Abstract
Background
Systemic sclerosis (SSc), a complex autoimmune disorder, manifests as a convergence of rheumatologic, dermatologic, and pulmonary challenges. Among the severe complications contributing to morbidity and mortality are SSc Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD) and pulmonary hypertension. Over the past decade, research on pulmonary involvement in SSc has intensified, leading to a heightened understanding of its pathogenesis, diagnostic methods, and therapeutic strategies.
Aim
This study aims to provide a data-driven overview of the current state of systemic sclerosis research, identifying emerging trends and fostering informed decisions regarding resource allocation and research priorities.
Methods
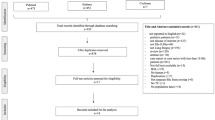
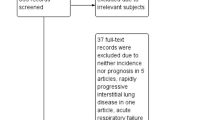
A literature search was conducted in the Scopus database, using MESH keywords such as “systemic sclerosis” AND “lungs” OR “pulmonary hypertension” OR "interstitial lung disease". After applying exclusion criteria, a thorough analysis was performed, considering factors such as document category, authorship, journal source, citation frequency, country of publication, language, and keywords. The bibliometric analysis utilized Scopus as the preferred database, leveraging its extensive coverage, user-friendly interface, and commitment to data accuracy. Visual networks were constructed using VOSviewer software to map the relationships between keywords, countries, and authors. Altmetric Attention Scores (AAS) were employed to assess the social impact of articles.
Results
The analysis revealed a total of 2538 scholarly items, with 55.7% identified as open access. The USA (n = 532), Italy (n = 458), France (n = 304), Japan (n = 271), and the UK (n = 236) emerged as primary contributors, with English being the predominant language. A notable upward tendency in annual publication and citation scores indicated sustained interest and relevance in SSc-ILD research. The top journals, including Rheumatology United Kingdom, Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, Clinical Rheumatology, Arthritis and Rheumatology, and Journal of Rheumatology, played a pivotal role in scholarly output. Original Articles (n = 1795; 70.7%) constituted the majority of publications, followed by Reviews, Letters, Notes, and Editorials. The analysis of publication impact within different scholarly formats revealed varying citation patterns, with Original Articles and Reviews leading in influence. The identification of influential research hubs and key contributors provided insights into collaborative efforts and geographic distribution. A strong correlation (rho = 0.612, p < 0.001) was observed between the quantity of Mendeley readers and the citations received by scholarly articles.
Conclusion
This bibliometric analysis offers a comprehensive overview of SSc-ILD research, highlighting its dynamic and interdisciplinary nature. The surge in publications, citation scores, and the identification of key contributors underscore the continued relevance and impact of this field. The nuanced relationships between social attention and scientific recognition, as revealed by Mendeley readership and AAS, contribute to a deeper understanding of the multifaceted nature of scholarly impact.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Sobolewski P, Maślińska M, Wieczorek M, Łagun Z, Malewska A, Roszkiewicz M et al (2019) Systemic sclerosis - multidisciplinary disease: clinical features and treatment. Reumatologia 57(4):221–233. https://doi.org/10.5114/reum.2019.87619
Cottin V, Brown KK (2019) Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD). Respir Res 20(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-019-0980-7
Makol A, Nagaraja V, Amadi C, Pugashetti JV, Caoili E, Khanna D (2023) Recent innovations in the screening and diagnosis of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 19(6):613–626. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2023.2198212
Gomis MKS, Oladinrin OT, Saini M, Pathirage C, Arif M (2023) A scientometric analysis of global scientific literature on learning resources in higher education. Heliyon 9(4):e15438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15438
Fedorchenko Y, Zimba O (2023) Comorbidities in the COVID-19 pandemic: scopus-based bibliometric analysis. J Korean Med Sci 38(11):e93. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e93
Doskaliuk B, Zaiats L, Yatsyshyn R, Gerych P, Cherniuk N, Zimba O (2020) Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis: exploring cellular, genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Rheumatol Int 40(10):1555–1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04658-6
Chen J (2023) A scientometric analysis of information technology in sustainable higher education: knowledge structure and frontier trends. Discov Sustain 4:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-023-00148-4
Ghaleb H, Alhajlah HH, Bin Abdullah AA, Kassem MA, Al-Sharafi MA (2022) A Scientometric Analysis and Systematic Literature Review for Construction Project Complexity. Buildings 12(4):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12040482
Umeokafor N, Umar T, Evangelinos K (2022) Bibliometric and scientometric analysis-based review of construction safety and health research in developing countries from 1990 to 2021. Saf Sci 156:105897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2022.105897
Zimba O, Radchenko O, Strilchuk L (2020) Social media for research, education and practice in rheumatology. Rheumatol Int 40:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04493-4
