Abstract
Key message
De novo transcriptome analysis from callus, leaf, and fruit of Trichosanthes cucumerina L. for the identification of genes associated with triterpenoid biosynthesis, especially bryonolic acid and cucurbitacin B.
Abstract
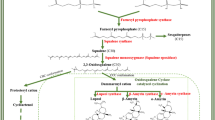
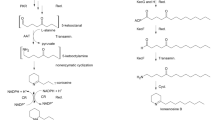
Trichosanthes cucumerina L. (TC) has been used as a medicinal plant in Thailand with various potential functions. Two major triterpenoids found in this plant, bryonolic acid and cucurbitacin B, are receiving increased attention for their activities. Here, we provide TC transcriptome data to identify genes involved in the triterpenoid biosynthetic pathway through callus, where was previously suggested as a novel source for bryonolic acid production as opposed to leaf and fruit. A de novo assembly of approximately 290-thousand transcripts generated from these tissues led to two putative oxidosqualene cyclases: isomultiflorenol synthase (IMS) and cucurbitadienol synthase (CBS). TcIMS and TcCBS, genes that encode substrates for two characteristic triterpenoids in cucurbitaceous plants, were identified as isomultiflorenol synthase and cucurbitadienol synthase, respectively. These two genes were functionally characterised in mutant yeast Gil77 systems, which led to the productions of isomultiflorenol and cucurbitadienol. Moreover, the callus-specific gene expression profiles were also presented. These obtained information showed candidate cytochrome P450s with predicted full-length sequences, which were most likely associated with triterpenoid biosynthesis, especially bryonolic acid. Our study provides useful information and a valuable reference for the further studies on cucurbitaceous triterpenoids.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TC:
-
Trichosanthes cucumerina L.
- CN:
-
TC callus
- LN:
-
TC leaf
- FN:
-
TC fruit peel
- AACT:
-
Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase
- HMGS:
-
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase
- HMGR:
-
Hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase
- MVK:
-
Mevalonate kinase
- PMK:
-
Mevalonate-5-phosephate kinase
- MVD:
-
Mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase
- IDI:
-
Isopentenyldiphosphateisomerase
- DXS:
-
1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase
- DXR:
-
1-Deoxy-d- xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase
- CMS:
-
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol synthase
- CMK:
-
4-Diphospho cytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol kinase
- MECS:
-
2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase
- HDS:
-
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl 4- diphosphate synthase
- HDR:
-
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase
- OSC:
-
Oxidosqualene cyclase
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
References
Akihisa T, Ghosh P, Thakur S, Rosenstein FU, Tamura T, Matsumoto T (1986) Widespread occurrence of cucurbita-5, 24-dienol in Cucurbitaceae. J Oleo Sci 35:1036–1040. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos1956.35.1036
Balliano G, Caputo O, Viola F, Delprino L, Cattel L (1983a) Cyclization of squalene-2,3-epoxide to 10α-cucurbita-5,24-dien-3β-ol by microsomes from Cucurbita maxima seedlings. Phytochemistry 22:915–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(83)85021-3
Balliano G, Caputo O, Viola F, DelPrino L, Cattel L (1983b) The transformation of 10α-cucurbita-5,24-dien-3β-ol into cucurbitacin C by seedlings of Cucumis sativus. Phytochemistry 22:909–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(83)85020-1
Bicalho KU, Santoni MM, Arendt P, Zanelli CF, Furlan M, Goossens A, Pollier J (2019) CYP712K4 catalyzes the C-29 oxidation of friedelin in the Maytenus ilicifolia quinone methide triterpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 60:2510–2522. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz144
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Cho HJ, Ito M, Tanaka S, Kamisako W, Tabata M (1993) Biosynthesis of bryonolic acid in cultured cells of watermelon. Phytochemistry 33(6):1407–1413
Cuong DM, Jeon J, Morgan AMA et al (2017) Accumulation of charantin and expression of triterpenoid biosynthesis genes in bitter melon (Momordica charantia). J Agric Food Chem 65:7240–7249. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01948
Dai L, Liu C, Zhu Y et al (2015) Functional characterization of cucurbitadienol synthase and triterpene glycosyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii. Plant Cell Physiol 56:1172–1182. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv034
Dewick PM (2009) Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. Wiley, West Sussex
Fanani MZ et al (2019) Molecular basis of C-30 product regioselectivity of legume oxidases involved in high-value triterpenoid biosynthesis. Front Plant Sci 10:1520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01520
Gong X, Chen N, Ren K, Jia J, Wei K, Zhang L, Lv Y, Wang J, Li M (2019) The fruits of Siratia grosvenorii: a review of a Chinese food-medicine. Front Pharmacol 10:1400. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01400
Götz S et al (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3420–3435. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn176
Grabherr MG et al (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883
Haas B, Papanicolaou A (2015) TransDecoder 5.5.0. https://github.com/TransDecoder/TransDecoder/wiki.
