Abstract
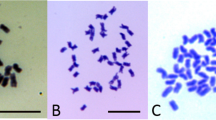
Eighty-four plants obtained from the pollination of the annual diploid cultivated sunflower, Helianthus annuus, by the perennial diploid species H. mollis were obtained naturally from mature seeds (62 plants) or following embryo rescue procedures (22 plants) and subsequently studied for phenotype traits and DNA markers. Twenty-two plants were obtained from the reverse cross as a result of natural seed development. The level of hybridization was determined using random amplified polymorphic DNA and restriction fragment length polymorphism markers. All of the resulting plants were found to be diploid 2n=34. Reciprocal crosses led to different progenies, with phenotypes that were predominantly similar to that of the female sunflower or the H. mollis type. The embryo rescue procedure enhanced the level of hybridization, whereas natural seed development led to fewer hybrids. Molecular markers unique to the female or the male parent indicated mechanisms leading to partial hybridization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faure, N., Serieys, H., Kaan, F. et al. Partial hybridization in crosses between cultivated sunflower and the perennial Helianthus mollis: effect of in vitro culture compared to natural crosses. Plant Cell Rep 20, 943–947 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-001-0426-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-001-0426-8