Abstract
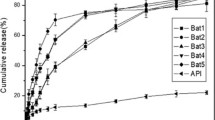
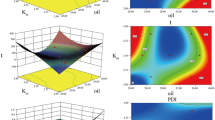
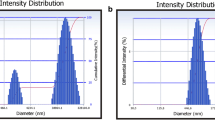
Many diseases exhibit circadian fluctuation, including diabetes, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and hypertension. These disorders cannot be effectively treated with conventional dosage forms and instead require time-scheduled drug release for pharmacological effectiveness. The objective of this work was to use simple process to overcome the solubility problem by employing a novel solubilizer and to generate peristaltic release based on the physical and chemical interactions between acrylic copolymer and organic acid. To address the solubility issue of nifedipine, sepitrap 4000 is being used as a solubilizer inside the core tablet. The resulting physical mixture underwent various analyzes including saturated solubility, in-vitro dissolution, FTIR, DSC, and PXRD. A saturation solubility analysis confirmed 368% improvement as significant impact of sepitrap 4000 on nifedipine solubility and bioavailability. The 32 complete factorial design was used to optimize press-coated pulsatile formulation, with lag time and time required to release 50% of drug, as responses and concentrations of eudragit RSPO and tartaric acid as independent variables. According to stability study, developed pulsatile product was found to be suitably stable under rapid and regulated settings. As a result, produced pulsatile tablet is suitable formulation for alleviation of early morning blood pressure spikes and other cardiac problems that follow a circadian rhythm.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data included in article/supplementary material/referenced in article.
References
Jagdale SC, Sali MS, Barhate AL, Kuchekar BS, Chabukswar AR (2013) Formulation, development, and evaluation of floating pulsatile drug delivery system of atenolol. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 67(3):214–228
Karavas E, Georgarakis E, Bikiaris DJ (2006) Application of PVP/HPMC miscible blends with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for adjusting drug release in predictable pulsatile chronotherapeutics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 64(1):115–126
Kashyap N, Viswanad B, Sharma G, Bhardwaj V, Ramarao P, Kumar MR (2007) Design and evaluation of biodegradable, biosensitive in situ gelling system for pulsatile delivery of insulin. Biomaterials 28(11):2051–2060
Lin HL, Lin SY, Lin YK, Ho HO, Lo YW, Sheu MT (2008) Release characteristics and in vitro–in vivo correlation of pulsatile pattern for a pulsatile drug delivery system activated by membrane rupture via osmotic pressure and swelling. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 70(1):289–301
Maroni A, Zema L, Cerea M, Sangalli ME (2005) Oral pulsatile drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2(5):855–871
Singh A, Dubey H, Shukla I, Singh DP (2012) Pulsatile drug delivery system: an approach of medication according to circadian rhythm. J Appl Pharm Sci 2(3):166–176
Zhang Z, Qi X, Li X, Xing J, Zhu X, Wu ZJ (2014) A novel pulsatile drug delivery system based on the physiochemical reaction between acrylic copolymer and organic acid: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 462(1–2):66–73
Mitchell SA, Reynolds TD, Dasbach TP (2003) A compaction process to enhance dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Int J Pharm 250(1):3–11
Jagtap RS, Doijad RC, Mohite SK, Technology. (2019) Adsorption of nifedipine on porous calcium silicate for enhancement of solubility and dissolution rate. Res J Pharm Technol 12(3):1273–1279
Jagtap S, Magdum C (2019) Influence of Water-soluble polymers on Epalrestat ternary complexation by kneading. Res J Pharm Technol 12(8):3602–3608
Jagtap RS, Doijad R, Mohite S (2018) Enhancement of solubility & dissolution rate of nifedipine by using novel solubilizer sepitrap 80 & sepitrap 4000. J Drug Deliv Therapeutics 8(5):293–300
Ahuja N, Katare OP, Singh BJ (2007) Biopharmaceutics. Studies on dissolution enhancement and mathematical modeling of drug release of a poorly watersoluble drug using watersoluble carriers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 65(1):26–38
Khandare J, Haag R (2010) Pharmaceutically used polymers: principles, structures, and applications of pharmaceutical delivery systems. In: Schäfer-Korting M (ed) Drug delivery. Springer, Berlin, pp 221–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00477-3_8
