Abstract
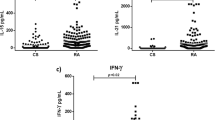
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a pleotrophic cytokine that is involved in the pathogenesis of diverse inflammatory rheumatic diseases. The aims of this study were to compare serum IL-15 levels and expression of its receptor (IL-15Rα) in Behçet’s disease (BD) with those in other rheumatic diseases and to identify the relationship between serum IL-15 levels and various clinical parameters in BD. One hundred fifty-eight subjects consisting of 40 BD, 38 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 40 rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and 40 healthy controls were enrolled. Serum IL-15 levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The proportion of IL-15Rα expression on each leukocyte subset was measured by flow cytometry. Erythrocyte sediment rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured for each enrolled subject. The clinical activity index of BD was assessed for BD patients. Serum IL-15 levels in BD patients are significantly higher than those of healthy controls, SLE, and RA patients (p < 0.001, p < 0.001, and p < 0.001, respectively). Serum IL-15 levels in BD were closely related to ESR (r = 0.405, p = 0.027), but not to CRP or the clinical activity index of BD (p > 0.05 for both). Additionally, there was no difference in serum IL-15 levels between active and inactive disease states in BD (p > 0.05). The proportion of IL-15Rα expression on total leukocytes was much lower for all rheumatic diseases, including BD, than in healthy controls (p < 0.01 for SLE, p < 0.01 for RA, and p < 0.05 for BD). IL-15 and IL-15Rα system may be involved in the inflammatory process and pathogenesis of BD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G (1999) Behcet’s disease. N Engl J Med 341:1284–1291
Suzuki Y, Hoshi K, Matsuda T, Mizushima Y (1992) Increased peripheral blood γδ+ T cells and natural killer cells in Behçet’s disease. J Rheumatol 19:588–592
Yu HG, Lee DS, Seo JM, Ahn JK, Yu YS, Lee WJ et al (2004) The number of CD8+ T cells and NKT cells increases in the aqueous humor of patients with Behçet’s uveitis. Clin Exp Immunol 137:437–443
Sahin S, Akoğlu T, Direskeneli H, Sen LS, Lawrence R (1996) Neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells and factors affecting adhesion in patients with Behçet’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis 55:128–133
Zouboulis CC, Katsantonis J, Ketteler R, Treudler R, Kaklamani E, Hornemann S et al (2000) Adamantiades-Behçet’s disease: interleukin-8 is increased in serum of patients with active oral and neurological manifestations and is secreted by small vessel endothelial cells. Arch Dermatol Res 292:279–284
Evereklioglu C, Er H, Türköz Y, Cekmen M (2002) Serum levels of TNF-α, sIL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8 are increased and associated with elevated lipid peroxidation in patients with Behçet’s disease. Mediators Inflamm 11:87–93
Grabstein KH, Eisenman J, Shanebeck K, Rauch C, Srinivasan S, Fung V et al (1994) Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science 264:965–968
Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y (1999) The multifaceted regulation of interleukin-15 expression and the role of this cytokine in NK cell differentiation and host response to intracellular pathogens. Annu Rev Immunol 17:19–49
Stonier SW, Schluns KS (2010) Trans-presentation: a novel mechanism regulating IL-15 delivery and responses. Immunol Lett 127:85–92
Dubois S, Mariner J, Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y (2002) IL-15Rα recycles and presents IL-15 In trans to neighboring cells. Immunity 17:537–547
Gonzalez-Alvaro I, Ortiz AM, Garcia-Vicuña R, Balsa A, Pascual-Salcedo D, Laffon A (2003) Increased serum levels of interleukin-15 in rheumatoid arthritis with long- term disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21:639–642
McInnes IB, Leung BP, Sturrock RD, Field M, Liew FY (1997) Interleukin-15 mediates T cell-dependent regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α production in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med 3:189–195
Suzuki J, Morimoto S, Amano H, Tokano Y, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H (2001) Serum levels of interleukin 15 in patients with rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol 28:2389–2391
Baranda L, de la Fuente H, Layseca-Espinosa E, Portales-Pérez D, Niño-Moreno P, Valencia-Pacheco G et al (2005) IL-15 and IL-15R in leucocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:1507–1513
Curnow SJ, Pryce K, Modi N, Knight B, Graham EM, Stewart JE et al (2008) Serum cytokine profiles in Behçet’s disease: is there a role for IL-15 in pathogenesis? Immunol Lett 121:7–12
Hamzaoui K, Hamzaoui A, Ghorbel I, Khanfir M, Houman H (2006) Levels of IL-15 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Behçet’s disease. Scand J Immunol 64:655–660
Ahn JK, Yu HG, Chung H, Park YG (2006) Intraocular cytokine environment in active Behçet uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 142:429–434
International Study Group for Behcet’s disease (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet’s disease. Lancet 335:1078–1080
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classifi cation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Fresko I, Soy M, Hamuryudan V, Yurdakul S, Yavuz S, Tümer Z et al (1998) Genetic anticipation in Behçet’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 57:45–48
Hirohata S, Oka H, Mizushima Y (1992) Streptococcal-related antigens stimulate production of IL6 and interferon-gamma by T cells from patients with Behcet’s disease. Cell Immunol 140:410–419
García VE, Jullien D, Song M, Uyemura K, Shuai K, Morita CT et al (1998) IL-15 enhances the response of human γδ T cells to nonpeptide microbial antigens. J Immunol 160:4322–4329
Jullien D, Sieling PA, Uyemura K, Mar ND, Rea TH, Modlin RL (1997) IL-15, an immunomodulator of T cell responses in intracellular infection. J Immunol 158:800–806
Oppenheimer-Marks N, Brezinschek RI, Mohamadzadeh M, Vita R, Lipsky PE (1998) Interleukin 15 is produced by endothelial cells and increases the transendothelial migration of T cells In vitro and in the SCID mouse-human rheumatoid arthritis model In vivo. J Clin Invest 101:1261–1272
Matsumoto K, Ohi H, Kanmatsuse K (1999) Effects of interleukin-15 on vascular permeability factor release by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal subjects and in patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 82:32–38
Aringer M, Stummvoll GH, Steiner G, Köller M, Steiner CW, Höfler E (2001) Serum interleukin-15 is elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40:876–881
Giri JG, Kumaki S, Ahdieh M, Friend DJ, Loomis A, Shanebeck K (1995) Identification and cloning of a novel IL-15 binding protein that is structurally related to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. EMBO J 14:3654–3663
Mortier E, Woo T, Advincula R, Gozalo S, Ma A (2008) IL-15Ralpha chaperones IL-15 to stable dendritic cell membrane complexes that activate NK cells via trans presentation. J Exp Med 205:1213–1225
Mortier E, Bernard J, Plet A, Jacques Y (2004) Natural, proteolytic release of a soluble form of human IL-15 receptor alpha-chain that behaves as a specific, high affinity IL-15 antagonist. J Immunol 173:1681–1688
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Ferreira SH, Wei X, Leung BP, Fraser A (2007) IL-15 mediates antigen-induced neutrophil migration by triggering IL-18 production. Eur J Immunol 37:3373–3380
Conflict of interest
Not declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choe, JY., Lee, H., Kim, S.G. et al. The distinct expressions of interleukin-15 and interleukin-15 receptor α in Behçet’s disease. Rheumatol Int 33, 2109–2115 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2705-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2705-4