Abstract
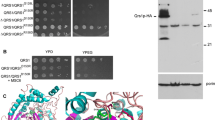
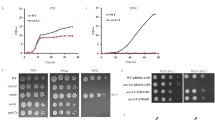
Nuclear-encoded Cbp1 stabilizes and promotes translation of mitochondrial cytochrome b (COB) mRNA. A CCG triplet within the 5′UTR of COB mRNA is essential for Cbp1-dependent stability. Like cbp1 mutations, mutation of any nucleotide in CCG results in degradation of COB transcripts. In this study, CBP1-linked pseudorevertants of the temperature-sensitive CCU strain were isolated. The suppressors are missense mutations within a central cluster or a carboxyl cluster in the linear sequence of Cbp1. Strains with mutations in the carboxyl half of the central cluster or the carboxyl cluster respire better than those with mutations in the amino half of the central cluster. COB mRNA levels in the suppressor strains were increased compared with that in the CCU strain and were positively correlated with respiratory capability. This correlation supports a model in which the primary role of Cbp1 is to protect COB mRNAs and deliver them to the mitochondrial translational apparatus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlin V, Brill JA, Trueheart J, Boeke JD, Fink GR (1991) Genetic screens and selections for cell and nuclear fusion mutants. Methods Enzymol 194:774–792
Bonitz SG, Homison G, Thalenfeld BE, Tzagoloff A, Nobrega FG (1982) Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system: processing of the apocytochrome b precursor RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D273-10B. J Biol Chem 257:6268–6274
Brower SM, Honts JE, Adams AEM (1995) Genetic analysis of the fimbrin-actin binding interaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 140:91–101
Bryan AC, Rodeheffer MS, Wearn CM, Shadel GS (2002) Sls1p is a membrane-bound regulator of transcription-coupled processes involved in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial gene expression. Genetics 160:75–82
Burns N, Grimwade B, Ross-Macdonald PB, Choi E-Y, Finberg K, Roeder GS, Snyder M (1994) Large-scale analysis of gene expression, protein localization, and gene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 8:1087–1105
Caponigro G, Muhlrad D, Parker R (1993) A small segment of the MATα1 transcript promotes mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a stimulatory role for rare codons. Mol Cell Biol 13:5141–5148
Chen W, Dieckmann CL (1994) Cbp1p is required for message stability following 5′-processing of COB mRNA. J Biol Chem 269:16574–16578
Chen W, Dieckmann CL (1997) Genetic evidence for interaction between Cbp1 and specific nucleotides in the 5′ untranslated region of mitochondrial cytochrome b mRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 17:6203–6211
Chen W, Islas-Osuna MA, Dieckmann CL (1999) Suppressor analysis of mutations in the 5′ untranslated region of COB mRNA identifies components of general pathways for mitochondrial mRNA processing and decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 151:1315–1325
Christianson T, Edwards JC, Mueller DM, Rabinowitz M (1983) Identification of a single transcriptional initiation site for the glutamic tRNA and COB genes in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:5564–5568
Cuff JA, Clamp ME, Siddiqui AL, Finlay M, Barton GJ (1994) Jpred: a consensus secondary structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 14:892–893
Dieckmann CL, Koerner TJ, Tzagoloff A (1984) Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP1, a yeast nuclear gene involved in 5′ end processing of cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem 259:4722–4731
Elion EA, Warner JR (1986) An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 6:2089–2097
Fox TD, Folley, LS, Mulero JJ, McMullin TW, Thorsness PE, Hedin LO, Costanzo MC (1991) Analysis and manipulation of yeast mitochondrial genes. Methods Enzymol 194:149–165
Goldsmith SC, Pokala N, Shen WY, Fedorov AA, Matsudaira P, Almo SC (1997) The structure of an actin-crosslinking domain from human fimbrin. Nat Struct Biol 9:708–712
Grivell LA, Artel-Sanz M, Hakkart G, Jong L de, Nijtmans LG, Oosterum K van, Siep M, Spek H van der (1999) Mitochondrial assembly in yeast. FEBS Lett 452:57–60
Islas-Osuna MA, Ellis TP, Marnell LL, Mittelmeier TM, Dieckmann CL (2002) Cbp1 is required for translation of the mitochondrial cytochrome b mRNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 277:37987–37990
Mayer SA, Dieckmann CL (1989) The yeast CBP1 gene produces two differentially regulated transcripts by alternative 3′ end formation. Mol Cell Biol 9:4161–4169
Michaelis U, Körte A, Rödel G (1991) Association of cytochrome b translational activator proteins with the mitochondrial membrane: implications for cytochrome b expression in yeast. Mol Gen Genet 230:177–185
Mittelmeier TM, Dieckmann CL (1990) CBP1 function is required for stability of a hybrid cob-oli1 transcript in yeast mitochondria. Curr Genet 18:421–428
Mittelmeier TM, Dieckmann CL (1993) In vivo analysis of sequences necessary for CBP1-dependent accumulation of cytochrome b transcripts in yeast mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 13:4203–4213
Mittelmeier TM, Dieckmann CL (1995) In vivo analysis of sequences required for translation of cytochrome b transcripts in yeast mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 15:780–789
Muhlrad D, Hunter R, Parker R (1992) A rapid method for localized mutagenesis of yeast genes. Yeast 8:79–82
Naithani S, Saracco SA, Butler A, Fox TD (2003) Interactions among COX1, COX2, and COX3 mRNA-specific translational activator proteins on the inner surface of the mitochondrial inner membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 14:324–333
Orr-Weaver TL, Szostak JW, Rothstein RJ (1981) Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:6354–6358
Rodeheffer MS, Boone BE, Bryan AC, Shadel GS (2001) Nam1p, a protein involved in RNA processing and translation, is coupled to transcription through an interaction with yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 276:8616–8622
Rose MD, Winston F, Hieter P (1990) Methods in yeast genetics: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Shortle D, Novick P, Botstein D (1984) Construction and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutant alleles of the yeast actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:4889–4893
Sikorski RS, Hieter P (1989) A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122:19–27
Sparks KA, Dieckmann CL (1998) Regulation of poly(A) site choice of several yeast mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 26:4676–4687
Staples RR, Dieckmann CL (1993) Generation of temperature-sensitive cbp1 strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by PCR mutagenesis and in vivo recombination: Characteristics of the mutant strains imply that CBP1 is involved in stabilization and processing of cytochrome b pre-mRNA. Genetics 135:981–991
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tzagoloff A, Dieckmann CL (1990) PET genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev 54:211–225
Weber ER, Dieckmann CL (1990) Identification of the CBP1 polypeptide in mitochondrial extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 265:1594–1600
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Melissa Iszard-Crowley for isolating suppressors during her rotation in the laboratory, Dr. Lorraine Marnell for technical assistance, and Drs. John Little and Elizabeth Vierling for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by assistance from CIAD (Mexico) and CONACYT (Programa de Consolidacion Institucional, Mexico) to M.A.I.-O., and NIH grant GM34893 to C.L.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Brunner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islas-Osuna, M.A., Ellis, T.P., Mittelmeier, T.M. et al. Suppressor mutations define two regions in the Cbp1 protein important for mitochondrial cytochrome b mRNA stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Curr Genet 43, 327–336 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0405-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0405-4