Abstract
Key message
Phosphate starvation increased the production of phenolic acids by inducing the key enzyme genes in a positive feedback pathway in Saliva miltiorrhiza hairy roots. SPX may be involved in this process.
Abstract
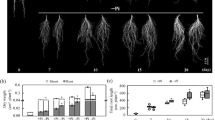
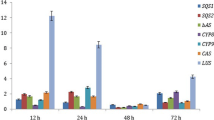
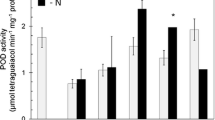
Salvia miltiorrhiza is a wildly popular traditional Chinese medicine used for the treatment of coronary heart diseases and inflammation. Phosphate is an essential plant macronutrient that is often deficient, thereby limiting crop yield. In this study, we investigated the effects of phosphate concentration on the biomass and accumulation of phenolic acid in S. miltiorrhiza. Results show that 0.124 mM phosphate was favorable for plant growth. Moreover, 0.0124 mM phosphate was beneficial for the accumulation of phenolic acids, wherein the contents of danshensu, caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid, and salvianolic acid B were, respectively, 2.33-, 1.02-, 1.68-, and 2.17-fold higher than that of the control. By contrast, 12.4 mM phosphate inhibited the accumulation of phenolic acids. The key enzyme genes in the phenolic acid biosynthesis pathway were investigated to elucidate the mechanism of phosphate starvation-induced increase of phenolic acids. The results suggest that phosphate starvation induced the gene expression from the downstream pathway to the upstream pathway, i.e., a feedback phenomenon. In addition, phosphate starvation response gene SPX (SYG1, Pho81, and XPR1) was promoted by phosphate deficiency (0.0124 mM). We inferred that SPX responded to phosphate starvation, which then affected the expression of later responsive key enzyme genes in phenolic acid biosynthesis, resulting in the accumulation of phenolic acids. Our findings provide a resource-saving and environmental protection strategy to increase the yield of active substance in herbal preparations. The relationship between SPX and key enzyme genes and the role they play in phenolic acid biosynthesis during phosphate deficiency need further studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel S, Ticconi CA, Delatorre CA (2002) Phosphate sensing in higher plants. Physiol Plant 115:1–8
Battini JL, Rasko JEJ, Miller AD (1999) A human cell-surface receptor for xenotropic and polytropic murine leukemia viruses: possible role in G protein-coupled signal transduction. PNAS 96:1385–1390
Chen H, Chen F (2000) Effect of yeast elicitor on the secondary metabolism of Ti-transformed cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep 619:710–717
Cheng HT, Li XL, Li XR, Li YH, Wang LJ, Xue M (2012) Simultaneous quantification of selected compounds from Salvia herbs by HPLC method and their application. Food Chem 130:1031–1035
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change 19:292–305
Desnos T (2008) Root branching responses to phosphate and nitrate. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:82–87
Doerner P (2008) Phosphate starvation signaling: a threesome controls systemic Pi homeostasis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:536–540
Duan K, Yi KK, Dang L, Huang HJ, Wu W, Wu P (2008) Characterization of a sub-family of Arabidopsis genes with the SPX domain reveals their diverse functions in plant tolerance to phosphorus starvation. Plant J 54:965–975
Ghillebert R, Swinnen E, Snijder PD, Smets B, Winderickx J (2011) Differential roles for the low-affinity phosphate transporters Pho87 and Pho90 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 434:243–251
Grennan AK (2008) Phosphate accumulation in plants: signaling. Plant Physiol 148:3–5
Hammond JP, Broadley MR, White PJ (2004) Genetic responses to phosphorus deficiency. Ann Bot 94:323–332
Han MY, Wl Guo, Liang ZS, Yang DF, Yan XJ (2015) Effects of cerous nitrate on growth and tanshinone production in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. J Rare Earths 33:1228–1235
Hou XL, Wu P, Jiao FC, Jia QJ, Chen HM, Yu J, Song XW, Yi KK (2005) Regulation of the expression of OsIPS1 and OsIPS2 in rice via systemic and local Pi signaling and hormones. Plant, Cell Environ 28:353–364
