Abstract
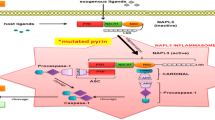
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is the most frequent hereditary inflammatory disease characterized by self-limited recurrent attacks of fever and serositis. It is transmitted in an autosomal recessive pattern and affects certain ethnic groups mainly Jews, Turks, Arabs, and Armenians. FMF is caused by mutations in MEFV gene, which encodes pyrin. This protein is expressed mainly in myeloid/monocytic cells and modulates IL-1β processing, NF-κB activation, and apoptosis. A mutated pyrin probably results in uncontrolled inflammation. The most devastating complication of FMF is amyloidosis, leading to chronic renal failure. M694V homozygocity, male gender and the α/α genotype of serum amyloid A1 gene are the currently established risk factors for development of amyloidosis. Daily colchicine is the mainstay of the therapy for the disease, resulting in complete remission or marked reduction in the frequency and duration of attacks in most patients. It is also effective in preventing and arresting renal amyloidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sohar E, Gafni J, Pras M, Heller H (1967) Familial Mediterranean fever. A survey of 470 cases and review of the literature. Am J Med 43:227–253
Ancient missense mutations in a new member of the RoRet gene family are likely to cause familial Mediterranean fever (1997) The international FMF consortium. Cell 90:797–807
A candidate gene for familial Mediterranean fever (1997) The French FMF consortium. Nat Genet 17:25–31
Yilmaz E, Ozen S, Balci B, Duzova A, Topaloglu R, Besbas N, Saatci U, Bakkaloglu A, Ozguc M (2001) Mutation frequency of familial Mediterranean fever and evidence for a high carrier rate in the Turkish population. Eur J Hum Genet 9:553–555
Shohat M, Magal N, Shohat T, Chen X, Dagan T, Mimouni A, Danon Y, Lotan R, Ogur G, Sirin A, Schlezinger M, Halpern GJ, Schwabe A, Kastner D, Rotter JI, Fischel-Ghodsian N (1999) Phenotype–genotype correlation in familial Mediterranean fever: evidence for an association between Met694Val and amyloidosis. Eur J Hum Genet 7:287–292
Livneh A, Langevitz P, Shinar Y, Zaks N, Kastner DL, Pras M, Pras E (1999) MEFV mutation analysis in patients suffering from amyloidosis of familial Mediterranean fever. Amyloid 6:1–6
Ben-Chetrit E, Urieli-Shoval S, Calko S, Abeliovich D, Matzner Y (2002) Molecular diagnosis of FMF: lessons from a study of 446 unrelated individuals. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:S25–S29
Majeed HA, El-Shanti H, Al-Khateeb MS, Rabaiha ZA (2002) Genotype/phenotype correlations in Arab patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Semin Arthritis Rheum 31:371–376
Brik R, Shinawi M, Kepten I, Berant M, Gershoni-Baruch R (1999) Familial Mediterranean fever: clinical and genetic characterization in a mixed pediatric population of Jewish and Arab patients. Pediatrics 103:e70
Cattan D, Dervichian M, Thomas M, Dode C, Touitou I (2001) MEFV mutations and phenotype-genotype correlations in North African Jews and Armenians with familial Mediterranean fever. Isr Med Assoc J 3:803–804
Gershoni-Baruch R, Shinawi M, Leah K, Badarnah K, Brik R (2001) Familial Mediterranean fever: prevalence, penetrance and genetic drift. Eur J Hum Genet 9:634–637
Yalcinkaya F, Cakar N, Misirlioglu M, Tumer N, Akar N, Tekin M, Tastan H, Kocak H, Ozkaya N, Elhan AH (2000) Genotype–phenotype correlation in a large group of Turkish patients with familial mediterranean fever: evidence for mutation-independent amyloidosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:67–72
