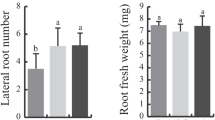
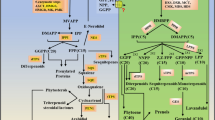
Abstract
The Arabidopsis HD2 family of histone deacetylases consist of 4 members (HD2A, HD2B, HD2C, HD2D) that play diverse roles in plant development and physiology through chromatin remodelling. Here, we show that the transcripts of HD2 family members selectively accumulate in response to glucose through a HXK1-independent signal transduction pathway during the early stages of seedling growth. Germination was enhanced in hd2a null mutants relative to wild-type seeds. In contrast, hd2c mutants were restrained in germination relative to wild-type seeds. In hd2a/hd2c double mutants, germination was restored to wild-type levels. The data suggests that HD2A and HD2C may have different and opposing functions in germination with the glucose/HD2A pathway acting to restrain germination and the HD2C pathway acting to enhance germination. These pathways may function early in the regulation of seedling germination, independently of the glucose/HXK1/ABA signal transduction pathway, to fine tune the onset of germination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhattab R (2009) Glucose signal transduction an the role of the HD2 family of histone deacetylases in Arabidopsis seedling germination and development. MSc thesis, Carleton University, Department of Biology, Ottawa, Canada
Alinsug MV, Yu C-W, Wu K (2009) Phylogenetic analysis, subcellular localization, and expression patterns of RPD3/HDA1 family histone deacetylases in plants. BMC Plant Biol 9:37
Ausin I, Alonso-Blanco C, Jarillo JA, Ruiz-Garcia L, Martínez-Zapater JM (2004) Regulation of flowering time by FVE, retinoblastoma-associated protein. Nat Genet 36:162–166
Bossi F, Cordoba E, Dupré P, Mendosa MS, Románcs CS, León P (2009) The Arabidopsis ABA- insensitive (ABI) 4 factor acts as a central transcription activator of the expression of its own gene, and for the induction of ABI5 and SBE2.2 genes during sugar signaling. Plant J 59:359–374
Chen Y, Ji F, Xie H, Liang J, Zhang J (2006) The regulator of G-protein signaling proteins involved in sugar and abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Physiol 140:302–310
Chen Z, Hafidh s, Poh SH, Twell D, Berger F (2009) Proliferation and cell fate establishment during Arabidopsis male gametogenesis depends on the Retinoblastoma protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7257–7262
Chinnusamy V, Gong Z, Zhu JK (2008) Abscisic acid-mediated epigenetic processes in plant development and stress responses. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1187–1195
Cho Y-H, Yoo S-D, Sheen J (2006) Regulatory functions of nuclear hexokinase 1 complex in glucose signaling. Cell 127:579–589
Cho Y-H, Yoo S-D, Sheen J (2007) Glucose signaling through nuclear hexokinase 1 complex in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 2(2):123–124
Colville AH (2007) Sugar and HD2 expression: new insights into the HD2 plant-specific class of histone deacetylases, MSc thesis, Carleton University, Department of Biology, Ottawa, Canada
Dekkers BJW, Schuurmans JAMJ, Smeekens SCM (2004) Glucose delays seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 218:579–588
Dekkers BJW, Schuurmans JAMJ, Smeekens SCM (2008) Interaction between sugar and abscisic acid signaling during early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67:151–167
Desvoyes B, Ramirez-Parra E, Xie Q, Chua N-H, Gutierrez C (2006) Cell type-specific role of the Retinoblastoma/E2F pathway during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Physiol 140:67–80
Dinneny JR, Benfey PN (2005) Stem cell research goes underground: the RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED gene in root development. Cell 123:1180–1182
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14:S15–S45
Fong PM, Tian L, Chen ZJ (2006) Arabidopsis thaliana histone deacetylase 1 (AtHD1) is localized in euchromatic regions and demonstrates histone deacetylase activity in vitro. Cell Res 16:479–488
Gibson SI (2005) Control of plant development and gene expression by sugar sensing. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:93–102
Gutierrez C, Ramirez-Parra E, Castellano MM, del Pozo JC (2002) G1 to S transition: more than a cell cycle engine switch. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:480–486
