Abstract
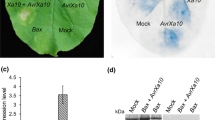
Emerging evidence suggests that plants and animals may share certain biochemical commonalities in apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD) pathways, though plants lack key animal apoptosis related genes. In plants, PCD has many important functions including a role in immunity and resistance to pathogen infection. In this study, a rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase promoter is used to regulate the expression of the mouse pro-apoptotic bax gene in transgenic tobacco plants. Ectopic expression of the bax negatively affects the growth of transgenic plants. Nonetheless, results show that the bax transgene is induced upon infection by plant pathogens and accumulation of Bax is observed by Western blot analysis. By estimating and measuring the extent of cell death, release of active oxygen species, and accumulation defense-associated gene transcripts, it is shown that bax transgenic plants mount a more robust cell death response compared to control plants. The bax transgenic tobacco plants are also more resistant to infection by Phytophthora parasitica and Ralstonia solanacearum, but have no obvious resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. These results substantiate past studies and illustrate the powerful effects mammalian bax genes may have on plant development and disease resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez ME, Pennell RL, Meijer RJ, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 92:773–784
Cao H, Glazebrook J, Clarke JD, Volko S, Dong XN (1997) The Arabidopsis NPR I gene that control systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell 88:57–63
Chichkova NV, Kim SH, Titova ES, Kalkum M, Morozov VS, Rubtsov YP, Kalinina NO, Taliansky ME, Vartapetian AB (2003) A plant Caspase-like protease activated during the hypersensitive response. Plant Cell 16:157–171
Clark MS (1997) Plant molecular biology: a laboratory manual. Springer, Berlin
Coffeen WC, Wolpert TJ (2004) Purification and characterization of serine proteases that exhibit caspase-like activity and are associated with programmed cell death in Avena sativa. Plant Cell 16:857–873
Dannon EA, Wydra K (2004) Interaction between silicon amendment, bacterial wilt development and phenotype of Ralstonia solanacearum in tomato genotypes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 64:33–243
Dickinson M, Beynon J (2003) Annual plant review molecular plant pathology. V4 Sheffield Academic, Sheffield
Dickman MB, Park YK, Oltersdorf T, Li W, Clemente T, French R (2001) Abrogation of disease development in plants expressing animal antiapoptotic genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6957–6962
Gechev TS, Hille J (2005) Hydrogen peroxide as a signal controlling plant programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 168:17–20
Gilchrist DG (1998) Programmed cell death in plant disease: the purpose and promise of cellular suicide. Annu Rev Phytopathol 36:393–414
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:91–923
Gopalan S, Wei W, He SY (1996) hrp gene-dependent induction of hin1: a plant gene activated rapidly by both harpins and the avrPto gene-mediated signal. Plant J 10:591–600
Govrin EM, Levine A (2000) The hypersensitive response facilitates plant infection by the necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Curr Biol 10:751–757
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Greenberg JT (1996) Programmed cell death: a way of life for plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12094–12097
Hansen G (2000) Evidence for Agrobacterium-iduced apoptosis in maize cells. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:649–656
Hatsugai N, Kuroyanagi M, Yamada K, Meshi T, Tsuda S, Kondo M, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2004) A plant vacuolar protease, VPE, mediates virus-induced hypersensitive cell death. Science 305:855–858
Hückelhoven R, Dechert C, Kogel KH (2003) Overexpression of barley Bax inhibitor 1 induces breakdown of mlo-mediated penetration resistance to Blumeria graminis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5555–5560
Ji R, Zhang ZG, Wang YC, Zheng XB (2005) Phytophthora elicitor PB90 induced apoptosis in suspension cultures of tobacco. Chin Sci Bull 50:435–439
Kamoun S, West PV, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Groot KE, Govers F (1998) Resistance of Nicotiana Benthamiana to Phytophtoara infestans is mediated by the recognition of the elicitor protein INF1. Plant Cell 10:1413–1425
Kawai-Yamada M, Jin LH, Yoshinaga K, Hirata A, Uchimiya H (2001) Mammalian Bax induced plant cell death can be down regulated by overexpression of arabidopsis bax inhibitor-1 (AtBI-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12295–12330
Kawai-Yamada M, Ohori Y, Uchimiya H (2004) Dissection of arabidopsis Bax inhibitor-1 suppressing Bax-, hydrogen peroxide-, and salicylic acid-induced cell death. Plant Cell 16:21–32
Kawai-Yamada M, Saito Y, Jin LH, Ogawa T, Kim KM, Yu LH, Tone Y, Hirata A, Umeda M, Uchimiya H (2005) A novel arabidopsis gene causes Bax-like lethality in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 280:39468–39473
