Summary
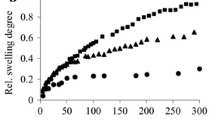
Influence of some simulated physiological body fluids on the dynamic swelling behaviour of polyelectrolytic hydroxamic acid hydrogels (PHA) was investigated at 37 °C in vitro. The simulated physiological body fluids are distilled water, human sera, physiological saline (0.89 % NaCl), isoosmotic phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, gastric fluid at pH 1. 1, (gylicine-HCl buffer), urea (0.3 mol L−1), and the aquatic solutions of K2HPO4 and KNO3 (the sources of K+). The values of equilibrium swelling of PHA hydrogels varied in the range of 130–4625%, while the values of equilibrium fluid content of the hydrogels varied in the range of 57–97%. The initial rate of swelling, diffusional exponent, and, diffusion coefficient were calculated using swelling kinetics data. Diffusion of the fluids into the hydrogel was found to be non-Fickian character. The diffusion coefficients of the hydrogel varied between 0.6×10−6– 8.1×10−6 cm2 s−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 March 2000/Accepted: 18 December 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saraydin, D., Çaldiran, Y. In vitro dynamic swelling behaviors of polyhydroxamic acid hydrogels in the simulated physiological body fluids. Polymer Bulletin 46, 91–98 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890170093
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890170093