Herve C, Dabos P, Bardet C, Jauneau A, Auriac MC, Ramboer A, Lacout F, Tremousaygue D (2009) In vivo interference with AtTCP20 function induces severe plant growth alterations and deregulates the expression of many genes important for development. Plant Physiol 149:1462–1477
Hill K, Wang H, Perry SE (2008) A transcriptional repression motif in the MADS factor AGL15 is involved in recruitment of histone deacetylase complex components. Plant J 53:172–185
Hirano H, Harashima H, Shinmyo A, Sekine M (2008) Arabidopsis RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED PROTEIN 1 is involved in G1 phase cell cycle arrest caused by sucrose starvation. Plant Mol Biol 66:259–275
Inzé D, De Veylder L (2006) Cell cycle regulation in plant development. Annu Rev Genet 40:77–105
Johnson CA, Taylor JP, Gao Y, Kimple AJ, Grigston JC, Chen J-G, Siderovski DP, Jones AM, Willard FS (2007) GTPase acceleration as the rate-limiting step in Arabidopsis G protein-coupled sugar signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17317–17322
Julien PE, Mosquna A, Ingouff M, Sakata T, Ohad N, Berger F (2008) Retinoblastoma and its binding partner MSI1 control imprinting in Arabidopsis. Plos Biol 6:1693–1705
Köhler C, Henning L, Bouveret R, Gheyselinck J, Grossniklaus U, Gruissem W (2003) Arabidopsis MSI1 is a component of the MEA/FIE Polycomb group complex and required for seed development. EMBO J 22:4804–4814
Lawrence RJ, Earley K, Pontes O, Siva M, Chen ZJ, Neves N, Viegas W, Pikkard CS (2004) A concerted DNA methylation/histone methylation switch regulates rRNA gene dosage control and nucleolar dominance. Mol Cell 13:599–609
Li C, Potuschak T, Colόn-Carmona A, Gutiérrez RA, Doerner P (2005) Arabidopsis TCP20 links regulation of growth and cell division control pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12978–12983
Li Y, Lee KK, Walsh S, Smith C, Hadingham S, Sorefan K, Cawley G, Bevan MW (2006) Establishing glucose- and ABA-regulated transcription networks in Arabidopsis by microarray analysis and promoter classification using a relevance vector machine. Genome Res 16:414–427
Lusser A, Brosch G, Loidl A, Haas H, Loidl P (1997) Identification of maize histone deacetylase HD2 as an acidic nucleolar phosphoprotein. Science 277:88–91
Manevski A, Bertoni G, Bardet C, Tremousaygue D, Lescure B (2000) In synergy with various cis-acting elements, plant interstitial telomere motifs regulate gene expression in Arabidopsis root meristems. FEBS Lett 483:43–46
Moore B, Zhou L, Rolland F, Hall Q, Cheng W-H, Liu Y-X, Hwang I, Jones T, Sheen J (2003) Role of the Arabidopsis glucose sensor HXK1 in nutrient, light, and hormonal signaling. Science 300:332–336
Nicolai M, Roncato MA, Canoy AS, Rouquie D, Sarda X, Freyssinet G, Robaglia C (2006) Large-scale analysis of mRNA translation states during sucrose starvation in Arabidopsis cells identifies cell proliferation and chromatin structure as targets of translational control. Plant Physiol 141:663–673
Ogas J, Kaufmann S, Henderson J, Somerville C (1999) PICKLE is a CHD3 chromatin-remodeling factor that regulates the transition from embryonic to vegetative development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13839–13844
Pandey R, Müller A, Napoli CA, Selinger DA, Pikkard CS, Richards EJ, Bender J, Mount DW, Jorgensen RA (2002) Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 30:5036–5055
Perruc E, Kinoshita N, Lopez-Molina L (2007) The role of chromatin-remodeling factor PKL in balancing osmotic stress responses during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J 52:927–936
Price J, Li T-C, Kang SG, Na JK, Jang J-C (2003) Mechanisms of glucose signaling during germinatin of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132:1424–1438
Price J, Laxmi A, St Martin SK, Jang J-C (2004) Global transcription profiling reveals multiple sugar signal transduction mechanisms in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2128–2150
Riou-Khamlichi C, Menges M, Healy JMS, Murray JAH (2000) Sugar control of the plant cell cycle: differential regulation of Arabidopsis D-type cyclin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 20:4513–4521
Rolland F, Baena-Gonzalez E, Sheen J (2006) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms. Ann Rev Plant Biol 57:675–709
