Abstract.
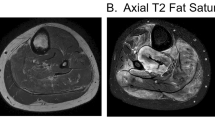
Acute inflammatory myopathy with severe subcutaneous edema is extremely rare and has been reported in only a handful of cases. We describe two similar patients presenting with this disorder and generalized rash. Unlike the five previously reported cases, the clinical and histologic features of our two patients are more suggestive of dermatomyositis than polymyositis. Nevertheless, scrutinizing all seven reported patients, a number of specific characteristics could be defined. All patients were adult males. Dysphagia was present in four. In six patients, acute inflammatory myopathy was idiopathic while malignancy was present in one. Two patients died despite intensive therapy, three improved on corticosteroid treatment, and two recovered spontaneously. In all patients, limb involvement with marked subcutaneous edema was present, clinically mimicking deep vein thrombosis in both our patients. The presence of severe subcutaneous edema may be a hallmark of a distinctive variant of acute inflammatory myopathy. More cases are needed to discern subtypes of this general entity and to establish guidelines for treatment and prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorelik, .O., Almoznino-Sarafian, .D., Alon, .I. et al. Acute inflammatory myopathy with severe subcutaneous edema, a new variant? Report of two cases and review of the literature. Rheumatol Int 20, 163–166 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960000093
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960000093