Akar N, Misiroglu M, Yalcinkaya F, Akar E, Cakar N, Tumer N, Akcakus M, Tastan H, Matzner Y (2000) MEFV mutations in Turkish patients suffering from familial Mediterranean fever. Hum Mutat 15:118–119
Touitou I (2001) The spectrum of familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 9:473–483
Tunca M, Akar S, Onen F, Ozdogan H, Kasapcopur O, Yalcinkaya F, Tutar E, Ozen S, Topaloglu R, Yilmaz E, Arici M, Bakkaloglu A, Besbas N, Akpolat T, Dinc A, Erken E (2005) Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) in Turkey: results of a nationwide multicenter study. Medicine (Baltimore) 84:1–11
Mansfield E, Chae JJ, Komarow HD, Brotz TM, Frucht DM, Aksentijevich I, Kastner DL (2001) The familial Mediterranean fever protein, pyrin, associates with microtubules and colocalizes with actin filaments. Blood 98:851–859
Masumoto J, Taniguchi S, Ayukawa K, Sarvotham H, Kishino T, Niikawa N, Hidaka E, Katsuyama T, Higuchi T, Sagara J (1999) ASC, a novel 22-kDa protein, aggregates during apoptosis of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem 274:33835–33838
Srinivasula SM, Poyet JL, Razmara M, Datta P, Zhang Z, Alnemri ES (2002) The PYRIN-CARD protein ASC is an activating adaptor for caspase-1. J Biol Chem 277:21119–21122
Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J (2002) The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell 10:417–426
Chae JJ, Komarow HD, Cheng J, Wood G, Raben N, Liu PP, Kastner DL (2003) Targeted disruption of pyrin, the FMF protein, causes heightened sensitivity to endotoxin and a defect in macrophage apoptosis. Mol Cell 11:591–604
Masumoto J, Dowds TA, Schaner P, Chen FF, Ogura Y, Li M, Zhu L, Katsuyama T, Sagara J, Taniguchi S, Gumucio DL, Nunez G, Inohara N (2003) ASC is an activating adaptor for NF-kappa B and caspase-8-dependent apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:69–73
Gumucio DL, Diaz A, Schaner P, Richards N, Babcock C, Schaller M, Cesena T (2002) Fire and ICE: the role of pyrin domain-containing proteins in inflammation and apoptosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:S45–S53
Ozen S, Uckan D, Baskin E, Besbas N, Okur H, Saatci U, Bakkaloglu A (2001) Increased neutrophil apoptosis during attacks of familial Mediterranean fever. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19:S68–S71
Shoham NG, Centola M, Mansfield E, Hull KM, Wood G, Wise CA, Kastner DL (2003) Pyrin binds the PSTPIP1/CD2BP1 protein, defining familial Mediterranean fever and PAPA syndrome as disorders in the same pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13501–13506
Wise CA, Gillum JD, Seidman CE, Lindor NM, Veile R, Bashiardes S, Lovett M (2002) Mutations in CD2BP1 disrupt binding to PTP PEST and are responsible for PAPA syndrome, an autoinflammatory disorder. Hum Mol Genet 11:961–969
Daniels M, Shohat T, Brenner-Ullman A, Shohat M (1995) Familial Mediterranean fever: high gene frequency among the non-Ashkenazic and Ashkenazic Jewish populations in Israel. Am J Med Genet 55:311–314
Ozen S, Karaaslan Y, Ozdemir O, Saatci U, Bakkaloglu A, Koroglu E, Tezcan S (1998) Prevalence of juvenile chronic arthritis and familial Mediterranean fever in Turkey: a field study. J Rheumatol 25:2445–2449
Onen F, Sumer H, Turkay S, Akyurek O, Tunca M, Ozdogan H (2004) Increased frequency of familial Mediterranean fever in Central Anatolia, Turkey. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:S31–S33
Rogers DB, Shohat M, Petersen GM, Bickal J, Congleton J, Schwabe AD, Rotter JI (1989) Familial Mediterranean fever in Armenians: autosomal recessive inheritance with high gene frequency. Am J Med Genet 34:168–172
Livneh A, Langevitz P, Zemer D, Padeh S, Migdal A, Sohar E, Pras M (1996) The changing face of familial Mediterranean fever. Semin Arthritis Rheum 26:612–627
