Abstract
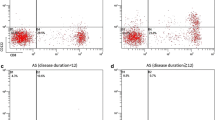
The pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) still remains an enigma. Although some studies have indicated the importance of T-cells and proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of the AS, it is still unknown whether co-stimulatory molecule CD154 participates in the pathogenesis of AS and how its level changes during the anti-TNF-α treatment of AS. This study is performed to evaluate the expression of CD154 in peripheral blood T-lymphocytes of patients with AS and observe the change of CD154 in etanercept-treated AS patient. We collected the peripheral blood and clinical data from 66 AS, 30 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and 30 healthy controls. Thirty-nine active AS patients were enrolled in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. We followed up 37 cases that fulfilled the ASAS20 response criteria after they finished etanercept treatment till week 48. The percentage of CD3+CD154+ in peripheral blood lymphocytes was evaluated by flow cytometry. We found that CD154 expression in AS patients was significantly higher than that in healthy volunteers and RA patients (both P < 0.001). The expressions of CD154 in AS patients at active stage or with peripheral joint involvement were significantly higher than those at stable stage or with axial involvement alone (P = 0.005 and 0.044, respectively). The expression of CD154 decreased in AS patients treated with etanercept compared with patients treated with placebo at week 6 (P < 0.001). Compared with healthy volunteers, the expression of CD154 in 16 AS patients who relapsed after finishing etanercept treatment was elevated again (P = 0.012). These findings show that co-stimulatory molecule CD154 is overexpressed on T-lymphocytes in peripheral blood of AS patients and can be down-regulated by etanercept treatment, which suggest that CD154 might be involved in the inflammatory evolvement of AS and might be a potential biomarker to monitor AS disease activity and the effect of etanercept treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quezada SA, Jarvinen LZ, Lind EF, Noelle RJ (2004) CD40/CD154 interactions at the interface of tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 22:307–328. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104533
Toubi E, Shoenfeld Y (2004) The role of CD40–CD154 interactions in autoimmunity and the benefit of disrupting this pathway. Autoimmunity 37:457–464. doi:10.1080/08916930400002386
Kelsoe G (2003) Therapeutic CD154 antibody for lupus: promise for the future? J Clin Invest 112:1480–1482
Koshy M, Berger D, Crow MK (1996) Increased expression of CD40 ligand on systemic lupus erythematosus lymphocytes. J Clin Invest 98:826–837. doi:10.1172/JCI118855
Wang CR, Liu MF (2003) Regulation of CCR5 expression and MIP-1alpha production in CD4 T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 132:371–378. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02126.x
Desai-Mehta A, Lu L, Ramsey-Goldman R, Datta SK (1996) Hyperexpression of CD40 ligand by B and T cells in human lupus and its role in pathogenic autoantibody production. J Clin Invest 97:2063–2073. doi:10.1172/JCI118643
Devi BS, Van Noordin S, Krausz T, Davies KA (1998) Peripheral blood lymphocytes in SLE—hyperexpression of CD154 on T and B lymphocytes and increased number of double negative T cells. J Autoimmun 11:471–475. doi:10.1006/jaut.1998.0213
Boumpas DT, Furie R, Manzi S, Illei GG, Wallace DJ, Balow JE, Vaishnaw A, BG9588 Lupus Nephritis Trial Group (2003) A short course of BG9588 (anti-CD40 ligand antibody) improves serologic activity and decreases hematuria in patients with proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:719–727. doi:10.1002/art.10856
Quezada SA, Eckert M, Adeyi OA, Schned AR, Noelle RJ, Burns CM (2003) Distinct mechanisms of action of anti-CD154 in early versus late treatment of murine lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2541–2554. doi:10.1002/art.11230
Kalunian KC, Davis JC Jr, Merrill JT, Totoritis MC, Wofsy D (2002) Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus by inhibition of T cell costimulation with anti-CD154: a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 46:3251–3258. doi:10.1002/art.10681
Szántó S, Aleksza M, Mihály E, Lakos G, Szabó Z, Végvári A, Sipka S, Szekanecz Z (2008) Intracytoplasmic cytokine expression and T cell subset distribution in the peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 35:2372–2375. doi:10.3899/jrheum.070839
