Summary
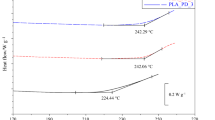
Polyhydroxyamic acid (PHAA) with an inherent viscosity of 0.45 dL/g was prepared from 3, 3'-dihydroxybenzidine and pyromellitic dianhydride. The mechanical and thermal properties of PHAA films and powders before and after annealing were investigated on the basis of their potential use as fire-safe polymers. Cyclization of PHAA to the corresponding hydroxy-containing polyimide is an endothermic reaction. During annealing of PHAA, water was released at 180 °C and carbon dioxide at over 400 °C. The weight residue of PHAA at 900 °C was about 38 %. After annealing at 500 °C, this value increased to 75 %. After annealing at 450 °C, the ultimate stress and initial modulus of the PHAA precursor films increased from 133.8 MPa and 5.86 GPa to 306.2 MPa and 11.0 GPa, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 September 2000/Revised version: 24 October 2000/Accepted: 24 October 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Farris, R. Effect of heat treatment on the thermal and mechanical properties of polyhydroxyamic acid presursor films. Polymer Bulletin 45, 405–410 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890070014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890070014