Ramana MV, Himaja M, Kamal Dua VK, Sharma KP (2008) A new approach: enhancement of solubility of rofecoxib. Asian J Pharm 2(2):96. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8398.42495
P Patil, SJ Killedar (2021) Technology. Formulation and characterization of gallic acid and quercetin chitosan nanoparticles for sustained release in treating colorectal cancer. JoDDS 63:102523
Narendra C, Srinath M, Rao BP (2005) Development of three layered buccal compact containing metoprolol tartrate by statistical optimization technique. Int J Pharm 304(1–2):102–114
Ozon EA, Novac M, Gheorghe D, Musuc AM, Mitu MA, Sarbu I et al (2022) Formation and physico-chemical evaluation of nifedipine-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and nifedipine-methyl-β-cyclodextrin: the development of orodispersible tablets. Pharmaceuticals 15(8):993
Jagtap S, Magdum C, Jagtap R (2021) Ameliorated solubility and dissolution of flurbiprofen using solubilizer Sepitrap 80 and Sepitrap 4000. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 14(1):21–27
Choi JS, Byeon JC, Park JS (2019) Naftopidil-fumaric acid interaction in a solid dispersion system: improving the dissolution rate and oral absorption of naftopidil in rats. Mater Sci Eng C 95:264–274
R Dhurke, D J Ramyasree (2022) Pulsatile Delivery System for Antihypertensive Drug. CAiPR, 9 DV 100–10
M Sarangi, S Padhi, G Rath. Non-invasive delivery of Insulin for breaching hindrances against Diabetes. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems
Alshaya HA, Alfahad AJ, Alsulaihem FM, Aodah AH, Alshehri AA, Almughem FA et al (2022) Fast-dissolving nifedipine and atorvastatin calcium electrospun nanofibers as a potential buccal delivery system. Pharmaceutics 14(2):358
Oo MK, Mahmood S, Wui WT, Mandal UK, Chatterjee BJ (2021) Effects of different formulation methods on drug crystallinity, drug-carrier interaction, and ex vivo permeation of a ternary solid dispersion containing nisoldipine. J Pharm Innov 16:26–37
Singh MK, Mazumder R, Padhi S, Singh DK (2022) Formulation development and optimization of bioenhanced sublingual tablets of rizatriptan benzoate to combat migraine. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 56(2):200–215
Jyothirmayi P, Devalarao G, Rao MVBJ (2020) Optimization of pulsatile compression coated floated tablets of tramadol HCL for chronopharmacotherapy of rheumatoid arthritic pain using 23factorial design. Res J Pharm Technol 13(12):5823–5830
Sindhu Chowdary M (2019) Design and development of press coated pulsatile release of ketoprofen tablets. KK College of Pharmacy, Chennai
Alam S, Sharma PJ (2016) Stability study of clobetasol propionate loaded tea tree oil nanoemulsion as per ICH guidelines. RJoP Technol 9(11):1999–2004
Yi T, Wan J, Xu H, Yang XJ (2008) A new solid self-microemulsifying formulation prepared by spray-drying to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 70(2):439–444
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Zydus Cadila ltd Ahmadabad for providing gift sample of nifedipine, Seppic India Ltd for providing gift sample of sepitrap 4000. Shivaji University, Kolhapur and Rajarambapu College of Pharmacy Kasegaon are acknowledged for assistance with analytical work.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RSJ contributed to formal analysis, experimental and writing—original draft; SKM contributed to supervision, review and editing; SRJ contributed to designing of experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data; PSS contributed to analysis and interpreted the data; SDC contributed to methodology and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval is not applicable for this article.
Consent to participate
The authors confirm that all information they provide for this study is realistic experimental data and findings.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jagtap, R., Mohite, S., Jagtap, S. et al. Acrylic co-polymer and organic acid-based press coated pulsatile tablet of nifedipine using 32 factorial design: use of novel solubilizer for solubility enhancement. Polym. Bull. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-024-05297-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-024-05297-8