Huang T, Gao WY, Wang J, Cao Y, Zhao YX (2010) Selection and optimization of a high-producing tissue culture of Panax ginseng C. A Meyer Acta Physiol Plant 32:765–772
Jiang CF, Gao XH, Liao LL, Harberd NP, Fu XD (2007) Phosphate starvation root architecture and anthocyanin accumulation responses are modulated by the gibberellin-DELLA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:1460–1470
Kai GY, Xu H, Zhou CC, Liao P, Xiao JB, Luo XQ, You LJ, Zhang L (2011) Metabolic engineering tanshinone biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. Metab Eng 13:319–327
Lenburg ME, O’Shea EK (1996) Signaling phosphate starvation. Trands in Biochem Sci 21:383–387
Liang ZS, Ma YN, Xu T, Cui BM, Liu Y, Guo ZX, Yang DF (2013) Effects of abscisic acid, gibberellin, ethylene and their interactions on production of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots. PLoS One 8:e72806
Liu F, Wang ZY, Ren HY, Shen CJ, Li Y, Ling HQ, Wu CY, Lian XM, Wu P (2010) OsSPX1 suppresses the function of OsPHR2 in the regulation of expression of OsPT2 and phosphate homeostasis in shoots of rice. Plant J 62:508–517
Liu JY, Osbourn A, Ma PD (2015) MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant 8:689–708
Lynch JP (2011) Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant Physiol 156:1041–1049
Misson J, Raghothama KG, Jain A, Jouhet J, Block MA et al (2005) A genome-wide transcriptional analysis using Arabidopsis thaliana Affymetrix gene chips determined plant responses to phosphate deprivation. PNAS 102:11934–11939
Morcuende R, Bari R, Gibon Y, Zheng WM, Pant BD et al (2007) Genome-wide reprogramming of metabolism and regulatory networks of Arabidopsis in response to phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ 30:85–112
Peret B, Clement M, Nussaume L, Desnos T (2011) Root developmental adaptation to phosphate starvation: better safe than sorry. Trends Plant Sci 16:1360–1385
Rouached H, Stefanovic A, Secco D, Arpat AB, Gout E, Bligny R, Poirier Y (2011) Uncoupling phosphate deficiency from its major effects on growth and transcriptome via PHO1 expression in Arabidopsis. Plant J 65:557–570
Sakano K, Matsumoto M, Yazaki Y, Kiyota S, Okihara K (1995) Inorganic phosphate as a negative conditioning factor in plant cell culture. Plant Sci 107:117–124
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling SM (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453
Schroeder JL, Delhaize E, Frommer WB, Guerinot ML, Harrison MJ (2013) Using membrane transporters to improve crops for sustainable food production. Nature 497:60–66
Secco D, Wang C, Arpat BA, Wang ZY, Poirier Y (2012) The emerging importance of the SPX domain-containing proteins in phosphate homeostasis. New Phytol 193:842–851
Shen S, Zhang SC, Yang DF, Liang ZS (2011) Effects of mediums on the growth of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots and accumulation of tanshinones in S. Miltiorrhiza. J Northwest A&F Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 39:130–139
Shi J, Hu H, Zhang KM, Zhang W, Yu YN, Wu ZC, Wu P (2014) The paralogous SPX3 and SPX5 genes redundantly modulate Pi homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot 65:859–870
Song J, Wang ZZ (2009) Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene (SmPAL1) from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Mol Biol Rep 36:939–952
Song J, Wang ZZ (2011) RNAi-mediated suppression of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene in Salvia miltiorrhiza causes abnormal phenotypes and a reduction in rosmarinic acid biosynthesis. J Plant Res 124:183–192
Song J, Ji YY, Xu K, Wang ZZ (2012) An integrated analysis of the rosmarinic acid-biosynthetic genes to uncover the regulation of rosmarinic acid pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1501–1511
Spain BH, Koo D, Ramakrishnan M, Dzudzor B, Colicelli J (1995) Truncated forms of a novel yeast protein suppress the lethality of a G protein a subunit deficiency by interacting with the b subunit. J Biol Chem 270:25435–25444
Suen PK, Zhang SY, Samuel Sun SM (2015) Molecular characterization of a tomato purple acid phosphatase during seed germination and seedling growth under phosphate Stress. Plant Cell Rep 34:981–992
Wang WL, Liang ZS, Sun Q, Han JP, Wei YS et al (2003) Study on N, P fertilization model of Salvia miltiorrhiza in different soil fertility. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica 23:1406–1410