Kiba A, Tomiyama H, Takahashi H, Hamada H, Ohnishi K, Okuno T, Hikichi Y (2003) Induction of resistance and expression of defense-related genes in tobacco leaves infiltrated with Ralstonia solanacearum. Plant Cell Physiol 44:287–295
Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD (2003) Bcl-2-family proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:1–9
Lacomme C, Cruz SS (1999) Bax-induced cell death in tobacco is similar to the hypersensitive response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7956–7961
Lam E, Kato N, Lawton M (2001) Programmed cell death, mitochondria and the plant hypersensitive response. Nature 411:848–853
Lincoln JE, Richael C, Overduin B, Smith K, Bostock R, Gilchrist DG (2002) Expression of the antiapoptotic baculovirus p35 gene in tomato blocks programmed cell death and provides broad-spectrum resistance to disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15217–15221
Liu Y, Schiff M, Czymmek K, Tallόczy Z, Levine B, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2005) Autophage regulates programmed cell death during the plant innate immune response. Cell 121:567–577
Madeo F, Fröhlich E, Ligr M, Grey M, Sigrist SJ, Wolf DH, Fröhlich KU (1999) Oxygen stress: a regulator of apoptosis in yeast. J Biol Chem 145:757–767
Manon S, Chaudhuri B, Bueerin M (1997) Release of cytochrome c and decrease of cytochrome c oxidase in Bax expressing yeast cells, and prevention of these effects by coexpression of Bcl-xl. FEBS Lett 415:29–32
Matsumura H, Nirasawa S, Kiba A, Urasaki N, Saitoh H, Ito M, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H, Terauchi R (2003) Overexpression of Bax inhibitor suppresses the fungal elicitor-induced cell death in rice (Oryza sativa L) cells. Plant J 33:425–434
Mitsuhara I, Malik KA, Miura M, Ohashi Y (1999) Animal cell-death suppressors Bcl-xl and Ced-9 inhibit cell death in tobacco plants. Curr Biol 9:775–778
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A reversed medium forrapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Pawlowski J, Kraft AS (2000) Bax-induced apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:529–532
Peng JL, Bao ZL, Ren HY, Wang JS, Dong HS (2003) Harpin-elicited hypersensitive cell death and pathogen resistance requires the NDR1 and EDS1 genes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 62:317–326
Priault M, Camougrand N, Kinnally KW, Vallette FM, Manon S (2003) Yeast as a tool to study Bax/mitochondrial interactions in cell death. FEMS Yeast Res 1576:1–13
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shadle GL, Wesley SV, Korth KL, Chen F, Lamb C, Dixon RA (2003) Pheynlpropanoid compounds and disease resistance in transgenic tobacco with altered expression of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Phytochemical 64:153–161
Torres MA, Dangl JL (2005) Function of the respiratory burst oxidase in biotic interactions, abiotic stress and development. Curr Opin Biol 8:397–403
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EHY, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic Bax and Bak: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292:727–730
Xu P, Rogers SJ, Roossinck MJ (2004) Expression of antiapoptotic genes bcl-xl and ced-9 in tomato enhances resistance to viral-induced necrosis and abiotic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15805–15810
Yoshinaga K, Arimura SI, Hirata A, Niwa Y, Yun DJ, Tsutsumi N, Uchimiya H, Kawai-Yamada M (2005) Mammalian bax initiates plant cell death through organelle destruction. Plant Cell Rep 24:408–417
Yoshioka H, Numata N, Nakajima K, Katou S, Kawakita K, Rowland O, Jones JDG, Doke N (2003) Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox Homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 15:706–718
Zhang ZG, Wang YC, Li J, Ji R, Shen G, Wang SC, Zhou X, Zheng XB (2004) The role of SA in the hypersensitive response and systemic acquired resistance induced by the elicitor PB90 of Phytophthora boehmeriae. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 65:31–38
Zhu Q, Dabi T, Beeche A, Yamamoto R, Lawton MA, Lamb C (1995) Cloning and properties of a rice gene encoding pheylalanine ammonia-lyase. Plant Mol Biol 29:535–550
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the NSFC project (30471124) and New Century Excellent Scholar Project of Ministry of Education of China (NCET-04-0503). We thank Prof. Guo Zejian (China Agricultural Univeristy, China) for donating PAL promoter as a gift and Prof. Guo Jianhua and Shao Ming (Nanjing Agricultural University, China) for providing bacteria strains. Dr. Mark Gijzen, Dr. Dinah Qutob and Dr. Katherine Dobinson, (Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Canada) are especially acknowledged for critical reading of the manuscript. We appreciate Dr. Paul Tyler (University of Melbourne, Australia) for helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.S. Judelson.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1097-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suomeng, D., Zhengguang, Z., Xiaobo, Z. et al. Mammalian pro-apoptotic bax gene enhances tobacco resistance to pathogens. Plant Cell Rep 27, 1559–1569 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0554-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0554-5