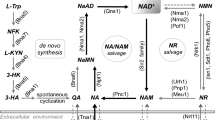
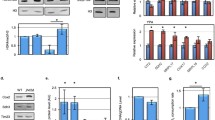
Abstract
Cells must appropriately sense available nutrients and accordingly regulate their metabolic outputs, to survive. This mini-review considers the idea that conserved chemical modifications of wobble (U34) position tRNA uridines enable cells to sense nutrients and regulate their metabolic state. tRNA wobble uridines are chemically modified at the 2- and 5- positions, with a thiol (s2), and (commonly) a methoxycarbonylmethyl (mcm5) modification, respectively. These modifications reflect sulfur amino acid (methionine and cysteine) availability. The loss of these modifications has minor translation defects. However, they result in striking phenotypes consistent with an altered metabolic state. Using yeast, we recently discovered that the s2 modification regulates overall carbon and nitrogen metabolism, dependent on methionine availability. The loss of this modification results in rewired carbon (glucose) metabolism. Cells have reduced carbon flux towards the pentose phosphate pathway and instead increased flux towards storage carbohydrates—primarily trehalose, along with reduced nucleotide synthesis, and perceived amino acid starvation signatures. Remarkably, this metabolic rewiring in the s2U mutants is caused by mechanisms leading to intracellular phosphate limitation. Thus this U34 tRNA modification responds to methionine availability and integratively regulates carbon and nitrogen homeostasis, wiring cells to a ‘growth’ state. We interpret the importance of U34 modifications in the context of metabolic sensing and anabolism, emphasizing their intimate coupling to methionine metabolism.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer VM, De Winde JH, Pronk JT, Piper MDW (2003) The genome-wide transcriptional responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown on glucose in aerobic chemostat cultures limited for carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209759200
Boer VMVM, Crutchfield CACA, Bradley PHPH et al (2010) Growth-limiting intracellular metabolites in yeast growing under diverse nutrient limitations. Mol Biol Cell 21:198–211. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-07-0597
Brauer MJMJ, Huttenhower C, Airoldi EMEM et al (2008) Coordination of growth rate, cell cycle, stress response, and metabolic activity in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 19:267–352. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E07-08-0779
Broach JR (2012) Nutritional control of growth and development in yeast. Genetics 192:73–105. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.111.135731
Cai L, Tu BP (2011) On acetyl-CoA as a gauge of cellular metabolic state. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 76:195–202
Cai L, Tu BP (2012) Driving the cell cycle through metabolism. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28:59–87. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154010
Candiracci J, Migeot V, Chionh Y-H et al (2019) Reciprocal regulation of TORC signaling and tRNA modifications by Elongator enforces nutrient-dependent cell fate. Sci Adv 5:eaav0184. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav0184
Chou H-J, Donnard E, Gustafsson HT et al (2017) Transcriptome-wide analysis of roles for tRNA modifications in translational regulation. Mol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.002
Eskes E, Deprez MA, Wilms T, Winderickx J (2018) pH homeostasis in yeast; the phosphate perspective. Curr, Genet
Glatt S, Zabel R, Kolaj-Robin O et al (2016) Structural basis for tRNA modification by Elp3 from Dehalococcoides mccartyi. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23:794–802. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3265
Goehring AS (2003) Urmylation: a ubiquitin-like pathway that functions during invasive growth and budding in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-02-0079
González A, Hall MN (2017) Nutrient sensing and TOR signaling in yeast and mammals. EMBO J 8:e201696010. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696010
Gresham D, Boer VM, Caudy A et al (2011) System-level analysis of genes and functions affecting survival during nutrient starvation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.120766
Gupta R, Walvekar AS, Liang S et al (2019) A tRNA modification balances carbon and nitrogen metabolism by regulating phosphate homeostasis. Elife 8:e44795. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795
Han L, Guy MP, Kon Y, Phizicky EM (2018) Lack of 2′-O-methylation in the tRNA anticodon loop of two phylogenetically distant yeast species activates the general amino acid control pathway. PLoS Genet 14:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007288
Hesketh A, Oliver SG (2019) High-energy guanine nucleotides as a signal capable of linking growth to cellular energy status via the control of gene transcription. Curr, Genet
Hesketh A, Vergnano M, Oliver SG (2019) Determination of the Global Pattern of Gene Expression in Yeast Cells by Intracellular Levels of Guanine Nucleotides. MBio 10:e02500–e02518. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02500-18
Hinnebusch AG (2005) translational regulation of GCN4 and the general amino acid control of yeast*. Annu Rev Microbiol 59:407–450. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.59.031805.133833
Kankipati HN, Rubio-Texeira M, Castermans D et al (2015) Sul1 and Sul2 sulfate transceptors signal to protein kinase A upon exit of sulfur starvation. J Biol Chem 290:10430–10446. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.629022
Klassen R, Ciftci A, Funk J et al (2016) TRNA anticodon loop modifications ensure protein homeostasis and cell morphogenesis in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw705
