yang P, Wu Z, Lei Z, Wang J (2020) Identification of novel genomic regions and superior alleles associated with Zn accumulation in wheat using a genome-wide association analysis method. Int J Mol Sci 21(6):1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21061928
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Dr. Zhang Chenyang in School of Chemistry & Materials Engineering, Xinxiang University for assistance in ICP analysis. This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0300703-2 and 2017YFD0301101); the Open Project Program (CSBAA2020001) of State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology for Arid Areas, NWAFU, Yangling, Shaanxi, 712100, China.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0300703-2 and 2017YFD0301101); the Open Project Program (CSBAA2020001) of State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology for Arid Areas, NWAFU, Yangling, Shaanxi, 712100, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM: Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. JR: validation, investigation, writing—original draft preparation. XY: validation, investigation. MY: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. DZ: investigation. CL: investigation. QZ: methodology, software, data curation. JW: methodology. DH: Conceptualization, methodology, software, resources, writing—review and editing. LJ: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Li Tian.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Ren, J., Yuan, X. et al. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic variation and candidate gene for grain calcium content in bread wheat. Plant Cell Rep 42, 1379–1390 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03036-3