Abstract
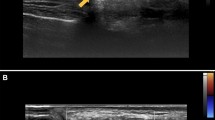
Acute peripheral facial nerve palsy is most frequently idiopathic (Bell’s palsy) or virally induced, but can also be due to several other conditions. A rare cause is underlying systemic or autoimmune disease. A 79-year-old man presented with peripheral facial nerve palsy, malaise, and fever. Physical examination revealed tenderness of the left temporal artery and reduced pulsatility. 18F-FDG-PET/CT and biopsy of the temporal artery confirmed the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis (GCA). Prompt institution of corticosteroid therapy produced rapid decrease in inflammatory markers and gradual improvement of the facial nerve palsy. We searched the MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus databases to identify previous reports of peripheral nerve palsy in GCA, other vasculitides, and autoimmune diseases. Facial nerve palsy as the presenting symptom of GCA has very rarely been reported. Although temporal artery biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosis, it may be negative in up to one-third of cases. In doubtful cases, imaging can help establish the diagnosis. Ultrasound, 3 T MRI, and 18F-FDG-PET/CT have all been previously reported to be useful. Peripheral facial nerve palsy may very rarely be the presenting symptom of GCA. Early correct diagnosis is essential for starting appropriate therapy. In patients with atypical features, 18F-FDG-PET/CT may be useful for establishing the diagnosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ (2014) Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. N Engl J Med 371:1653. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1409206
Hohman MH, Hadlock TA (2014) Etiology, diagnosis, and management of facial palsy: 2000 patients at a facial nerve center. Laryngoscope 124:E283–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24542
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Martinez-Dubois C, Agudo M, Pompei O, Blanco R, Llorca J (2010) Giant cell arteritis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-010-0135-9
Tm O (2018) Medical management of acute facial paralysis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 51:1051–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2018.07.004
Balquet MH, Gosset D, Bouchez B, Mellin D, Hatron PY, Devulder B (1991) Peripheral nerve diseases disclosing Horton's disease (2 cases). Rev Med Intern 12:57–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0248-8663(05)81356-6
Taillan B, Fuzibet JG, Vinti H, Castela J, Gratecos N, Dujardin P, Pesce A (1989) Peripheral facial paralysis disclosing Horton's disease. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 56:342
Treves R, Archambeaud-Mouveroux F, Liozon E (1991) Rare neurologic forms disclosing Horton's disease. 2 cases. Ann Med Intern 142:318–319
Roomet A, Allen JS (1974) Temporal arteritis heralded by facial nerve palsy. JAMA 228:870–871
Sotoudeh Anvari M, Masoudkabir F, Abbasi K, Boroumand MA, Zarghampour M, Goodarzynejad H (2016) Takayasu's arteritis presenting with headache and peripheral facial palsy: a case report. J Tehran Heart Cent 11:195–197
Joglekar S, Deroee AF, Morita N, Cureoglu S, Schachern PA, Paparella M (2010) Polyarteritis nodosa: a human temporal bone study. Am J Otolaryngol 31:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2009.02.006
Teichman JM, Mattrey RF, Demby AM, Schmidt JD (1993) Polyarteritis nodosa presenting as acute orchitis: a case report and review of the literature. J Urol 149:1139–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36322-x
Iannella G, Greco A, Granata G, Manno A, Pasquariello B, Angeletti D, Didona D, Magliulo G (2016) Granulomatosis with polyangiitis and facial palsy: literature review and insight in the autoimmune pathogenesis. Autoimmun Rev 15:621–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2016.02.005
Renz LD, Seidl R, Dreyer J, Niedobitek G, Ernst A (2019) Case report: a 20 years old patient with chronic mastoiditis and facial nerve palsy within a major-recidive of a granulomatosis with polyangiits. Laryngo Rhino Otol 98:1
Preuss SF, Stenner M, Beutner D, Laudes M, Klussmann JP (2008) Fatal course of Wegener's granulomatosis with bilateral otomastoiditis and bilateral facial nerve palsy. Otolaryngol Head Neck 138:799–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2007.12.045
Byun JH, Lee JH, Choi IS (2014) Churg-strauss syndrome presented with hearing impairment and facial palsy. Ann Rehabil Med 38:852–855. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.852
Cikes N (2006) Central nervous system involvement in systemic connective tissue diseases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2005.11.009
Hadithi M, Stam F, Donker AJ, Dijkmans BA (2001) Sjogren's syndrome: an unusual cause of Bell's palsy. Ann Rheum Dis 60:724–725. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.60.7.724
Hatzitolios A, Savopoulos C, Ntaios G, Tsirogianni E, Baltatzi M, Apostolopoulou M, Dimitrakoudi E (2008) Recurrent peripheral facial paresis may constitute the sole clinical manifestation in neuro-behcet disease. Neurologist 14:77. https://doi.org/10.1097/NRL.0b013e31815879f5
Tsirogianni ES, Hatzitolios AI, Savopoulos CG, Baltatzi MS, Apostolopoulou MI, Magripli CM, Dimitrakoudi ET (2004) Neuro-Behcet's syndrome may present with peripheral paresis of the facial nerve. J Peripher Nerv Syst 9:59–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1085-9489.2004.009203.x
Amaral TN, Peres FA, Lapa AT, Marques-Neto JF, Appenzeller S (2013) Neurologic involvement in scleroderma: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.05.002
Vrancken AF, Said G (2013) Vasculitic neuropathy. Handbook of clinical neurology., pp 463–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52902-2.00026-6
Imboden JB (2017) Involvement of the peripheral nervous system in polyarteritis nodosa and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 43:633–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2017.06.011
