Abstract
Key message
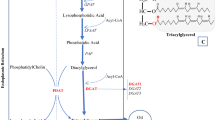
Proteomic and lipidomics analyses of WT and GmDGAT1-2 transgenic soybeans showed that GmDGAT1-2 over-expression induced lipoxygenase down-regulatation and oleoin up-regulatation, which significantly changed the compositions and total fatty acid.
Abstract
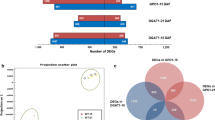
The main goal of soybean breeding is to increase the oil content. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) is a key rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid metabolism and may regulate oil content. Herein, 10 GmDGAT genes were isolated from soybean and transferred into wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis. The total fatty acid was 1.2 times higher in T3 GmDGAT1-2 transgenic Arabidopsis seeds than in WT. Therefore, GmDGAT1-2 was transferred into WT soybean (JACK), and four T3 transgenic soybean lines were obtained. The results of high-performance gas chromatography and Soxhlet extractor showed that, compared with those of JACK, oleic acid (18:1), and total fatty acid levels in transgenic soybean plants were much higher, but linoleic acid (18:2) was lower than WT. Palmitic acid (16:0), stearic acid (18:0), and linolenic acid (18:3) were not significantly different. For mechanistic studies, 436 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) and 180 differentially expressed metabolites (DEMs) were identified between WT (JACK) and transgenic soybean pods using proteomic and lipidomics analyses. Four lipoxygenase proteins were down-regulated in linoleic acid metabolism while four oleosin proteins were up-regulated in the final oil formation. The results showed an increase in the total fatty acid and 18:1 composition, and a decrease in the 18:2 composition of fatty acid. Our study brings new insights into soybean genetic transformation and the deep study of molecular mechanism that changes the total fatty acid, 18:1, and 18:2 compositions in GmDGAT1-2 transgenic soybean.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DGAT:
-
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real time PCR
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- ACP:
-
Acyl carrier protein
- PAT:
-
Phosphinothricin-N-acetyltransferase
- MBOAT:
-
Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Bao X, Ohlrogge J (1999) Supply of fatty acid is one limiting factor in the accumulation of triacylglycerol in developing embryos. Plant Physiol 120:1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.120.4.1057
Barthole G, Lepiniec L, Rogowsky PM et al (2012) Controlling lipid accumulation in cereal grains. Plant Sci 185–186:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.09.002
Bouvier-Navé P, Benveniste P, Oelkers P et al (2000) Expression in yeast and tobacco of plant cDNAs encoding acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase. Eur J Biochem 267(1):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.00961.x
Broun P, Gettner S, Somerville C (1999) Genetic engineering of plant lipids. Annu Rev Nutr 19:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.19.1.197
Browse J, McCourt PJ, Somerville CR (1986) Fatty acid composition of leaf lipids determined after combined digestion and fatty acid methyl ester formation from fresh tissue. Anal Biochem 152:141–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(86)90132-6
Cases S, Smith SJ, Zheng YW (1998) Identification of a gene encoding an acyl-Co A: diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a key enzyme in triacylglycerol synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95(22):13018–13023. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/129.2.449S
Chen BB, Wang JJ, Zhang GY (2016) Two types of soybean diacylglycerol acyltransferases are differentially involved in triacylglycerol biosynthesis and response to environmental stresses and hormones. Sci Rep 6:28541. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28541
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S (2013) STRING V.91: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):808–815. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1094
Guo R, Shi LX, Yan CR et al (2017) Ionomic and metabolic responses to neutral salt or alkaline salt stresses in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 17:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-0994-6
Haspel JA, Chettimada S, Shaik RS et al (2014) Circadian rhythm reprogramming during lung inflammation. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5753
He XH, Grace QC, Lin JT et al (2004) Regulation of diacylglycerolacy transferase in developing seeds of castor. Lipids 39(9):865–871
Heischmann S, Kevin Q et al (2016) Exploratory metabolomics profiling in the kainic acid rat model reveals depletion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 during epileptogenesis. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31424
Hernandez ML, Whitehead L, He Z et al (2012) A cytosolic acyltransferase contributes to triacylglycerol synthesis in sucrose- rescued Arabidopsis seed oil catabolism mutants. Plant Physiol 160:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.201541
Hobbs DH, Lu C, Hills M (1999) Cloning of a cDNA encoding acyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana and its functional expression. FEBS Lett 452:145–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00646-8
Hu RB, Fan CM, Li HY, Zhang QZ et al (2009) Evaluation of putative reference genes for gene expression normalization in soybean by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-93
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn923
Islam N, Bates PD, John KMM et al (2019) Quantitative proteomic analysis of low linolenic acid transgenic soybean reveals perturbations of fatty acid metabolic pathways. Proteomics 19:1800379. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201800379
Jako C, Kumar A, Wei YD et al (2001) Seed-specific over-expression of an Arabidopsis cDNA encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase enhances seed oil content and seed weight. Plant Physiol 126:861–874. https://doi.org/10.2307/4279946
