Abstract
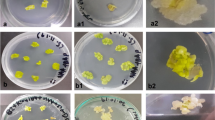
An efficient system for shoot regeneration and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Brassica oleracea cv. Green Marvel cultivar is described. This study focuses on developing shoot regeneration from hypocotyl explants of broccoli cv. Green Marvel using thidiazuron (TDZ), zeatin, and kinetin, the optimization of factors affecting Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the hypocotyl explants with heat-resistant cDNA, followed by the confirmation of transgenicity of the regenerants. High shoot regeneration was observed in 0.05–0.1 mg dm−3 TDZ. TDZ at 0.1 mg dm−3 produced among the highest percentage of shoot regeneration (96.67 %) and mean number of shoot formation (6.17). The highest percentage (13.33 %) and mean number (0.17) of putative transformant production were on hypocotyl explants subjected to preculture on shoot regeneration medium (SRM) with 200 µM acetosyringone. On optimization of bacterial density and inoculation time, the highest percentage and mean number of putative transformant production were on hypocotyl explants inoculated with a bacterial dilution of 1:5 for 30 min. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay indicated a transformation efficiency of 8.33 %. The luciferase assay showed stable integration of the Arabidopsis thaliana HSP101 (AtHSP101) cDNA in the transgenic broccoli regenerants. Three out of five transgenic lines confirmed through PCR showed positive hybridization bands of the AtHSP101 cDNA through Southern blot analysis. The presence of AtHSP101 transcripts in the three transgenic broccoli lines indicated by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) confirmed the expression of the gene. In conclusion, an improved regeneration system has been established from hypocotyl explants of broccoli followed by successful transformation with AtHSP101 for resistance to high temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AtHSP101:
-
Arabidopsis thaliana heat shock protein 101
- BAP:
-
Benzyl amino purine
- CIM:
-
Callus induction medium
- CRD:
-
Completely randomized design
- DNMRT:
-
Duncan new multiple range test
- h:
-
Hour
- LB medium:
-
Luria–Bertani broth medium
- MCS:
-
Multiple cloning site
- min:
-
Minute
- MS medium:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RLU:
-
Relative light unit
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SRM:
-
Shoot regeneration medium
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Abuodeh RO, Orbach MJ, Mandel MA, Das A, Galgiani JN (2000) Genetic transformation of Coccidioidesimmitis facilitated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Infect Dis 181:2106–2110
Cao J, Earle ED (2003) Transgene expression in broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) clones propagated in vitro via leaf explants. Plant Cell Rep 21:789–796
Cardoza V, Stewart CN Jr (2003) Increased Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and rooting efficiencies in canola (Brassica napus L.) from hypocotyl explants. Plant Cell Rep 21:599–604
Cardoza V, Stewart CN Jr (2004) Brassica biotechnology: progress in cellular and molecular biology. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 40:542–551
Cardoza V, Stewart CN Jr (2006) Agrobacterium protocols, Canola (Brassica napus L.). Meth Mol Biol 343(IV):257–266
Chakrabarty R, Viswakarma N, Bhat SR, Kirti PB, Singh BD, Chopra VL (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cauliflower: optimization of protocol and development of Bt-transgenic cauliflower. J Biosci 27:495–502
Chen FO, Hwang JY, Charng YY, Sun CW, Yang SF (2001) Transformation of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) with isopentenyltransferase gene via Agrobacterium tumefaciens for post-harvest yellowing retardation. Mol Breed 7(3):243–257
Dai XG, Shi XP, Ye YM, Fu Q, Bao MZ (2009) High frequency plant regeneration from cotyledon and hypocotyl explants of ornamental kale. Biol. Plan. 53:769–773
Deng-xia Y, Lei C, Yu-mei L, Mu Z, Yang-yong Z, Zhi-yuan F, Li-mei Y (2011) Transformation of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) with Btcry1Ba3 gene for control of diamondback Moth. Agr Sci China 10(11):1693–1700
Gelvin SB (2003) Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: the biology behind the “gene-jockeying” tool. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:16–37
Guang MA, Bo Z, Yu-hua L (2008) Establishment and optimization of a high-frequency shoot regeneration system of turnip (Brassica rapa L. ssp. rapifera). Acta. Hort Sin 35(6):833–840
Guo DP, Zhu ZJ, Hu XX, Zheng SJ (2005) Effect of cytokinins on shoot regeneration from cotyledon and leaf segment of stem mustard (Brassica juncea var. tsatsai). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 83:123–127
Haddadi F (2013) Development of heat tolerant strawberry (Fragaria x ananassaduch., cv. Camarosa) plants through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Ph.D thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia
Jonoubi P, Mousavi A, Majd A, Daneshian J (2004) Improved Brassica napus L., regeneration from hypocotyls using thidiazuronand benzyladenine as cytokinin sources. Pak J Bot 36(2):321–329
Jonoubi P, Mousavi A, Majd A, Salmanian AH, JalaliJavaran M, Dane Shian J (2005) Efficient regen- eration of Brassica napus L. hypocotyls and genetic transformation by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Biol Plant 49:175–180
