Abstract
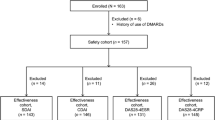
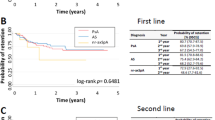
In the present study, we determined from a single-center data the treatment continuation, discontinuation and reasons for discontinuation in the patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthropathies (SpA) who were treated with etanercept or adalimumab. All RA and SpA patients, who were treated with etanercept (n = 53) or adalimumab (n = 43) as their first biological treatment according to national guidelines in the Center for Rheumatic Diseases, Tampere University Hospital during the years 1999–2005, were analyzed at baseline and after 1-year treatment. The treatment was regarded ineffective if the clinical response was lower than ACR50 in RA or the reduction of BASDAI was lower than 50% or 2 cm in SpA. After 1 year, the continuation rate was 74% with etanercept and 60% with adalimumab. Mean prednisolone dose among continuers was diminished by 52% in etanercept-treated patients and by 44% in adalimumab-treated patients. During 1-year follow-up, 14 (26%) of the etanercept-treated patients and 17 (40%) of the adalimumab-treated patients discontinued the medication. Eleven patients were regarded as poor responders, seven in etanercept group and four in adalimumab group. Adverse events (mainly infections and injection reactions) caused six discontinuations in etanercept-treated group and 11 discontinuations in adalimumab-treated group. Etanercept was discontinued due to other adverse event in two patients: in one patient due to adenocarcinoma of ovary and in one patient due to drug-related leukopenia. One patient treated with adalimumab developed clinical and immunological features of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In the present study, etanercept and adalimumab treatments were started in patients who had active RA or SpA despite ongoing treatment with combinations of traditional disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Thirty-nine (74%) patients and twenty-six (60%) patients achieved at least 50% response when etanercept or adalimumab was added to their earlier DMARD treatment. Adverse events (mainly infections and injection reactions) were in line with previous reports. Three rare adverse events were reported: one patient with ovarial carcinoma, one with leukopenia and one with features of drug-induced SLE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreland LW, Schiff MH, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Bulpitt KJ, Weaver AL, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Mease PJ, Ruderman EM, Horwitz DA, Arkfeld DG, Garrison L, Burge DJ, Blosch CM, Lange ML, McDonnell ND, Weinblatt ME (1999) Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 130:478–486
Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Moreland LW, Weisman MH, Birbara CA, Teoh LA, Fischkoff SA, Chartash EK (2003) Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum 48:35–45
Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP, Gough A, Kalden J, Malaise M, Martin Mola E, Pavelka K, Sany J, Settas L, Wajdula J, Pedersen R, Fatenejad S, Sanda M, TEMPO (trial of etanercept, methotrexate with radiographic patient outcomes) study investigators (2004) Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 363:675–681
van de Putte LB, Atkins C, Malaise M, Sany J, Russell AS, van Riel PL, Settas L, Bijlsma JW, Todesco S, Dougados M, Nash P, Emery P, Walter N, Kaul M, Fischkoff S, Kupper H (2004) Efficacy and safety of adalimumab as monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis for whom previous disease modifying antirheumatic drug treatment has failed. Ann Rheum Dis 63:508–516
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Sieper J (2005) Therapy of ankylosing spondylitis. Part II: biological therapies in the spondyloarthritides. Scand J Rheumatol 34:178–190
Hyrich KL, Lunt M, Watson KD, Symmons DP, Silman AJ, British society for rheumatology biologics register (2007) Outcomes after switching from one anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agent to a second anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a large UK national cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 56:13–20
Listing J, Strangfeld A, Kary S, Rau R, von Hinueber U, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Gromnica-Ihle E, Antoni C, Herzer P, Kekow J, Schneider M, Zink A (2005) Infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum 52:3403–3412
Dixon WG, Watson K, Lunt M, Hyrich KL, Silman AJ, Symmons DP, British society for rheumatology biologics register (2006) Rates of serious infection, including site-specific and bacterial intracellular infection, in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheum 54:2368–2376
Salliot C, Gossec L, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Luc M, Duclos M, Guignard S, Dougados M (2006) Infections during tumour necrosis factor-{alpha} blocker therapy for rheumatic diseases in daily practice: a systematic retrospective study of 709 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford)
Working group set by Finnish Medical Society Duodecim and Finnish Society for Rheumatology, Helsinki, Finland. (Updated 08.06.2003) Rheumatoid arthritis Current Care Guideline. Finnish Medical Society Duodecim. Available at http://www.kaypahoito.fi (in Finnish)
