Abstract
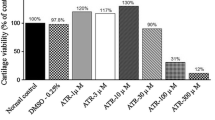
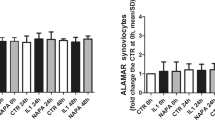
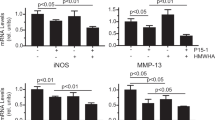
The purpose of the present study was to elucidate the possible signal transduction pathway involved in the underlying mechanism of glucosamine (GLN)’s influence on the gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in chondrocytes stimulated with IL-1β. Using chondrosarcoma cells stimulated with IL-1β, the effects of GLN on the mRNA and protein levels of MMP-3, the activation of JNK, ERK, p38, NF-κB, and AP-1, the nuclear translocation of NF-κB/Rel family members, and PI3-kinase/Akt activation were studied. GLN inhibited the expression and the synthesis of MMP-3 induced by IL-1β, and that inhibition was mediated at the level of transcription involving both the NF-κB and AP-1 transcription factors. Translocation of NF-κB was reduced by GLN as a result of the inhibition of IκB degradation. A slightly synergistic effect on the activation of AP-1 induced by IL-1β was shown in the presence of GLN. Among MAPK pathways involved in the transcriptional regulation of AP-1, phosphorylation of JNK and ERK was found to increase with the presence of GLN under IL-1β treatment, while that for p38 decreased. It was also found that GLN alone, but also synergistically with IL-1β, was able to activate the Akt pathway. The requirements of NF-κB translocation and p38 activity are indispensably involved in the induction of MMP-3 expression in chondrosarcoma cells stimulated by IL-1β. Inhibition of the p38 pathway in the presence of GLN substantially explains the chondroprotective effect of GLN on chondrocytes that regulate COX-2 expression, PGE2 synthesis, and NO expression and synthesis. The chondroprotective effect of GLN through the decrease in MMP-3 production and stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis may follow another potential signaling pathway of Akt.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson SB, Amin A (2002) Blocking the effects of IL-1 in rheumatoid arthritis protects bone and cartilage. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:972–980
Lotz M (2001) Cytokines in cartilage injury and repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res 391(Suppl):S108–115
Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE (2001) Early response genes induced in chondrocytes stimulated with the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta. Arthritis Res 3:381–388
Gouze JN, Bianchi A, Becuwe P, Dauca M, Netter P, Magadalou J, Terlain B, Bordji K (2002) Glucosamine modulates IL-1-induced activation of rat chondrocytes at a receptor level, and by inhibiting the NF-kappa B pathway. FEBS Lett 510:166–170
Ciaraldi TP, Carter L, Nikoulina S, Mudallar S, McClain DA, Henry RR (1999) Glucosamine regulation of glucose metabolism in cultured human skeletal muscle cells: divergent effects on glucose transport/phosphorylation and glycogen synthase in non-diabetic and type 2 diabetic subjects. Endocrinology 140:3971–3980
Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Kishimoto K, Hiyama A, Inoue J, Cao Z, Matsumoto K (1999) The kinase TAK1 can activate the NIK-I kappaB as well as the MAP kinase cascade in the IL-1 signalling pathway. Nature 398:252–256
Firestein GS, Manning AM (1999) Signal transduction and transcription factors in rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum 42:609–621
Gouze JN, Bordji K, Gulberti S, Terlain B, Netter P, Magdalou J, Fournel-Gigleux S, Ouzzine M (2001) Interleukin-1beta down-regulates the expression of glucuronosyltransferase I, a key enzyme priming glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis: influence of glucosamine on interleukin-1beta-mediated effects in rat chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 4:351–360
Gomez-Garre D, Largo R, Tejera N, Fortes J, Manzarbeitia F, Egido J (2001) Activation of NF-kappaB in tubular epithelial cells of rats with intense proteinuria: role of angiotensin II and endothelin-1. Hypertension 37:1171–1182
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156
Dodge GR, Jimenez SA (2003) Glucosamine sulfate modulates the levels of aggrecan and matrix metalloproteinase-3 synthesized by cultured human osteoarthritis articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartilage 11:424–432
Reddy SA, Huang JH, Liao WS (1997) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in interleukin 1 signaling. Physical interaction with the interleukin 1 receptor and requirement in NFkappaB and AP-1 activation. J Biol Chem 272:29167–29173
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401:82–85
Largo R, Alvarez-Soria MA, Diez-Ortego I, Calvo E, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Egido J, Herrero-Beaumont G (2003) Glucosamine inhibits IL-1beta-induced NFkappaB activation in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartilage 11:290–298
Borden P, Heller RA (1997) Transcriptional control of matrix metalloproteinases and the tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 7:159–178
Bond M, Baker AH, Newby AC (1999) Nuclear factor kappaB activity is essential for matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 upregulation in rabbit dermal fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264:561–567
Liacini A, Sylvester J, Li WQ, Zafarullah M (2002) Inhibition of interleukin-1-stimulated MAP kinases, activating protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) transcription factors down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in articular chondrocytes. Matrix Biol 21:251–262
Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Coon CI, Barchowsky A, Brinckerhoff C (2000) Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor kappaB: differential regulation of collagenase 1 and collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum 43:801–811
Thomas B, Thirion S, Humbert L, Tan L, Goldring MB, Bereziat G (2002) Differentiation regulates interleukin-1beta-induced cyclo-oxygenase-2 in human articular chondrocytes: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem J 362:367–373
Masuko-Hongo K, Berenbaum F, Humbert L, Salvat C, Goldring MB, Thirion S (2004) Up-regulation of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 in osteoarthritic human cartilage: critical roles of the ERK-1/2 and p38 signaling pathways. Arthritis Rheum 50:2829–2838
Liu R, Liote F, Rose DM, Merz D, Terkeltaub R (2004) Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and Src kinase signaling transduce monosodium urate crystal-induced nitric oxide production and matrix metalloproteinase 3 expression in chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 50:247–258
Chan PS, Caron JP, Rosa GJM, Orth MW (2005) Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate regulate gene expression and synthesis of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E(2) in articular cartilage explants. Osteoarthr Cartilage 13:387–394
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, Ten Dijke P, Saltoh M (1997) Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 275:90–94
Starkman BG, Cravero JD, DelCarlo M, Loeser RF (2005) IGF-I stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis by chondrocytes requires activation of the PI 3-kinase pathway but not ERK MAPK. Biochem J 389(Pt 3):723–729
Acknowledgments
Financial support by Mackay Memorial Hospital (94MMH-TMU-14) is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yi-Cheng Lin and Yu-Chih Liang equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Liang, YC., Sheu, MT. et al. Chondroprotective effects of glucosamine involving the p38 MAPK and Akt signaling pathways. Rheumatol Int 28, 1009–1016 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0561-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0561-4