Kanrar S, Venkateswari J, Kirti PB, Chopra VL (2002) Transgenic Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) with resistance to the mustard aphid (LipaphiserysimiKalt.). Plant Cell Rep 20:976–981
Kirsh VA, Peters U, Mayne ST, Subar AF, Chatterjee N, Johnson CC, Hayes RB (2007) Prospective study of fruit and vegetable intake and risk of prostate cancer. J Nat Cancer Inst 99(15):1200–1209
Kong F, Li J, Tan X, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Ma CQX (2009) A new time-saving transformation system for Brassica napus. Afr J Biotech 8(11):2497–2502
Lawrence PK, Koundal KR (2001) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of pigeon pea (Cajanuscajan L. Millsp.) and molecular analysis of regenerated plants. Curr Sci 80:1428–1432
Metwali EMR, Fuller MP, Jellings AJ (2012) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of anti-stress genes into cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis L.). 2. transformation and confirmation of stress tolerance. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 6(5):31–39
Metz RD, Dixit R, Earle ED (1995) Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) and cabbage (B. oleracea var. capitata). Plant Cell Rep 15:287–292
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ow DW, Wood KV, DeLuk M, Wet JR, Helinski DR, Howell SH (1986) Transient and stable expression of the firefly luciferase gene in plant cells and transgenic plants. Sci 234:856–859
Park BJ, Zaochang L, Akira K, Kameya T (2005) Genetic improvement of Chinese cabbage for salt and drought tolerance by constitutive expression of a B. napus LEA gene. Plant Sci 169:553–558
Rafat A, Aziz MA, Rashid AA, Abdullah SNA, Kamaladini H, Sirchi MHT, Javadi MB (2010) Optimization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation and shoot regeneration after co-cultivation of cabbage (Brassica oleracea subsp. capitata) cv. KY Cross with AtHSP101 gene. Sci Hort 124:1–8
Ravanfar SA (2012) Development of plant regeneration system and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Brassica oleracea L. subsp.italicacv. Green Marvel with HSP101 gene. Ph.D thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia
Ravanfar SA, Aziz MA, Kadir MA, Rashid AA, Sirchi MHT (2009) Plant regeneration of Brassica oleracea subsp. italica (broccoli) cv. Green Marvel as affected by plant growth regulators. Afr J Biotech 8(11):2523–2528
Ravanfar SA, Aziz MA, Kadir MA, Rashid AA, Haddadi F (2011) In vitro adventitious shoot regeneration and acclimatization of Brassica oleracea subsp. italica cv. Green Marvel. Afr J Biotech 10(29):5614–5619
Ravanfar SA, Aziz MA, Shabanimofrad M, Samarfard S (2013) Greenhouse evaluation on the performance of heat tolerant transgenic broccoli and genetic diversity analysis using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Electron J Biotech 16(5):1–10
Ravanfar SA, Shahida S, Aziz MA, Abdullah SNA, Rashid AA (2014) Influence of phenyl-urea and adenine-type cytokinins on direct adventitious shoot regeneration of cabbage (Brassica oleracea subsp. capitata) “KY Cross” Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology. Plant Biotech 31(3):275–280. doi:10.5511/plantbiotechnology.14.0514a
Sadasivam S, Gallie DR (1994) Isolation and transformation of rice aleurone protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 13:394–396
Salas MG, Park SH, Srivatanakul M, Smith RH (2001) Temperature influence on stable T-DNA integration in plant cells. Plant Cell Rep 20:701–705
Suri SS, Saini ARK, Ramawat KG (2005) High frequency regeneration and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica). Eur J Hort Sci 70(2):71–78
Vasudevan A, Selvaraj N, Ganapathi A, Choi CW (2007) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation in cucumber (Cucumissativus L.). Am J Biotechnol Biochem 3:24–32
Widiyanto SN, Erytrina D (2001) Clonal propagation of broccoli, Brassica oleracea L. var. italicathrough in vitro shoot multiplication. J Math Sci 6(1):101–111
Wolff JB, Harwood WA, Lonsdale DA, Harvey A, Hull R, Snape JW (1999) Luciferase as a reporter gene for transformation studies in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 18:715–720
Xiang Y, Wong WKR, Ma MC, Wong RSC (2000) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Brassica campestris ssp. Parachinensis with synthetic Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ab and cry1Ac genes. Plant Cell Rep 19:251–256
Xing Y, Yang Q, Ji Q, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Gu K, Wang D (2007) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation parameters for sweet potato embryogenic callus using b-glucuronidase (GUS) as a reporter. Afr J Biotech 6:2578–2584
Zhao ZY, Gu W, Cai T, Tagliani L, Hondred D, Bond D, Schroeder S, Rudert M, Pierce D (2001) High throughput genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in maize. Mol Breed 8:323–333
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Department of Agriculture Technology, Faculty of Agriculture, Universiti Putra Malaysia, for the laboratory facilities provided and the financial support in the form of a research Grant No. 01/01/07/0300RU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravanfar, S.A., Aziz, M.A., Saud, H.M. et al. Optimization of in vitro regeneration and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation with heat-resistant cDNA in Brassica oleracea subsp. italica cv. Green Marvel. Curr Genet 61, 653–663 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-015-0494-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-015-0494-x