Schwabe AD, Peters RS (1974) Familial Mediterranean fever in Armenians. Analysis of 100 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 53:453–462
Heller H, Gafni J, Michaeli D, Shahin N, Sohar E, Ehrlich G, Karten I, Sokoloff L (1966) The arthritis of familial Mediterranean fever (FMF). Arthritis Rheum 9:1–17
Majeed HA, Rawashdeh M (1997) The clinical patterns of arthritis in children with familial Mediterranean fever. QJM 90:37–43
Sneh E, Pras M, Michaeli D, Shanin N, Gafni J (1997) Protracted arthritis in familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol Rehabil X 16:102–106
Salai M, Langevitz P, Blankstein A, Zemmer D, Chechick A, Pras M, Horoszowski H (1993) Total hip replacement in familial Mediterranean fever. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 53:25–28
Besbas N, Ozdemir S, Saatci I, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Saatci U (1999) Sacroiliitis in familial Mediterranean fever: an unusual presentation in childhood. Turk J Pediatr 41:387–390
Langevitz P, Zemer D, Livneh A, Shemer J, Pras M (1994) Protracted febrile myalgia in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. J Rheumatol 21:1708–1709
Pras M, Bronshpigel N, Zemer D, Gafni J (1982) Variable incidence of amyloidosis in familial Mediterranean fever among different ethnic groups. Johns Hopkins Med J 150:22–26
Konstantopoulos K, Kanta A, Tzoulianos M, Dimou S, Sotsiou F, Politou M, Loukopoulos D (2001) Familial Mediterranean fever phenotype II in Greece. Isr Med Assoc J 3:862–863
Kutlay S, Yilmaz E, Koytak ES, Tulunay OO, Keven K, Ozcan M, Erturk S (2001) A case of familial Mediterranean fever with amyloidosis as the first manifestation. Am J Kidney Dis 38:E34
Melikoglu M, Ozdogan H, Korkmaz C, Kasapcopur O, Arisoy N, Akkus S, Fresko Z, Yazici H (2000) A survey of phenotype II in familial Mediterranean fever. Ann Rheum Dis 59:910–913
Cazeneuve C, Ajrapetyan H, Papin S, Roudot-Thoraval F, Genevieve D, Mndjoyan E, Papazian M, Sarkisian A, Babloyan A, Boissier B, Duquesnoy P, Kouyoumdjian JC, Girodon-Boulandet E, Grateau G, Sarkisian T, Amselem S (2000) Identification of MEFV-independent modifying genetic factors for familial Mediterranean fever. Am J Hum Genet 67:1136–1143
Booth DR, Gillmore JD, Booth SE, Pepys MB, Hawkins PN (1998) Pyrin/marenostrin mutations in familial Mediterranean fever. QJM 91:603–606
Samuels J, Aksentijevich I, Torosyan Y, Centola M, Deng Z, Sood R, Kastner DL (1998) Familial Mediterranean fever at the millennium. Clinical spectrum, ancient mutations, and a survey of 100 American referrals to the National Institutes of Health. Medicine (Baltimore) 77:268–297
Yalcinkaya F, Akar N, Misirlioglu M (1998) Familial Mediterranean fever—amyloidosis and the Val726Ala mutation. N Engl J Med 338:993–994
Tekin M, Yalcinkaya F, Cakar N, Akar N, Misirlioglu M, Tastan H, Tumer N (2000) MEFV mutations in multiplex families with familial Mediterranean fever: is a particular genotype necessary for amyloidosis? Clin Genet 57:430–434
Yilmaz E, Balci B, Kutlay S, Ozen S, Erturk S, Oner A, Besbas N, Bakkaloglu A (2003) Analysis of the modifying effects of SAA1, SAA2 and TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms on development of amyloidosis in FMF patients. Turk J Pediatr 45:198–202
Bakkaloglu A, Duzova A, Ozen S, Balci B, Besbas N, Topaloglu R, Ozaltin F, Yilmaz E (2004) Influence of serum amyloid A (SAA1) and SAA2 gene polymorphisms on renal amyloidosis, and on SAA/C-reactive protein values in patients with familial mediterranean fever in the Turkish population. J Rheumatol 31:1139–1142
