Abstract
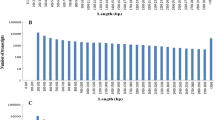
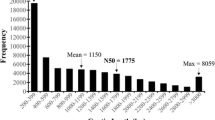
Garlic is widely used as a spice throughout the world for the culinary value of its flavor and aroma, which are created by the chemical transformation of a series of organic sulfur compounds. To analyze the transcriptome of Allium sativum and discover the genes involved in sulfur metabolism, cDNAs derived from the total RNA of Allium sativum buds were analyzed by Illumina sequencing. Approximately 26.67 million 90 bp paired-end clean reads were achieved in two libraries. A total of 127,933 unigenes were generated by de novo assembly and were compared with the sequences in public databases. Of these, 45,286 unigenes had significant hits to the sequences in the Nr database, 29,514 showed significant similarity to known proteins in the Swiss-Prot database and, 20,706 and 21,952 unigenes had significant similarity to existing sequences in the KEGG and COG databases, respectively. Moreover, genes involved in organic sulfur biosynthesis were identified. These unigenes data will provide the foundation for research on gene expression, genomics and functional genomics in Allium sativum.
Key message The obtained unigenes will provide the foundation for research on functional genomics in Allium sativum and its closely related species, and fill the gap of the existing plant EST database.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACSO:
-
Sulfur-alk(en)yl cysteine sulfoxide
- BLAST:
-
Basic local alignment search tool
- COG:
-
Cluster of orthologous group
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
References
Agarwal A, Koppstein D, Rozowsky J, Sboner A, Habegger L, Hillier LW, Sasidharan R, Reinke V, Waterston RH, Gerstein M (2010) Comparison and calibration of transcriptome data from RNA-Seq and tiling arrays. BMC Genomics 11:383
Arumuganathan A, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676
Garber M, Grabherr MG, Guttman M, Trapnell C (2011) Computational methods for transcriptome annotation and quantification using RNA-seq. Nat Methods 8:469–477
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, Palma Fd, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652
Ikegami F, Murakoshi I (1994) Enzymic synthesis of non-protein β-substituted alanines and some higher homologues in plants. Phytochemistry 35:1089–1104
Ikegami F, Takayama K, Tajima C, Murakoshi I (1988) Purification and properties of β-cyano-l-alanine synthase from Spinacia oleracea. Phytochemistry 27:2011–2016
Iseli C, Jongeneel C, Bucher P (1999) ESTScan: a program for detecting, evaluating, and reconstructing potential coding regions in EST sequences. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 1:134–148
Jones MG, Hughes J, Tregova A, Milne J, Tomsett AB, Collin HA (2004) Biosynthesis of the flavour precursors of onion and garlic. J Exp Bot 55:1903–1918
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277–D280
Kuhl JC, Cheung F, Yuan Q, Martin W, Zewdie Y, McCallum J, Catanach A, Rutherford P, Sink KC, Jenderek M, Prince JP, Town CD, Havey MJ (2004) A unique set of 11,008 onion expressed sequence tags reveals expressed sequence and genomic differences between the monocot orders Asparagales and Poales. Plant Cell 16:114–125
Lawson LD (1996) The composition and chemistry of garlic cloves and processed garlic. In: Koch HP, Lawson LD (eds) The science and therapeutic application of Allium sativum L. and related species. Williams and Wilkins, Maryland, pp 37–108
Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res 20:265–272
Marioni JC, Mason CE, Mane SM, Stephens M, Gilad Y (2008) RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Res 18:1509–1517
Martin KW, Ernst E (2003) Herbal medicines for treatment of bacterial infections: a review of controlled clinical trials. J Antimicrob Chemother 51:241–246
McCallum J, Pither-Joyce M, Shaw M, Kenel F, Davis S, Butler R, Scheffer J, Jakse J, Havey MJ (2006) Genetic mapping of sulfur assimilation genes reveals a QTL for onion bulb pungency. Theor Appl Genet 114:815–822
McCallum J, Thomas L, Shaw M, Pither-Joyce M, Leung S, Cumming M, McManus MT (2011) Genotypic variation in the sulfur assimilation and metabolism of onion (Allium cepa L.) I. Plant composition and transcript accumulation. Phytochemistry 72:882–887
Ness RW, Siol M, Barrett SC (2011) De novo sequence assembly and characterization of the floral transcriptome in cross- and self-fertilizing plants. BMC Genomics 12:298
Ohri D, Pistrick K (2001) Phenology and genome size variation in Allium L.—a tight correlation? Plant Biol 3:654–660
Shi CY, Yang H, Wei CL, Yu O, Zhang ZZ, Jiang CJ, Sun J, Li YY, Chen Q, Xia T, Wan XC (2011) Deep sequencing of the Camellia sinensis transcriptome revealed candidate genes for major metabolic pathways of tea-specific compounds. BMC Genomics 12:131
Wang Z, Fang B, Chen J, Zhang X, Luo Z, Huang L, Chen X, Li Y (2010) De novo assembly and characterization of root transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing and development of cSSR markers in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). BMC Genomics 11:726
Yang SS, Tu ZJ, Cheung F, Xu WW, Lamb JF, Jung H-JG, Vance CP, Gronwald JW (2011) Using RNA-Seq for gene identification, polymorphism detection and transcript profiling in two alfalfa genotypes with divergent cell wall composition in stems. BMC Genomics 12:199
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Chinese National Department Public Benefit Research Foundation (No. 200903018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Quiros.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Zhou, S., Meng, F. et al. De novo assembly and characterization of the garlic (Allium sativum) bud transcriptome by Illumina sequencing. Plant Cell Rep 31, 1823–1828 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1295-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1295-z