Rook R, Hadingham SA, Li Y, Bevan MW (2006) Sugar and ABA response pathways and the control of gene expression. Plant Cell Environ 29:426–434
Rossi V, Locatelli S, Lanzanova C, Boniotti MB, Varotto S, Pipal A, Goralik-Schramel M, Lusser A, Gatz C, Gutierrez C, Motto M (2003) A maize histone deacetylase and retinoblastoma-related protein physically interact and cooperate in repressing gene transcription. Plant Mol Biol 51:401–413
Rossignol P, Stevens R, Perennes C, Jasinski S, Cella R, Tremousaygue D, Bergounioux C (2002) AtE2F-a and AtAP-a, members of the E2F family of transcription factors, induce Arabidopsis leaf cells to re-enter S phase. Mol Genet Genomics 266:995–1003
Sridha S, Wu K (2006) Identification of AtHD2C as a novel regulator of abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 46:124–133
Tanaka M, Kikuchi A, Kamada H (2008) The Arabidopsis histone deacetylases HD6 and HDA19 contribute to the repression of the embryonic properties after germination. Plant Physiol 146:149–161
Tian L, Chen ZJ (2001) Blocking histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis induces pleiotropic effects on plant gene regulation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:33–37
Tian L, Fong MP, Wang JJ, Wei NE, Jing H, Doerge RW (2005) Reversible histone acetylation and deacetylation mediate genome-wide, promoter-dependent and locus-specific changes in gene expression during plant development. Genetics 169:337–345
Trémousaygue D, Manevski A, Bardet C, Lescure N, Lescure B (1999) Plant interstitial telomere motifs participate in the control of gene expression in root meristems. Plant J 20:553–561
Trémousaygue D, Garnier L, Bardet C, Dabos P, Hervé C, Lescure B (2003) Internal telomeric repeats and ‘TCP’ domain protein-binding sites co-operate to regulate gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana cycling cells. Plant J 33:957–966
Tsukagoshi H, Morikami A, Nakamura K (2007) Two B3 domain transcriptional repressors prevent sugar- inducible expression of seed maturation genes in Arabidopsis seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2543–2547
Villadsen D, Smith SM (2004) Identification of more than 200 glucose-responsive Arabidopsis genes none of which responds to 3-o-methylglucose or 6-deoxyglucose. Plant Mol Biol 55:467–477
Welchen E, Gonzalez DH (2006) Overrepresentation of elements recognized by TCP-domain transcription factors in the upstream regions of nuclear genes encoding components of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation machinery. Plant Physiol 141:540–545
Wildwater M, Campilho A, Perez–Perez JM, Heidstra R, Blilou I, Korthout H, Chatterjee J, Mariconti L, Gruissem W, Scheres B (2005) The RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED gene regulates stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis roots. Cell 123:1337–1349
Wu K, Tian L, Malik K, Brown D, Miki B (2000) Functional analysis of HD2 histone deacetylase homologs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 20:19–28
Xiao W, Sheen J, Jang J-C (2000) The role of hexokinase in plant sugar signal transduction and growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 44:451–461
Yuan K, Wysocka-Diller J (2006) Phytohormone signaling pathways interact with sugars during seed germination and seedling development. J Exp Bot 57:3359–3367
Zhou C, Labbe H, Sridha S, Wang L, Tian L, Latoszek-Green M, Yang Z, Brown D, Miki B, Wu K (2004) Expression and function of HD2-type histone deacetylases in Arabidopsis development. Plant J 38:715–724
Zhou C, Zhang L, Duan J, Miki B, Wu K (2005) Histone deacetylase19 HDA19 is involved in jasmonic acid and ethylene signaling of pathogen-response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:1196–1204
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by an NSERC Discovery Grant to BM and by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Jordan.
A. Colville and R. Alhattab have contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colville, A., Alhattab, R., Hu, M. et al. Role of HD2 genes in seed germination and early seedling growth in Arabidopsis . Plant Cell Rep 30, 1969–1979 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1105-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1105-z