Touitou I, Picot MC, Domingo C, Notarnicola C, Cattan D, Demaille J, Kone-Paut I (2001) The MICA region determines the first modifier locus in familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum 44:163–169
Flatau E, Kohn D, Schiller D, Lurie M, Levy E (1982) Schonlein-Henoch syndrome in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum 25:42–47
Glikson M, Galun E, Schlesinger M, Cohen D, Haskell L, Rubinow A, Eliakim M (1989) Polyarteritis nodosa and familial Mediterranean fever: a report of 2 cases and review of the literature. J Rheumatol 16:536–539
Ozen S, Ben-Chetrit E, Bakkaloglu A, Gur H, Tinaztepe K, Calguneri M, Turgan C, Turkmen A, Akpolat I, Danaci M, Besbas N, Akpolat T (2001) Polyarteritis nodosa in patients with familial Mediterranean fever (FMF): a concomitant disease or a feature of FMF? Semin Arthritis Rheum 30:281–287
Akar S, Goktay Y, Akinci B, Tekis D, Biberoglu K, Birlik M, Onen F, Tunca M, Akkoc N (2005) A case of familial Mediterranean fever and polyarteritis nodosa complicated by spontaneous perirenal and subcapsular hepatic hemorrhage requiring multiple arterial embolizations. Rheumatol Int 25:60–64
Schwartz T, Langevitz P, Zemer D, Gazit E, Pras M, Livneh A (2000) Behcet’s disease in familial Mediterranean fever: characterization of the association between the two diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum 29:286–295
Touitou I, Magne X, Molinari N, Navarro A, Quellec AL, Picco P, Seri M, Ozen S, Bakkaloglu A, Karaduman A, Garnier JM, Demaille J, Kone-Paut I (2000) MEFV mutations in Behcet’s disease. Hum Mutat 16:271–272
Atagunduz P, Ergun T, Direskeneli H (2003) MEFV mutations are increased in Behcet’s disease (BD) and are associated with vascular involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21:S35–S37
Gershoni-Baruch R, Broza Y, Brik R (2003) Prevalence and significance of mutations in the familial Mediterranean fever gene in Henoch-Schonlein purpura. J Pediatr 143:658–661
Ozen S, Bakkaloglu A, Yilmaz E, Duzova A, Balci B, Topaloglu R, Besbas N (2003) Mutations in the gene for familial Mediterranean fever: do they predispose to inflammation? J Rheumatol 30:2014–2018
Ehrenfeld M, Brzezinski A, Levy M, Eliakim M (1987) Fertility and obstetric history in patients with familial Mediterranean fever on long-term colchicine therapy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 94:1186–1191
Ehrenfeld EN, Polishuk WZ (1970) Gynecological aspects of recurrent polyserositis (familial Mediterranean fever, periodic disease). Isr J Med Sci 6:9–13
Ben-Chetrit E, Levy M (2003) Reproductive system in familial Mediterranean fever: an overview. Ann Rheum Dis 62:916–919
Gang N, Drenth JP, Langevitz P, Zemer D, Brezniak N, Pras M, van der Meer JW, Livneh A (1999) Activation of the cytokine network in familial Mediterranean fever. J Rheumatol 26:890–897
Frensdorff A, Sohar E, Heller H (1961) Plasma fibrinogen in familial Mediterranean fever. Ann Intern Med 55:448–455
Moutereau S, Narwa R, Matheron C, Vongmany N, Simon E, Goossens M (2004) An improved electronic microarray-based diagnostic assay for identification of MEFV mutations. Hum Mutat 23:621–628
Delague V, Kriegshauser G, Oberkanins C, Megarbane A (2004) Reverse hybridization vs. DNA sequencing in the molecular diagnosis of Familial Mediterranean fever. Genet Test 8:65–68
Drenth JP, van der Meer JW (2001) Hereditary periodic fever. N Engl J Med 345:1748–1757
Hoffman HM, Mueller JL, Broide DH, Wanderer AA, Kolodner RD (2001) Mutation of a new gene encoding a putative pyrin-like protein causes familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome and Muckle–Wells syndrome. Nat Genet 29:301–305