Stupphann D, Rauner M, Krenbek D, Patsch J, Pirker T, Muschitz C, Resch H, Pietschmann P (2008) Intracellular and surface RANKL are differentially regulated in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 28:987–993. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0567-y
Lu MC, Yang KL, Tung CH, Huang KY, Yu HC, Liu SQ, Lai NS (2008) Higher LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha mRNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from Chinese ankylosing spondylitis patients with -308G/A polymorphism in promoter region of tumor necrosis factor: association with distinct A33/B58/Cw10 haplotypes. Rheumatol Int 29:189–195. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0671-z
Toussirot E, Lafforgue P, Boucraut J, Despieds P, Schiano A, Bernard D (1994) Serum levels of interleukin 1-beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha soluble interleukin 2 receptor and soluble CD8 in seronegative spondylarthropathies. Rheumatol Int 13:175–180. doi:10.1007/BF00390264
Gorman JD, Sack KE, Davis JC Jr (2002) Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha. N Engl J Med 346:1349–1356. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012664
McLeod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Dagenais P, Dickson R, Dundar Y (2007) Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 11:1–158 iii–iv
Davis JC Jr, van der Heijde DM, Braun J, Dougados M, Clegg DO, Kivitz AJ (2008) Efficacy and safety of up to 192 weeks of etanercept therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:346–352. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.078139
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Sieper J (2005) Therapy of ankylosing spondylitis. Part II: biological therapies in the spondyloarthritides. Scand J Rheumatol 34:178–190. doi:10.1080/03009740510026599
Kruithof E, De Rycke L, Roth J, Mielants H, Van den Bosch F, De Keyser F (2005) Immunomodulatory effects of etanercept on peripheral joint synovitis in the spondylarthropathies. Arthritis Rheum 52:3898–3909. doi:10.1002/art.21426
Woo JH, Lee HJ, Sung IH, Kim TH (2007) Changes of clinical response and bone biochemical markers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis taking etanercept. J Rheumatol 34:1753–1759
Van der Linden SJ, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368. doi:10.1002/art.1780270401
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS (1988) The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324. doi:10.1002/art.1780310302
Braun J, Davis J, Dougados M, Sieper J, van der Linden S, van der Heijde D (2006) First update of the international ASAS consensus statement for the use of anti-TNF agents in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:316–320. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.040758
Gotoh H, Kawaguchi Y, Harigai M, Hara M, Saito S, Yamaguchi T, Shimada K, Kawamoto M, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N (2004) Increased CD40 expression on articular chondrocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: contribution to production of cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. J Rheumatol 31:1506–1512
Harigai M, Hara M, Kawamoto M, Kawaguchi Y, Sugiura T, Tanaka M, Nakagawa M, Ichida H, Takagi K, Higami-Ohsako S, Shimada K, Kamatani N (2004) Amplification of the synovial inflammatory response through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB using ligation of CD40 on CD14+ synovial cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:2167–2277. doi:10.1002/art.20340
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients who volunteered to take part in this study. We acknowledge the help of Dr. Haixia Xu and Jijun Zhao for collecting the materials of this study. This study was supported by National Natural Sciences Foundations of China (No. 30325019, 30571735, and 30471611), Ministry of health key clinical project and Science foundation of Guangdong province of China (No. 2002Z3-E4021 and 2005A30801005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Q. Lin and Z. Lin equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Q., Lin, Z., Gu, J. et al. Abnormal high-expression of CD154 on T lymphocytes of ankylosing spondylitis patients is down-regulated by etanercept treatment. Rheumatol Int 30, 317–323 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0958-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0958-8