Abstract
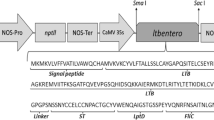
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is one of the main causative agents of diarrhea in infants and for travelers. Inclusion of a heat-stable (ST) toxin into vaccine formulations is mandatory as most ETEC strains can produce both heat-labile (LT) and ST enterotoxins. In this study, a genetic fusion gene encoding for an LTB:ST protein has been constructed and transferred into tobacco via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Transgenic tobacco plants carrying the LTB:ST gene are then subjected to GM1-ELISA revealing that the LTB:ST has assembled into pentamers and displays antigenic determinants from both LTB and ST. Protein accumulation of up to 0.05% total soluble protein is detected. Subsequently, mucosal and systemic humoral responses are elicited in mice orally dosed with transgenic tobacco leaves. This has suggested that the plant-derived LTB:ST is immunogenic via the oral route. These findings are critical for the development of a plant-based vaccine capable of eliciting broader protection against ETEC and targeting both LTB and ST. Features of this platform in comparison to transplastomic approaches are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken R, Hirst TR (1992) Development of an immunoassay using recombinant maltose-binding protein-STa fusions for quantitating antibody responses against STa, the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 30:732–734
Bosch D, Schots A (2010) Plant glycans: friend or foe in vaccine development? Expert Rev Vaccines 9:835–842
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cardenas L, Clements JD (1993) Development of mucosal protection against the heat stable enterotoxin (ST) of Escherichia coli by oral immunization with a genetic fusion delivered by a bacterial vector. Infect Immun 61:4629–4636
Chikwamba R, McMurray J, Shou H, Frame B, Pegg SE, Scott P, Mason H, Wang K (2002) Expression of a synthetic E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin B sub-unit (LT-B) in maize. Mol Breed 10:253–265
Clements JD (1990) Construction of a nontoxic fusion peptide for immunization against Escherichia coli strains that produce heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins. Infect Immun 58:1159–1166
Clements JD, Sack DA, Harris JR, Chakraborty J, Neogy PK, Stanton B, Huda N, Khan MU, Kay BA, Khan MR (1988) Crossprotection by B subunit-whole cell cholera vaccine against diarrhea associated with heat-labile toxin-producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: results of a large-scale field trial. J Infect Dis 158:372–377
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Faye L, Gomord V (2010) Success stories in molecular farming—a brief overview. J. Plant Biotechnol 8:525–528
Field M (1979) Modes of action of enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis 1:918–926
Granell A, Fernández del-Carmen A, Orázez D (2010) In planta production of plant-derived and non-plant-derived adjuvants. Expert Rev Vaccines 8:843–858
Horsch RB, Fraley RT, Rogers SG, Sanders PR, Lloyd A (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Kang TJ, Han SC, Yang MS (2005) Expression of the B subunit of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin in tobacco using a herbicide resistance gene as a selection marker. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 81:165–174
Munro S, Pelham HRB (1987) A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell 48:899–907
Pereira CM, Guth BE, Sbrogio-Almeida ME, Castilho BA (2001) Antibody response against Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin expressed as fusions to flagellin. Microbiology 147:861–867
Rosales-Mendoza S, Soria-Guerra RE, Olivera-Flores MTJ, Lopez-Revilla R, Argüello-Astorga GR, Jimenez-Bremont JF, Garcia de la Cruz RF, Loyola-Rodriguez JP, Alpuche-Solis AG (2007) Expression of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (LT-B) in carrot (Daucus carota L.). Plant Cell Rep 26:969–976
Rosales-Mendoza S, Soria-Guerra RE, López-Revilla R, Moreno-Fierros L, Alpuche-Solís A (2008) Ingestion of transgenic carrots expressing the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit protects mice against cholera toxin challenge. Plant Cell Rep 27:79–84
Rosales-Mendoza S, Alpuche-Solís AG, Soria-Guerra RE, Moreno-Fierros L, Martínez-González L, Herrera-Díaz A, Korban SS (2009) Expression of an Escherichia coli antigenic fusion protein comprising the heat labile toxin B subunit and the heat stable toxin, and its assembly as a functional oligomer in transplastomic tobacco plants. Plant J 57:45–54
Saarilahti HT, Palva ET, Holmgren J, Sanchez J (1989) Fusion of genes encoding Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin and outer membrane protein OmpC. Infect Immun 57:3663–3665
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sanchez J, Johansson S, Löwenadler B, Svennerholm AM, Holmgren J (1990) Recombinant cholera toxin B subunit and gene fusion proteins for oral vaccination. Res Microbiol 141:971–979
Sato T, Shimonishi Y (2004) Structural features of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin that activates membrane-associated guanylyl cyclase. J Peptide Res 63:200–206
Svennerholm AM, Tobias J (2008) Vaccines against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Expert Rev Vaccines 7:795–804
Taxt A, Aasland R, Sommerfelt H, Nataro J, Puntervoll P (2010) Heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli as a vaccine target. Infect Immun 78:1824–1831
Walker RI, Steele D, Aguado T, the Ad Hoc ETEC Technical Expert Committee (2007) Analysis of strategies to successfully vaccinate infants in developing countries against enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) disease. Vaccine 25:2545–2566
WHO (2010) http://www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/e_e_coli/en/
Zhang W, Francis DH (2010) Genetic fusions of heat-labile toxoid (LT) and heat-stable toxin b (STb) of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit protective anti-LT and anti-STb antibodies. Clinical Vaccine Immunol 17:1223–1231
Zhang W, Zhang C, Francis DH, Fang Y, Knudsen D, Nataro JP, Robertson DC (2010) Genetic fusions of heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) toxoids of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit neutralizing anti-LT and anti-STa antibodies. Infect Immun 78:316–325
Zheng JP, Zhang ZS, Li SQ, Liu XX, Yuan SL, Wang P, Zhan DW, Wang LC, Huang CF (2005) Construction of a novel Shigella live-vector strain co-expressing CS3 and LTB/STm of enterotoxigenic E. coli. World J Gastroenterol 11:3411–3418
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by grants El Potosí estudiantil 2004 (IPICYT), 37048-B, 56980 and 102109 from CONACYT and PROMEP 103.5/10/5460. Thanks to Dr. John Clements for providing the LTB protein and Dr. Jim Carrington for supplying the pTRL0027 vector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Lakshmanan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosales-Mendoza, S., Soria-Guerra, R.E., Moreno-Fierros, L. et al. Immunogenicity of nuclear-encoded LTB:ST fusion protein from Escherichia coli expressed in tobacco plants. Plant Cell Rep 30, 1145–1152 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1023-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1023-0