Haas BJ et al (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8:1494–1512. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.084
Harinaatenaina L, Tanaka M, Takaoka S, Oda M, Mogami O, Uchida M, Asakawa Y (2006) Momordica charantia constituents and antidiabetic screening of the isolated major compounds. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 54:1017–1021. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.54.1017
Hayashi H, Huang P, Inoue K et al (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of isomultiflorenol synthase, a new triterpene synthase from Luffa cylindrica, involved in biosynthesis of bryonolic acid. Eur J Biochem 268:6311–6317. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02588.x
Hu X, Liao Z, Zhang B, Yue J, Wang Z et al (2020) Transcriptome sequencing and screening of genes related to sex determination of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. PLoS One 15:e0239230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239230
Hua D, Fu J, Liu L, Yang X, Zhang Q, Xie M (2019) Change in bitterness, accumulation of cucurbitacin B and expression patterns of CuB biosynthesis-related genes in melon during fruit development. Hort J 88:253–262. https://doi.org/10.2503/hortj.UTD-004
Isaev MI (1995) Isoprenoids of Bryonia I. Pentacyclic triterpenes and sterol of Bryonia melanocarpa. Chem Nat Compd 31:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01165197
Itkin M, Davidovich-Rikanati R, Cohen S et al (2016) The biosynthetic pathway of the nonsugar, high-intensity sweetener mogroside V from Siraitia grosvenorii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:7619–7628. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1604828113
Itoh T, Tamura T, Jeong TM, Tamura T, Matsumoto TJL (2006) 10α-Cucurbita-5,24-dien-3β-ol from gourd seed oil. Lipids 15:122–123
Kongtun S, Jiratchariyakul W, Kummalue T, Tan-ariya P, Kunnachak S, Frahm AW (2009) Cytotoxic properties of root extract and fruit juice of Trichosanthes cucumerina. Planta Med 75:839–842. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1185455
Kriventseva EV, Kuznetsov D, Tegenfeldt F, Manni M, Dias R, Simão FA, Zdobnov EM (2019) OrthoDB v10: sampling the diversity of animal, plant, fungal, protist, bacterial and viral genomes for evolutionary and functional annotations of orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D807-d811. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1053
Kushiro T, Shibuya M, Ebizuka Y (1998) Beta-amyrin synthase—cloning of oxidosqualene cyclase that catalyzes the formation of the most popular triterpene among higher plants. Eur J Biochem 256:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2560238.x
Lertphadungkit P, Suksiriworapong J, Satitpatipan V, Sirikantaramas S, Wongrakpanich A, Bunsupa S (2020) Enhanced production of bryonolic acid in Trichosanthes cucumerina L (Thai Cultivar) cell cultures by elicitors and their biological activities. Plants (Basel) 9:709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060709
Liu Y, Ali Z, Khan IA (2008) Cucurbitane-type triterpene glycosides from the fruits of Momordica charantia. Planta Med 74:1291–1294. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1081297
Ma L, Wang Q, Mu J, Fu A, Wen C, Zhao X et al (2020) The genome and transcriptome analysis of snake gourd provide insights into its evolution and fruit development and ripening. Hortic Res 7:199. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-020-00423-9
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2009) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Seki H, Sawai S, Ohyama K et al (2011) Triterpene functional genomics in licorice for identification of CYP72A154 involved in the biosynthesis of glycyrrhizin. Plant Cell 23:4112. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.082685
Seppey M, Manni M, Zdobnov EM (2019) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness. Methods Mol Biol 1962:227–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_14
