Abstract
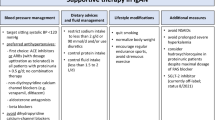
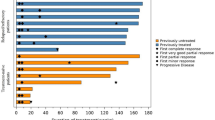
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic fibro-inflammatory disease. This disease may be associated with elevated serum and tissue IgG4 levels. Early treatment prevents fibrosis and organ damage. We retrospectively studied the clinicopathologic correlation and outcome of treatment in IgG4-RD. This single-center retrospective study was done using electronic records of patients subjected to assay of serum IgG4 levels in our laboratory by nephelometry. There were 473 patients with suspected IgG4-RD. Of them, 41 patients fulfilled comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD and 432 had diseases other than IgG4-RD. Clinical and histopathological data including tissue IgG4/IgG ratio, other relevant laboratory findings as well as management data of 41 patients with IgG4-RD were analyzed. There were 29 males and 12 females with mean age of 44.1 ± 2.19 years. Thirteen patients had definite, 19 had probable and 9 had possible IgG4-RD. Male predominance, multiple organ involvement and IgG4 responder Index were significantly higher in definite IgG4-RD as compared to probable and possible IgG4-RD. Serum IgG4 level was elevated in 37 patients (90.2%). Glucocorticoids were used in 35 patients (85.4%) and second-line immunosuppressive agent in 23 patients (65.7%). Of the 21 patients on follow-up, 19 (90.7%) had clinical improvement at the first follow-up visit. Nine (90%) out of the ten patients who were assessed by IgG4 responder index, also had shown improved score with treatment. Patients with IgG4-RD in our series showed favorable responses to treatment with glucocorticoids and addition of steroid sparing immunosuppressive agents (mainly mycophenolate mofetil) helped successful tapering of steroids, while maintaining the improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V (2012) IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 366:539–551. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1104650
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A et al (2001) High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 344:732–738. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103083441005
Wibmer T, Kropf-Sanchen C, Rüdiger S et al (2013) Isolated IgG4-related interstitial lung disease: unusual histological and radiological features of a pathologically proven case. Multidiscip Respir Med 8:22. doi:10.1186/2049-6958-8-22
Ikeda T, Oka M, Shimizu H et al (2013) IgG4-related skin manifestations in patients with IgG4-related disease. Eur J Dermatol EJD 23:241–245. doi:10.1684/ejd.2013.1958
Hsing M-T, Hsu H-T, Cheng C-Y, Chen C-M (2013) IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease. Asian J Surg 36:93–97. doi:10.1016/j.asjsur.2012.04.013
Kim S, Kim TG, Choi S-K et al (2013) Immunoglobulin G4-related systemic sclerosing disease: a case involving the ureter and kidney. Korean J Urol 54:209–211. doi:10.4111/kju.2013.54.3.209
Watanabe T, Maruyama M, Ito T et al (2013) Clinical features of a new disease concept, IgG4-related thyroiditis. Scand J Rheumatol 42:325–330. doi:10.3109/03009742.2012.761281
Cheuk W, Chan JKC (2012) Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related disease: an underdiagnosed and overdiagnosed entity. Semin Diagn Pathol 29:226–234. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2012.07.001
Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Deshpande V, Khosroshahi A (2012) Development of an IgG4-RD Responder Index. Int J Rheumatol 2012:e259408. doi:10.1155/2012/259408
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y et al (2012) Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol 22:21–30. doi:10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z
Ebbo M, Daniel L, Pavic M et al (2012) IgG4-related systemic disease: features and treatment response in a French cohort: results of a multicenter registry. Medicine (Baltimore) 91:49–56. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e3182433d77
Kuruma S, Kamisawa T, Tabata T et al (2013) Clinical characteristics of patients with autoimmune pancreatitis with or without Mikulicz’s disease and Mikulicz’s disease alone. Gut Liver 7:96–99. doi:10.5009/gnl.2013.7.1.96
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S et al (2010) Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: iII. Treatment and prognosis of AIP. J Gastroenterol 45:471–477. doi:10.1007/s00535-010-0221-9
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K et al (2009) Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 58:1504–1507. doi:10.1136/gut.2008.172908
Nizar A-H, Toubi E (2015) IgG4-related disease: case report and literature review. Auto-Immun Highlights 6:7–15. doi:10.1007/s13317-015-0069-3
Lin W, Lu S, Chen H et al (2015) Clinical characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a prospective study of 118 Chinese patients. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 54:1982–1990. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev203
Umemura T, Zen Y, Hamano H et al (2007) IgG4 associated autoimmune hepatitis: a differential diagnosis for classical autoimmune hepatitis. Gut 56:1471–1472. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.122283
Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A et al (2015) Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1171–1177. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206605
Sah RP, Chari ST (2011) Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:108–113. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283413469
Nada R, Ramachandran R, Kumar A et al (2016) IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: a prospective analysis. Int J Rheum Dis 19:721–729. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12675
Rohan A, Ravishankar B, Vishwanath S et al (2014) IgG4 related renal disease: a wolf in sheep’s clothing. Indian J Nephrol 24:382–386. doi:10.4103/0971-4065.133022
Prabhu SM, Yadav V, Irodi A et al (2014) IgG4-related disease with sinonasal involvement: a case series. Indian J Radiol Imaging 24:117–120. doi:10.4103/0971-3026.134384
Chougule A, Bal A, Das A, Singh G (2015) IgG4 related sclerosing mastitis: expanding the morphological spectrum of IgG4 related diseases. Pathology (Phila) 47:27–33. doi:10.1097/PAT.0000000000000187
Author contributions
Study conception and design: NG, JK, DD. Acquisition of data: HM, SDC, RTK, DJC, BT, MA, AS, TV, ATV, JM. Analysis and interpretation of data: MG, NG, JK, DD. Drafting the manuscript: NG, JK. Critical revision: DD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Institutional Review Board
Funding
This work was not funded by any grant.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, N., Mathew, J., Mohan, H. et al. Addition of second-line steroid sparing immunosuppressants like mycophenolate mofetil improves outcome of Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD): a series from a tertiary care teaching hospital in South India. Rheumatol Int 38, 203–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3730-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3730-5