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, Katz LM, Lightfoot R Jr, Paulus H, Strand V (1995) American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:727–735
Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, Nissila M, Kautiainen H, Korpela M, Laasonen L, Julkunen H, Luukkainen R, Vuori K, Paimela L, Blafield H, Hakala M, Ilva K, Yli-Kerttula U, Puolakka K, Jarvinen P, Hakola M, Piirainen H, Ahonen J, Palvimaki I, Forsberg S, Koota K, Friman C (1999) Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised trial. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet 353:1568–1573
Feltelius N, Fored CM, Blomqvist P, Bertilsson L, Geborek P, Jacobsson LT, Lindblad S, Lysholm J, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Saxne T, Klareskog L, ARTIS Group (2005) Results from a nationwide postmarketing cohort study of patients in Sweden treated with etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis 64:246–252
Brocq O, Roux CH, Albert C, Breuil V, Aknouche N, Ruitord S, Mousnier A, Euller-Ziegler L (2007) TNFalpha antagonist continuation rates in 442 patients with inflammatory joint disease. Joint Bone Spine 74:148–154
Kristensen LE, Saxne T, Nilsson JA, Geborek P (2006) Impact of concomitant DMARD therapy on adherence to treatment with etanercept and infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Results from a six-year observational study in southern Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R174
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, Sharp J, Perez JL, Spencer-Green GT (2006) The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54:26–37
Flendrie M, Creemers MC, Welsing PM, den Broeder AA, van Riel PL (2003) Survival during treatment with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(Suppl2):ii30–ii33
Zink A, Listing J, Kary S, Ramlau P, Stoyanova-Scholz M, Babinsky K, von Hinueber U, Gromnica-Ihle E, Wassenberg S, Antoni C, Herzer P, Kekow J, Schneider M, Rau R (2005) Treatment continuation in patients receiving biological agents or conventional DMARD therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1274–1279
Carmona L, Gomez-Reino JJ, BIOBADASER Group (2006) Survival of TNF antagonists in spondylarthritis is better than in rheumatoid arthritis. Data from the Spanish registry BIOBADASER. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R72
Mutru O, Laakso M, Isomaki H, Koota K (1985) Ten year mortality and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 290:1797–1799
Doran MF, Crowson CS, Pond GR, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (2002) Predictors of infection in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:2294–2300
Capell HA (2001) Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs: longterm safety issues. J Rheumatol Suppl 62:10–15
Scallon B, Cai A, Solowski N, Rosenberg A, Song XY, Shealy D, Wagner C (2002) Binding and functional comparisons of two types of tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:418–426
Nestorov I (2005) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J Rheumatol Suppl 74:13–18
Furst DE, Wallis R, Broder M, Beenhouwer DO (2006) Tumor necrosis factor antagonists: different kinetics and/or mechanisms of action may explain differences in the risk for developing granulomatous infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36:159–167
Brassard P, Kezouh A, Suissa S (2006) Antirheumatic drugs and the risk of tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis 43:717–722
van Rijthoven AW, Bijlsma JW, Canninga-van Dijk M, Derksen RH, van Roon JA (2006) Onset of systemic lupus erythematosus after conversion of infliximab to adalimumab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis with a pre-existing anti-dsDNA antibody level. Rheumatology 45:1317–1319
Konttinen L, Honkanen V, Uotila T, Pollanen J, Waahtera M, Romu M, Puolakka K, Vasala M, Karjalainen A, Luukkainen R, Nordstrom DC, for the ROB-FIN study group (2006) Biological treatment in rheumatic diseases: results from a longitudinal surveillance: adverse events. Rheumatol Int 26:916–922
Hyrich KL, Silman AJ, Watson KD, Symmons DP (2004) Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: an update on safety. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1538–1543
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Heli Määttä and Mrs. Heli Pikkuharju for excellent secretarial help. Clinical rheumatologists and the staff in the Center for Rheumatic Diseases, Tampere University Hospital, are gratefully acknowledged. The study was supported by Clinical Drug Research Graduate School, Finland and the competitive research funding of the Pirkanmaa Hospital District.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levälampi, T., Korpela, M., Vuolteenaho, K. et al. Etanercept and adalimumab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathies in clinical practice: adverse events and other reasons leading to discontinuation of the treatment. Rheumatol Int 28, 261–269 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0436-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0436-0