Abstract
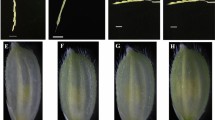
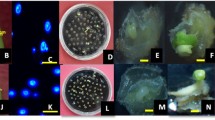
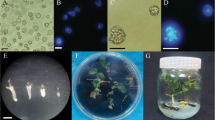
We report high frequencies of embryo production and plant regeneration through isolated microspore culture of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Microspores cultured in modified NLN medium (NLNS) divided and developed to embryos. Globular and heart-shaped embryos were observed from 3 weeks after the beginning of culture, and many embryos reached the cotyledonary stage after 4 weeks of culture. These cotyledonary embryos developed to plantlets after transfer to solid B5 basal medium. We also optimized conditions for embryo production by varying the pretreatment media, the carbon sources, and culture densities. Heat shock treatment in sucrose-starvation medium was more effective than in B5 medium. Direct comparisons of sucrose and maltose as carbon sources clearly demonstrated the superiority of sucrose compared to maltose, with the highest frequency of embryo production being obtained in 9% (w/v) sucrose. Microspore plating density was critical for efficient embryonic induction and development, with an optimal plating density of 8 × 104–10 × 104/ml. Under our optimized culture conditions, we obtained over 54 embryos, and an average of 5.5 cotyledonary embryos when 10 × 104 microspores were grown on an individual plate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baillie AMR, Epp DJ, Hutcheson D, Keller WA (1992) In vitro culture of isolated microspores and regeneration of plants in Brassica campestris. Plant Cell Rep 11:234–237
Bárány I, Testillano PS, Mityko J, Risueno MC (2001) The switch of the microspore developmental program in Capsicum involves HSP70 expression and leads to the production of haploid plants. Int J Dev Biol 45(S1):S39–S40
Bárány I, González-Melendi P, Fadón B, Mitykót J, Risueño MC, Testillano PS (2005) Microspore-derived embryogenesis in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): subcellular rearrangements through development. Biol Cell 97:709–722
Custers JBM, Cordewener JHG, Nöllen Y, Dons HJM, van Lookeren Campagne MM (1994) Temperature controls both gametophytic and sporophytic development in microspore cultures of Brassica napus. Plant Cell Rep 13:267–271
Datta SK (2001) Androgenesis in cereals. In: Bhojwani SS, Soh WY (eds) Current trends in the embryology of angiosperms. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 471–488
Davies PA, Morton S (1998) A comparison of barley isolated microspore and anther culture and the influence of cell culture density. Plant Cell Rep 17:206–210
Dolcet-Sanjuan R, Claveria E, Huerta A (1997) Androgenesis in Capsicum annuum L.—effects of carbohydrate and carbon dioxide enrichment. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 122:468–475
Dumas de Vaulx R, Chambonnet D, Pochard E (1981) In vitro culture of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) anthers: high rate plant production from different genotypes by +35°C treatments. Agronomie 1:859–864
Ferrie AMR, Taylor DC, Mackenzie SL, Keller WA (1999) Microspore embryogenesis of high sn-2 erucic acid Brassica oleracea germplasm. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 57:79–84
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
González-Melendi P, Testillano PS, Ahmadian P, Fadon B, Risueno MC (1996) New in situ approaches to study the induction of pollen embryogenesis in Capsicum annuum L. Eur J Cell Biol 69:373–386
Graner A (1996) RELP-mapping the haploid genome of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In vitro haploid production in higher plants, vol 3. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 127–150
Guo YD, Pulli S (2000) An efficient androgenic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method through isolated microspore culture in timothy (Phleum pratense L.). Plant Cell Rep 19:761–767
Gustafson VD, Stephen Benziger P, Wright MS, Stroup WW, Yen Y (1995) Isolated wheat microspore culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 42:207–213
Hoekstra S, van Zijderveld MH, Heidekamp F, van der Mark F (1993) Microspore culture of Hordeum vulgare L.: the influence of density and osmolality. Plant Cell Rep 12:661–665
Hoekstra S, van Bergen S, van Brouwershaven IR, Schilperoort RA, Wang M (1997) Androgenesis in Hordeum vulgare L.: effects of mannitol, calcium and abscisic acid on anther pretreatment. Plant Sci 126:211–218
Höfer M (2004) In vitro androgenesis in apple—improvement of the induction phase. Plant Cell Rep 22:365–370
Hu T, Kasha KJ (1997) Improvement of isolated microspore culture of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through ovary co-culture. Plant Cell Rep 16:520–525
Hu TC, Ziauddin A, Simion E, Kasha KJ (1995) Isolated microspore culture of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in a defined media I. Effects of pretreatment, isolation methods, and hormones. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 31:79–83
Huang B, Brid S, Kemble R, Simmonds D, Keller W, Miki B (1990) Effects of culture density, conditioned medium and feeder cultures on microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus L. cv. Topas. Plant Cell Rep 8:594–597
Indrianto A, Barinova I, Touraev A, Heberle-Bors E (2001) Tracking individual wheat microspores in vitro: identification of embryogenic microspores and body axis formation in the embryo. Planta 212:163–174