Wang ZY, Hu H, Huang HJ, Duan K, Wu ZC, Wu P (2009) Regulation of OsSPX1 and OsSPX3 on expression of OsSPX domain genes and Pi-starvation signaling in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 51:663–674
Wen ZY, Zhong JJ (1997) Effects of initial phosphate concentration on physiological aspects of suspension cultures of rice cells: a kinetic study. J Fermen Bioeng 83:381–385
Xiao Y, Zhang L, Gao SH, Saechao Saengking, Di P, Chen JF, Chen WS (2011) The c4 h, tat, hppr and hppd genes prompted engineering of rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. PLoS One 6:e29713
Xing BC, Yang DF, Guo WL, Liang ZS, Yan XJ (2015) Ag+ as a more effective elicitor for production of tanshinones than phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Molecules 20:309–324
Xu H, Zhang L, Zhou CC, Xiao JB, Liao P, Kai GY (2010) Metabolic regulation and genetic engineering of pharmaceutical component tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Med Plant Res 4:2591–2597
Xu L, Jin L, Long L, Liu LL, He X (2012) Overexpression of GbWRKY1 positively regulates the Pi starvation response by alteration of auxin sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31:2177–2188
Yan YP, Wang ZZ (2007) Genetic transformation of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 88:175–184
Yan Q, Shi M, Janet Ng WuJY (2006) Elicitor-induced rosmarinic acid accumulation and secondary metabolism enzyme activities in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Plant Sci 170:853–858
Yin SS, Gao WY, Liang YY, Wang J, Liu H (2013) Influence of sucrose concentration and phosphate source on biomass and metabolite accumulation in adventitious roots of Pseudostellaria heterophylla. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1579–1585
Yin SS, Zhang Y, Gao WY, Wang J, Man SL, Liu H (2014) Effects of nitrogen source and phosphate concentration on biomass and metabolites accumulation in adventitious root culture of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Acta Physiol Plant 36:915–921
Yuan Y, Liu YJ, Lu DM, Huang LQ, Liang RX (2009) Genetic stability, active constituent, and pharmacoactivity of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots and wild plant. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 64:557–563
Zhang SC, Liu Y, Shen S, Liang ZS, Yang DF (2011) Effects of elicitors on accumulation of phenolic acids and tanshinones in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root. China J Chin Mater Med 36:1269–1274
Zhang Y, Jiang PX, Ye M, Kim SH, Jiang C, Lü JX (2012) Tanshinones: sources, pharmacokinetics and anti-cancer activities. Int J Mol Sci 13:13621–13666
Zhang SC, Ma PD, Yang DF, Li WJ, Liang ZS, Liu Y, Liu FH (2014a) Cloning and characterization of a putative R2R3 MYB transcriptional repressor of the rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway from Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS One 8:e73259
Zhang SC, Yan Y, Wang BQ, Liang ZS, Liu Y, Liu FH, Qi ZH (2014b) Selective responses of enzymes in the two parallel pathways of rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway to elicitors in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. J Biosci Bioeng 117:645–651
Zhang ZL, Liao H, Lucas WJ (2014c) Molecular mechanisms underlying phosphate sensing, signaling, and adaptation in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 56:192–220
Zhu ZB, Liang ZS, Han RL, Dong JE (2009) Growth and saikosaponin production of the medicinal herb Bupleurum chinense DC. under different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus. Ind Crops Prod 29:96–101
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LZ16H280001), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373908, 81403033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Zhao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Yang, D., Liang, T. et al. Phosphate starvation promoted the accumulation of phenolic acids by inducing the key enzyme genes in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1933–1942 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2007-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2007-x