Kocyigit E, Kocak T (2023) Rheumatic diseases and gut microbiota publications in 2002–2022: a Scopus-based bibliometric analysis. Rheumatol Int 43(11):2115–2124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05408-0
Li M, Yin F, He Y, Zhang X, Yu H, Yang Q et al (2023) Bibliometric and altmetric analyses of publication activity in the field of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy in 2011–2021 based on web of science core collection databases. Rheumatol Int 43(6):1121–1133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-022-05211-3
Zhang Y, Hu L, Liao S, Wang Y, Ji X, Liu X et al (2023) Bibliometric analysis of publications on enthesitis in spondyloarthritis in 2012–2021 based on web of science core collection databases. Rheumatol Int 43(1):173–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-022-05227-9
https://www.elsevier.com/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/114533/Scopus_GlobalResearch_Factsheet2019_FINAL_WEB.pdf Accessed on 26.11.2023
AlRyalat SAS, Malkawi LW, Momani SM (2019) Comparing bibliometric analysis using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases. JoVE 152:e58494. https://doi.org/10.3791/58494
Perianes-Rodriguez A, Waltman L, Van Eck NJ (2016) Constructing bibliometric networks: a comparison between full and fractional counting. J Informetrics 10(4):1178–1195
Richardson MA, Park W, Echternacht SR, Bell DE (2021) Altmetric attention score: evaluating the social media impact of burn research. J Burn Care Res 42(6):1181–1185. https://doi.org/10.1093/jbcr/irab026
Koca TT (2023) Bibliometric analysis of “sarcopenia” in Web of Science. Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil 50:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43166-023-00194-w
Xu J, Yu J, Jiao W, Chen G, Liu ZM et al (2022) Scientific knowledge of rheumatoid arthritis: a bibliometric analysis from 2011 to 2020. J Pain Res 15:2761–2772. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S362717
Koo M (2021) Systemic lupus erythematosus research: a bibliometric analysis over a 50-year period. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(13):7095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18137095
Doskaliuk B, Yatsyshyn R, Klishch I, Zimba O (2021) COVID-19 from a rheumatology perspective: bibliometric and altmetric analysis. Rheumatol Int 41(12):2091–2103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-021-04987-0
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A et al (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 72(11):1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424
Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y et al (2017) Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 76(8):1327–1339. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209909
Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M, Azuma A, Fischer A, Mayes MD et al (2019) Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med 380(26):2518–2528. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1903076
Khanna D, Denton CP, Jahreis A, van Laar JM, Frech TM, Anderson ME et al (2016) Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): a phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 387(10038):2630–2640. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00232-4
Jordan S, Distler JH, Maurer B, Huscher D, van Laar JM, Allanore Y, Distler O, EUSTAR Rituximab study group (2015) Effects and safety of rituximab in systemic sclerosis: an analysis from the European Scleroderma Trial and Research (EUSTAR) group. Ann Rheum Dis 74(6):1188–1194. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204522
Coghlan JG, Denton CP, Grünig E, Bonderman D, Distler O, Khanna D et al (2014) Evidence-based detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: the DETECT study. Ann Rheum Dis 73(7):1340–1349. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203301
Nihtyanova SI, Schreiber BE, Ong VH, Rosenberg D, Moinzadeh P, Coghlan JG et al (2014) Prediction of pulmonary complications and long-term survival in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(6):1625–1635. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38390
Denton CP, Khanna D (2017) Systemic sclerosis. Lancet (London, England) 390(10103):1685–1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30933-9
Allanore Y, Simms R, Distler O, Trojanowska M, Pope J, Denton CP, Varga J (2015) Systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.2
van Bon L, Affandi AJ, Broen J, Christmann RB, Marijnissen RJ, Stawski L et al (2014) Proteome-wide analysis and CXCL4 as a biomarker in systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med 370(5):433–443. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1114576
Kocyigit BF, Akyo A (2021) Bibliometric and altmetric analyses of publication activity in the field of behcet’s disease in 2010–2019. J Korean Med Sci 36(32):e207. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e207
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BD and RY designed the study. BD, IK and YuF reviewed the articles and provided the data. BD, LZ and IK analyzed the data. BD wrote the initial manuscript; IK, YuF, LZ and RY reviewed drafts of the paper. BD prepared the figures. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No human participants/animals were evaluated. These data are public. Therefore, there was no requirement for ethics committee approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Doskaliuk, B., Kreminska, I., Fedorchenko, Y. et al. Systemic sclerosis associated respiratory involvement: Scopus-based analysis of articles in 2013–2022. Rheumatol Int 44, 693–702 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-024-05535-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-024-05535-2