McDermott MF, Aksentijevich I, Galon J, McDermott EM, Ogunkolade BW, Centola M, Mansfield E, Gadina M, Karenko L, Pettersson T, McCarthy J, Frucht DM, Aringer M, Torosyan Y, Teppo AM, Wilson M, Karaarslan HM, Wan Y, Todd I, Wood G, Schlimgen R, Kumarajeewa TR, Cooper SM, Vella JP, Amos CI, Mulley J, Quane KA, Molloy MG, Ranki A, Powell RJ, Hitman GA, O’Shea JJ, Kastner DL (1999) Germline mutations in the extracellular domains of the 55 kDa TNF receptor, TNFR1, define a family of dominantly inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Cell 97:133–144
Aksentijevich I, Galon J, Soares M, Mansfield E, Hull K, Oh HH, Goldbach-Mansky R, Dean J, Athreya B, Reginato AJ, Henrickson M, Pons-Estel B, O’Shea JJ, Kastner DL (2001) The tumor-necrosis-factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: new mutations in TNFRSF1A, ancestral origins, genotype–phenotype studies, and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity of periodic fevers. Am J Hum Genet 69:301–314
Dode C, Andre M, Bienvenu T, Hausfater P, Pecheux C, Bienvenu J, Lecron JC, Reinert P, Cattan D, Piette JC, Szajnert MF, Delpech M, Grateau G (2002) The enlarging clinical, genetic, and population spectrum of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 46:2181–2188
Aganna E, Hammond L, Hawkins PN, Aldea A, McKee SA, van Amstel HK, Mischung C, Kusuhara K, Saulsbury FT, Lachmann HJ, Bybee A, McDermott EM, La Regina M, Arostegui JI, Campistol JM, Worthington S, High KP, Molloy MG, Baker N, Bidwell JL, Castaner JL, Whiteford ML, Janssens-Korpola PL, Manna R, Powell RJ, Woo P, Solis P, Minden K, Frenkel J, Yague J, Mirakian RM, Hitman GA, McDermott MF (2003) Heterogeneity among patients with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum 48:2632–2644
Hull KM, Drewe E, Aksentijevich I, Singh HK, Wong K, McDermott EM, Dean J, Powell RJ, Kastner DL (2002) The TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS): emerging concepts of an autoinflammatory disorder. Medicine (Baltimore) 81:349–368
Drenth JP, Haagsma CJ, van der Meer JW (1994) Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome. The clinical spectrum in a series of 50 patients. International Hyper-IgD Study Group. Medicine (Baltimore) 73:133–144
Drenth JP, Cuisset L, Grateau G, Vasseur C, van de Velde-Visser SD, de Jong JG, Beckmann JS, van der Meer JW, Delpech M (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding mevalonate kinase cause hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome. International Hyper-IgD Study Group. Nat Genet 22:178–181
Muckle TJ, Wellsm (1962) Urticaria, deafness, and amyloidosis: a new heredo-familial syndrome. Q J Med 31:235–248
Prieur AM, Griscelli C, Lampert F, Truckenbrodt H, Guggenheim MA, Lovell DJ, Pelkonnen P, Chevrant-Breton J, Ansell BM (1987) A chronic, infantile, neurological, cutaneous and articular (CINCA) syndrome. A specific entity analysed in 30 patients. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 66:57–68
Padeh S, Brezniak N, Zemer D, Pras E, Livneh A, Langevitz P, Migdal A, Pras M, Passwell JH (1999) Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and adenopathy syndrome: clinical characteristics and outcome. J Pediatr 135:98–101
Goldfinger SE (1972) Colchicine for familial Mediterranean fever. N Engl J Med 287:1302
Zemer D, Revach M, Pras M, Modan B, Schor S, Sohar E, Gafni J (1974) A controlled trial of colchicine in preventing attacks of familial Mediterranean fever. N Engl J Med 291:932–934
Livneh A, Zemer D, Langevitz P, Laor A, Sohar E, Pras M (1994) Colchicine treatment of AA amyloidosis of familial Mediterranean fever. An analysis of factors affecting outcome. Arthritis Rheum 37:1804–1811