Nesher G (2000) Neurologic manifestations of giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:S24–26
Caselli RJ, Daube JR, Hunder GG, Whisnant JP (1988) Peripheral neuropathic syndromes in giant cell (temporal) arteritis. Neurology 38:685–689. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.38.5.685
Meadows SP (1966) Temporal or giant cell arteritis. Proc R Soc Med 59:329–334
Broussalis E, Luthringshausen G, Kunz AB, McCoy M, Weiss S, Killer-Oberpfalzer M, Trinka E, Kraus J (2011) Isolated facial palsy and ophthalmoplegia–first symptoms of a cerebral granulomatous vasculitis with giant cells–a diagnostic challenge. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:686–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.04.007
Kazzaz NM, El-Rifai R (2013) Unusual aetiology of isolated lower motor neuron facial palsy: systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with cranial nerve palsy and nephritis. BMJ Case Rep 2013:200378. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-200378
Pavlakis PP, Alexopoulos H, Kosmidis ML, Mamali I, Moutsopoulos HM, Tzioufas AG, Dalakas MC (2012) Peripheral neuropathies in Sjogren's syndrome: a critical update on clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms. J Autoimmun 39:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2012.01.003
Sene D, Jallouli M, Lefaucheur JP, Saadoun D, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Maisonobe T, Diemert MC, Musset L, Haroche J, Piette JC, Amoura Z, Cacoub P (2011) Peripheral neuropathies associated with primary Sjogren syndrome: immunologic profiles of nonataxic sensory neuropathy and sensorimotor neuropathy. Medicine 90:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0b013e31820fd2d1
Ramos-Casals M, Anaya JM, Garcia-Carrasco M, Rosas J, Bove A, Claver G, Diaz LA, Herrero C, Font J (2004) Cutaneous vasculitis in primary Sjogren syndrome: classification and clinical significance of 52 patients. Medicine 83:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.md.0000119465.24818.98
Paik JJ, Mammen AL, Wigley FM, Shah AA, Hummers LK, Polydefkis M (2016) Symptomatic and electrodiagnostic features of peripheral neuropathy in scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res 68:1150–1157. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22818
Siva A, Saip S (2009) The spectrum of nervous system involvement in Behcet's syndrome and its differential diagnosis. J Neurol 256:513–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0145-6
Farahani SA, Hosseini MME, Nozarian Z, Yazdani N (2019) IgG4-Related disease causing facial and recurrent laryngeal nerve palsies: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res 13:3
Wick CC, Zachariah J, Manjila S, Brown WC, Malla P, Katirji B, Cohen M, Megerian CA (2016) IgG4-related disease causing facial nerve and optic nerve palsies: Case report and literature review. Am J Otolaryngol 37:567–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.08.005
Ninan JV, Lester S, Hill CL (2017) Giant cell arteritis: beyond temporal artery biopsy and steroids. Intern Med J 47:1228–1240. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.13483
Schmidt WA (2018) Ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex461
Rheaume M, Rebello R, Pagnoux C, Carette S, Clements-Baker M, Cohen-Hallaleh V, Doucette-Preville D, Stanley Jackson B, Salama Sargious Salama S, Ioannidis G, Khalidi NA (2017) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of scalp arteries for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: results of a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol 69:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39824
Slart R, Writing G, Reviewer G, Members of EC, Members of EI, Inflammation, Members of Committees SC, Members of Council PETIG, Members of A, Coordinator EC (2018) FDG-PET/CT(A) imaging in large vessel vasculitis and polymyalgia rheumatica: joint procedural recommendation of the EANM, SNMMI, and the PET Interest Group (PIG), and endorsed by the ASNC. Eur J Nucl Med Mol 45:1250–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-3973-8
Salvarani C, Soriano A, Muratore F, Shoenfeld Y, Blockmans D (2017) Is PET/CT essential in the diagnosis and follow-up of temporal arteritis? Autoimmun Rev 16:1125–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.007
Hellmich B, Agueda A, Monti S, Buttgereit F, de Boysson H, Brouwer E, Cassie R, Cid MC, Dasgupta B, Dejaco C, Hatemi G, Hollinger N, Mahr A, Mollan SP, Mukhtyar C, Ponte C, Salvarani C, Sivakumar R, Tian X, Tomasson G, Turesson C, Schmidt W, Villiger PM, Watts R, Young C, Luqmani RA (2020) 2018 Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 79:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215672
Nielsen BD, Hansen IT, Kramer S, Haraldsen A, Hjorthaug K, Bogsrud TV, Ejlersen JA, Stolle LB, Keller KK, Therkildsen P, Hauge EM, Gormsen LC (2019) Simple dichotomous assessment of cranial artery inflammation by conventional 18F-FDG PET/CT shows high accuracy for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a case-control study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-4106-0
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EC and LH performed the literature search and wrote the manuscript in consultation with OG, BD, EV and WM. OG interpreted the PET-CT images and provided corresponding images and caption. EV interpreted the anatomopathological data and provided corresponding images and caption. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript as submitted, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Informed consent
We obtained written informed consent of the patient prior to the submission of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claeys, E., Gheysens, O., Meersseman, W. et al. Facial nerve palsy in giant-cell arteritis: case-based review. Rheumatol Int 41, 481–486 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04673-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04673-7