Summary
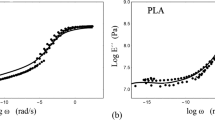
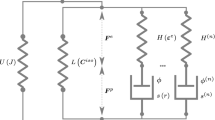
Constitutive equations are derived for enthalpy recovery in amorphous glassy polymers. The model is based on the concept of cooperative relaxation which treats a polymer as an ensemble of flow units rearranging at random times. The rate of rearrangement is determined by the Eyring theory of thermally activated processes. Fair agreement is demonstrated between results of numerical simulation and experimental data for polycarbonate, poly(ether imide), poly(methyl methacrylate), polystyrene and a glycerol glass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 December 1999/Revised version: 28 February 2000/Accepted: 2 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drozdov, A. Enthalpy relaxation in glassy polymers. Polymer Bulletin 44, 353–360 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890050613
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890050613