Jian B, Liu B, Bi YR, Hou WS, Wu CX et al (2008) Validation of internal control for gene expression study in soybean by quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 9(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-9-59
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30(9):1236–1240
Kroon JT, Wei WX, Simon WJ et al (2006) Identification and functional expression of a type 2 acyl-CoA:diacylglycerolacyl transferase (DGAT2) in developing castor bean seeds which has high homology to the major triglyceride biosynthetic enzyme of fungi and animals. Phytochemistry 67(23):2541–2549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.09.020
Lardizabal KD, Mai JT, Wagner NW et al (2001) DGAT2 is a new diacylglycerolacyl transferase gene family: purification, cloning, and expression in insect cells of two polypeptides from Mortierella ramanniana with diacylglycerolacyl transferase activity. J Biol Chem 276(42):38862–38869
Lardizabal K, Effertz R, Levering C et al (2008) Expression of Umbelopsis ramanniana DGAT2A in seed increases oil in soybean. Plant Physiol 148:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.123042
Le DT, Donavan LA, Babu V, Yasuko W et al (2012) Evaluation of candidate reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in soybean tissues under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046487
Li F, Wu X, Lam P, Bird D, Zheng H, Samuels L et al (2008) Identification of the was ester synthase/acyl-coenzyme A: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase WSD1 required for stem was ester biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 148:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.123471
Matyash V, Liebisch G, Kurzchalia TV et al (2008) Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J Lipid Res 5:1137–1146. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.D700041-JLR200
Mekhedov S, De Ilárduya OM, Ohlrogge J (2000) Toward a functional catalog of the plant genome. A survey of genes for lipid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 122(2):389–402. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.2.389
Niu LJ, Zhang H, Wu ZK et al (2018) Modified TCA/acetone precipitation of plant proteins for proteomic analysis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202238
Okuley J, Lightner J, Feldmann K et al (1994) Arabidopsis FAD2 gene encodes the enzyme that is essential for polyunsaturated lipid synthesis. Plant Cell 6:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.1.147
Padula MP, Berry IJ, O’Rourke M (2017) A comprehensive guide for performing sample preparation and top-down protein analysis. Proteomes 5:11. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5020011
Reed DW, Schafer UA, Covello PS (2000) Characterization of the Brassica napus extraplastidial linoleate desaturase by expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Physiol 122:715–720
Ross PL, Huang YN, Marchese JN et al (2004) Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol Cell Proteomics 3(12):1154–1169. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M400129-MCP200
Saha S, Enugutti B, Rajakumari S et al (2006) Cytosolic triacylglycerol biosynthetic pathway in oilseeds. Molecular cloning and expression of peanut cytosolic diacylglycerol acyltransferase. Plant Physiol 141(4):1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.082198
Salanoubat M, Lemcke K, Rieger M et al (2000) Sequence and analysis of chromosome 3 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408(6814):820–822. https://doi.org/10.1038/35048706
Shimada TL, Hara-Nishimura I (2010) Oil-body-membrane proteins and their physiological functions in plants. Biol Pharm Bull 33:360–363. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.33.360
Shockey JM, Gidda SK, Chapital DC et al (2006) Tung tree DGAT1 and DGAT2 have nonredundant functions in triacylglycerol biosynthesis and are localized to different subdomains of the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 18(9):2294–2313. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.043695
Tang HY, Wang CH, Ho HY et al (2018) Lipidomics reveals accumulation of the oxidized cholesterol in erythrocytes of heart failure patients. Redox Biol 14:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.020
Xu JY, Francis T, Mietkiewska E et al (2008) Cloning and characterization of an acyl- CoA-dependent diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) gene from Tropaeolum majus, and a study of the functional motifs of the DGAT protein using site-directed mutagenesis to modify enzyme activity and oil content. Plant Biotechnol J 6(8):799–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00358.x
Yen CE, Stone SJ, Koliwad S et al (2008) Thematic review series: glycerolipids. DGAT enzymes and triacylglyrol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res 49:2283–2301. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R800018-JLR200
Zhang H, Liu T, Zhang Z et al (2016) Integrated proteogenomic characterization of human high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.069
Zheng PZ, Allen WB, Roesler K et al (2008) A phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize. Nat Genet 40(3):267–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.85
Funding
This research was funded by the Major Science and Technology Sponsored Program for Transgenic Biological Breeding (No. 2016ZX08004-003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32001572), and Science and Technology Department of Jilin Province (No. 20180201030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Hiroshi Ezura.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Yan, F., Liu, Y. et al. Quantitative proteomic and lipidomics analyses of high oil content GmDGAT1-2 transgenic soybean illustrate the regulatory mechanism of lipoxygenase and oleosin. Plant Cell Rep 40, 2303–2323 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02768-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02768-4