Shang Y et al (2014) Biosynthesis, regulation, and domestication of bitterness in cucumber. Plant Sci 346:1084–1088. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259215
Shibuya M, Adachi S, Ebizuka Y (2004) Cucurbitadienol synthase, the first committed enzyme for cucurbitacin biosynthesis, is a distinct enzyme from cycloartenol synthase for phytosterol biosynthesis. Tetrahedron 60:6995–7003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.04.088
Suebsakwong P, Chulrik W, Chunglok W, Li J, Yao Z-j, Suksamrarn AJRA (2020) New triterpenoid saponin glycosides from the fruit fibers of Trichosanthes cucumerina L. RSC Adv 10:10461–10470. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA01176B
Takase S et al (2019a) Identification of triterpene biosynthetic genes from Momordica charantia using RNA-seq analysis. Biosci 83:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1530096
Takase S et al (2019b) Allylic hydroxylation of triterpenoids by a plant cytochrome P450 triggers key chemical transformations that produce a variety of bitter compounds. J Biol Chem 294:18662–18673. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra119.009944
Tang Q, Ma X, Mo C, Wilson IW, Song C, Zhao H, Yang Y, Fu W, Qiu D (2011) An efficient approach to finding Siraitia grosvenorii triterpene biosynthetic genes by RNA-seq and digital gene expression analysis. BMC Genomics 12:343. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-343
Thimmappa R, Geisler K, Louveau T, O’Maille P, Osbourn A (2014) Triterpene biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:225–257. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120229
Vitiello A, Rao R, Corrado G, Chiaiese P, Digilio MC, Cigliano RA, D’Agostino N (2018) De novo transcriptome assembly of Cucurbita Pepo L. leaf tissue infested by Aphis Gossypii. Data 3:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3030036
Xanthopoulou A, Psomopoulos F, Ganopoulos I, Manioudaki M, Tsaftaris A, Nianiou-Obeidat I, Madesis P (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly of two contrasting pumpkin cultivars. Genomics Data 7:200–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gdata.2016.01.006
Yang J, Zhan Y, Xiao J, Yin J (2018) Advances in the function of cytochrome P450 in structural modifications of triterpenoid and sterol skeletons in plants. Scientia Sinica Vitae 48:1065. https://doi.org/10.1360/N052018-00103
Zhou Y et al (2016) Convergence and divergence of bitterness biosynthesis and regulation in Cucurbitaceae. Nat Plants 2:16183. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2016.183
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Young Researcher Development Program from National Research Council of Thailand and Mahidol Medical Scholars Program (MSP), Mahidol University, Thailand. We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Weena Jiratchariyakul, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mahidol University, Thailand, for providing the TC seeds and the cucurbitacin B and bryonolic acid standards.
Funding
This work was supported by Young Researcher Development Program from National Research Council of Thailand, Chulalongkorn University (GRU 6203023003-1), and Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China (No. JQ18027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: PL, SS, VS, and SB; Methodology: PL; Analysis: PL; Resources: MY, QX, SS, VN, and SB; Writing—original draft preparation: PL; Writing—review and editing: MY, QX, SS, VN, and SB; Funding acquisition: MY, QX, SS, and SB; Supervision: MY, QX, SS, VN, and SB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Fumihiko Sato.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lertphadungkit, P., Qiao, X., Sirikantaramas, S. et al. De novo transcriptome analysis and identification of candidate genes associated with triterpenoid biosynthesis in Trichosanthes cucumerina L.. Plant Cell Rep 40, 1845–1858 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02748-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02748-8