Zemer D, Pras M, Sohar E, Modan M, Cabili S, Gafni J (1986) Colchicine in the prevention and treatment of the amyloidosis of familial Mediterranean fever. N Engl J Med 314:1001–1005
Lidar M, Scherrmann JM, Shinar Y, Chetrit A, Niel E, Gershoni-Baruch R, Langevitz P, Livneh A (2004) Colchicine nonresponsiveness in familial Mediterranean fever: clinical, genetic, pharmacokinetic, and socioeconomic characterization. Semin Arthritis Rheum 33:273–282
Lidar M, Kedem R, Langevitz P, Pras M, Livneh A (2003) Intravenous colchicine for treatment of patients with familial Mediterranean fever unresponsive to oral colchicine. J Rheumatol 30:2620–2623
Ben-Chetrit E, Levy M (1998) Colchicine: 1998 update. Semin Arthritis Rheum 28:48–59
Amital H, Ben-Chetrit E (2004) Therapeutic approaches to familial Mediterranean fever. What do we know and where are we going to? Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:S4–S7
Ozkaya N, Yalcinkaya F (2003) Colchicine treatment in children with familial Mediterranean fever. Clin Rheumatol 22:314–317
Tunca M, Tankurt E, Akbaylar Akpinar H, Akar S, Hizli N, Gonen O (1997) The efficacy of interferon alpha on colchicine-resistant familial Mediterranean fever attacks: a pilot study. Br J Rheumatol 36:1005–1008
Tunca M, Akar S, Soyturk M, Kirkali G, Resmi H, Akhunlar H, Gonen O, Gallimore JR, Hawkins PN, Tankurt E (2004) The effect of interferon alpha administration on acute attacks of familial Mediterranean fever: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:S37–S40
Calguneri M, Apras S, Ozbalkan Z, Ozturk MA (2004) The efficacy of interferon-alpha in a patient with resistant familial Mediterranean fever complicated by polyarteritis nodosa. Intern Med 43:612–614
Seyahi E, Ozdogan H, Masatlioglu S, Yazici H (2002) Successful treatment of familial Mediterranean fever attacks with thalidomide in a colchicine resistant patient. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:S43–S44
Drenth JP, Vonk AG, Simon A, Powell R, van der Meer JW (2001) Limited efficacy of thalidomide in the treatment of febrile attacks of the hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1221–1226
Sampaio EP, Sarno EN, Galilly R, Cohn ZA, Kaplan G (1991) Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med 173:699–703
Milledge J, Shaw PJ, Mansour A, Williamson S, Bennetts B, Roscioli T, Curtin J, Christodoulou J (2002) Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: cure for familial Mediterranean fever. Blood 100:774–777
Touitou I, Ben-Chetrit E, Gershoni-Baruch R, Grateau G, Kastner DL, Kone-Paut I, Livneh A, Manna R, Mansour I, Ozdogan H, Ozen S, Sarkisian T, Tunca M, Yalcinkaya F (2003) Allogenic bone marrow transplantation: not a treatment yet for familial Mediterranean fever. Blood 102:409
Keven K, Sengul S, Kutlay S, Ekmekci Y, Anadol E, Nergizoglu G, Ates K, Erturk S, Erbay B (2004) Long-term outcome of renal transplantation in patients with familial Mediterranean fever amyloidosis: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc 36:2632–2634
Altiparmak MR, Pamuk ON, Ataman R, Serdengecti K (2004) Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in familial Mediterranean fever amyloidosis patients with end-stage renal failure: a single-centre experience from Turkey. Nephron Clin Pract 98:c119–c123
Rawashdeh MO, Majeed HA (1996) Familial Mediterranean fever in Arab children: the high prevalence and gene frequency. Eur J Pediatr 155:540–544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onen, F. Familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol Int 26, 489–496 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-005-0074-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-005-0074-3