Kudlicki A, Rowicka M, Otwinowski Z (2007) SCEPTRANS: an online tool for analyzing periodic transcription in yeast. Bioinformatics 23:1559–1561
Laxman S, Tu BP (2011) Multiple TORC1-associated proteins regulate nitrogen starvation-dependent cellular differentiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026081
Laxman S, Sutter BMBM, Wu XX et al (2013) Sulfur amino acids regulate translational capacity and metabolic homeostasis through modulation of tRNA thiolation. Cell 154:416–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.043
Leidel S, Pedrioli PGA, Bucher T et al (2009) Ubiquitin-related modifier Urm1 acts as a sulphur carrier in thiolation of eukaryotic transfer RNA. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07643
Li Q, Fazly AM, Zhou H et al (2009) The elongator complex interacts with PCNA and modulates transcriptional silencing and sensitivity to DNA damage agents. PLoS Genet 5:e1000684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000684
Lin TY, Abbassi NEH, Zakrzewski K et al (2019) The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08579-2
Liu N-N, Flanagan PR, Zeng J et al (2017) Phosphate is the third nutrient monitored by TOR in Candida albicans and provides a target for fungal-specific indirect TOR inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1617799114
Nakai Y, Umeda N, Suzuki T et al (2004) Yeast Nfs1p is involved in thio-modification of both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic tRNAs. J Biol Chem 279:12363–12368. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312448200
Nakai Y, Nakai M, Lill R et al (2007) Thio modification of yeast cytosolic tRNA is an iron-sulfur protein-dependent pathway. Mol Cell Biol 27:2841–2847. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01321-06
Nakai Y, Nakai M, Hayashi H (2008) Thio-modification of yeast cytosolic tRNA requires a ubiquitin-related system that resembles bacterial sulfur transfer systems. J Biol Chem 283:27469–27476. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804043200
Nedialkova DD, Leidel SA (2015) Optimization of codon translation rates via tRNA modifications maintains proteome integrity. Cell 161:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.022
Phizicky EM, Hopper AK (2010) tRNA biology charges to the front. Genes Dev 24:1832–1860. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1956510
Rapino F, Delaunay S, Rambow F et al (2018) Codon-specific translation reprogramming promotes resistance to targeted therapy. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0243-7
Saldanha A, Brauer M, Botstein D (2004) Nutritional homeostasis in batch and steady-state culture of yeast. Mol Biol Cell. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E04-04-0306
Scheidt V, Juedes A, Baer C et al (2014) Loss of wobble uridine modification in tRNA anticodons interferes with TOR pathway signaling. Microb Cell 1:416–424. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2014.12.179
Schmelzle T, Hall MN (2000) TOR, a central controller of cell growth. Cell 103:253–262
Schmitz J, Chowdhury MM, Hänzelmann P et al (2008) The sulfurtransferase activity of Uba4 presents a link between ubiquitin-like protein conjugation and activation of sulfur carrier proteins. Biochemistry 47:6479–6489. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi800477u
Schneper L, Düvel K, Broach JR (2004) Sense and sensibility: nutritional response and signal integration in yeast. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:624–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.002
Slavov N, Botstein D (2011) Coupling among growth rate response, metabolic cycle, and cell division cycle in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 22:1997–2009. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0132
Teng X, Hardwick JM (2019) Whi2: a new player in amino acid sensing. Curr, Genet
Tu BP, Kudlicki A, Rowicka M, McKnight SL (2005a) Logic of the yeast metabolic cycle: temporal compartmentalization of cellular processes. Science 310:1152–1158. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120499
Tu BP, Tu BP, Kudlicki A et al (2005b) Logic of the yeast metabolic cycle: of cellular processes. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120499
Tu BP, Mohler RE, Liu JC et al (2007) Cyclic changes in metabolic state during the life of a yeast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16886–16891. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0708365104
Walvekar AS, Srinivasan R, Gupta R, Laxman S (2018) Methionine coordinates a hierarchically organized anabolic program enabling proliferation. Mol Biol Cell 29:3183–3200. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E18-08-0515
Wellen KE, Thompson CB (2012) A two-way street: reciprocal regulation of metabolism and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3305
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN (2006) TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124:471–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.016
Zinshteyn B, Gilbert WV (2013) Loss of a conserved tRNA anticodon modification perturbs cellular signaling. PLoS Genet 9:e1003675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003675
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Wellcome Trust-DBT India Alliance grant IA/I/14/2/501523 (SL) and the DST-SERB National Postdoctoral Fellowship grant PDF/2016/000416 (RG) for funding and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Laxman, S. tRNA wobble-uridine modifications as amino acid sensors and regulators of cellular metabolic state. Curr Genet 66, 475–480 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-019-01045-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-019-01045-y