Jähne A, Lörz H (1995) Cereal microspore culture. Plant Sci 109:1–12
Kernan Z, Ferrie AM (2006) Microspore embryogenesis and the development of a double haploidy protocol for cow cockle (Saponaria vaccaria). Plant Cell Rep 25:274–280
Kim M (1999) The influence of temperature pretreatment on the production of microspore embryos in anther culture of Capsicum annuum L. Kor J Plant Tissue Cult 26:71–76
Kim M, Kim J, Yoon M, Choi DI, Lee KM (2004) Origin of multicellular pollen and pollen embryos in cultured anthers of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 77:63–72
Kott LS, Polsoni L, Ellis B, Beversdorf WD (1988) Autotoxicity in isolated microspore cultures of Brassica napus. Can J Bot 66:1665–1670
Kuhlmann U, Foroughi-Wehr B (1989) Production of doubled haploid lines in frequencies sufficient for barley breeding programs. Plant Cell Rep 8:78–81
Kunz C, Islam SMS, Berberat J, Peter SO, Buter B, Stamp P, Schmid JE (2000) Assessment and improvement of wheat microspore derived embryo induction and regeneration. J Plant Physiol 156:190–196
Kyo M, Harada H (1985) Studies on conditions for cell division and embryogenesis in isolated pollen culture of Nicotiana rustica. Plant Physiol 79:90–94
Kyo M, Harada H (1986) Control of the developmental pathway of tobacco pollen in vitro. Planta 168:427–432
Li H, Devaux P (2001) Enhancement of microspore culture efficiency of recalcitrant barley genotypes. Plant Cell Rep 20:475–481
Ma R, Guo YD, Pulli S (2004) Comparison of anther and microspore culture in the embryogenesis and regeneration of rye (Secale cereale). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 76:147–157
Mitykó J, Fári M (1997) Problems and results of doubled haploid plant production in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) via anther- and microspore culture. Hort Biotech In Vitro Culture Breed 447:281–288
Miyoshi K (1996) Callus induction and plantlet formation through culture of isolated microspores of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Cell Rep 15:391–395
Nitsch C (1974) Pollen culture—a new technique for mass production of haploid and homozygous plants. In: Kasha KJ (ed) Haploids in higher plants: advances and potential. University of Guelph Press, Guelph, pp 123–135
Obert B, Preťová A, Büter B, Schmid JE (2000) Effect of different saccharides on viability of isolated microspores and androgenic induction in Zea mays. Biol Plant 43:125–128
Orshinsky BB, McGregor LG, Johnson GIE, Huel P, Kartha KK (1990) Improved embryoid-induction and green shoot regeneration from wheat anther culture in medium with maltose. Plant Cell Rep 9:365–369
Palmer CE, Keller WA, Arnison PG (1996) Experimental haploidy in Brassica species. In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In vitro haploid production in higher plants, vol 2. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 143–172
Pescitelli SM, Johnson CD, Petolino JF (1990) Isolated microspore culture of maize: effects of isolation technique, reduced temperature, and sucrose level. Plant Cell Rep 8:628–631
Polsoni L, Kott LS, Beversdorf WD (1988) Large-scale microspore culture technique for mutation selection studies in Brassica napus. Can J Bot 66:1681–1685
Raina SK, Irfan ST (1998) High-frequency embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from isolated microspores of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 17:957–962
Regner F (1996) Anther and microspore culture in Capsicum, In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In vitro haploid production in higher plants, vol 3. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 77–89
Scott P, Lyne RL (1994) The effect of different carbohydrate sources upon the initiation of embryogenesis from barley microspores. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 36:129–133
Stöger E, Fink C, Pfosser M, Heberle-Bors E (1995) Plant transformation by particle bombardment of embryogenic pollen. Plant Cell Rep 14:273–278
Supena EDJ, Suharsono S, Jacobsen E, Custers JBM (2006) Successful development of a shed-microspore culture protocol for doubled haploid production in Indonesian hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Cell Rep 25:1–10
Swanson EB (1990) Microspore culture in Brassica: In: Pollard JW, Walker JM (eds) Methods in molecular biology, vol 6. Plant cell and tissue culture. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp 159–170
Touraev A, Ilham A, Vicente O, Heberle-Bors E (1996a) Stress-induced microspore embryogenesis in tobacco : an optimized system for molecular studies. Pant Cell Rep 15:561–565
Touraev A, Indrianto A, Wratschko I, Vicente O, Heberle-Bors E (1996b) Efficient microspore embryogenesis in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) induced by starvation at high temperature. Sex Plant Reprod 9:209–215
Zhou H, Zheng Y, Konzak CF (1991) Osmotic potential of media affecting green plant percentage in wheat anther culture. Plant Cell Rep 10:63–66
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by Korean government (MOST) (No. R01-2005-000-10338-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J.R. Liu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Jang, IC., Kim, JA. et al. Embryogenesis and plant regeneration of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) through isolated microspore culture. Plant Cell Rep 27, 425–434 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0442-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0442-4