Abstract
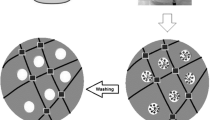
In the present study, anionic hydrogels, acrylamide (AAm) monomer, and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid (AMPSA) comonomer were prepared in the presence of two different cross-linkers. Then, super-anionic hydrogels were prepared by converting the amide groups of neutral AAm in anionic hydrogels to hydroxamic acid with hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The hydrogels were characterized by FTIR, SEM, TG, and DSC analyses. Uranyl adsorption in the hydrogels was investigated by spectroscopic, kinetic, and equilibrium studies. It was determined that uranyl adsorption kinetics in hydrogels were compatible with pseudo-second-order and intra-particular diffusion models. It was determined that the uranyl adsorption isotherms on the hydrogels were L-type according to the Giles isotherm classification. Adsorption parameters were calculated by applying Freundlich and Langmuir models to these isotherms. In addition, it was determined that the amount of adsorbed uranyl increased with the increase in adsorbent mass, did not change with temperature, decreased in the range of pH 2–4, and increased at pH 4–7. It was observed that super-anionic hydrogels had the highest adsorption capacity among these new hydrogels. In addition, molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) mapping was performed to predict the reactive regions of the hydrogels. The results showed that the theoretical and experimental data of hydrogels are in agreement with each other. In conclusion, it can be said that the anionic and super-anionic hydrogels prepared in this study are unique hydrogels with fast and effective properties in removing uranyl.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozay O, Ekici S, Baran Y, Aktas N, Sahiner N (2009) Removal of toxic metal ions with magnetic hydrogels. Water Res 43(17):4403–4411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.058
Li J, Wang X, Zhao G, Chen C, Chai Z, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2018) Metal–organic framework-based materials: superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem Soc Rev 47(7):2322–2356. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00543a
Sahiner N, Ozay H, Ozay O, Aktas N (2010) A soft hydrogel reactor for cobalt nanoparticle preparation and use in the reduction of nitrophenols. Appl Catal B 101(1–2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.09.022
Atta AM, Wahab ZHAE, Shafey ZAE, Zidan WI, Akl ZF (2010) Uranyl ions uptake from aqueous solutions using crosslinked ionic copolymers based on 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid copolymers. J Dispersion Sci Technol 31(12):1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690903296977
Saraydin D, Karadağ E, Güven O (1995) Adsorptions of some heavy metal ions in aqueous solutions by acrylamide/maleic acid hydrogels. Sep Sci Technol 30(17):3287–3298. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399508013145
Sang K, Mei D, Wang Y, Liu L, Li H, Yang G, Ma F, Zhang C, Dong H (2022) Amidoxime-functionalized zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with antimicrobial property for the removal of U (VI) from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 10(5):10834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108344
Saraydin D, Şolpan D, Işıkver Y, Ekici S, Güven O (2002) Radiation crosslinked poly(acrylamide/2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate/maleic acid) and their usability in the uptake of uranium. J Macromol Sci Part A 39(9):969–990. https://doi.org/10.1081/ma-120013574
Karadağ E, Saraydin D, Güven O (1995) Behaviors of acrylamide/itaconic acid hydrogels in uptake of uranyl ions from aqueous solutions. Sep Sci Technol 30(20):3747–3760. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399508015140
Saraydin D, Isikver Y, Sahiner N (2001) Uranyl ion binding properties of poly(hydroxamic acid) hydrogels. Polym Bull 47(1):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890170024
Işıkver Y (2017) Synthesis of anionic hydrogels for uranyl ion adsorption. CSJ 38(4):770–780. https://doi.org/10.17776/csj.345147
Kundakcı S, Üzüm ÖB, Karadağ E (2008) Behaviors of chemically crosslinked CAAMPS hydrogels in uptake of uranyl ions from aqueous solutions. Polym Plast Technol Eng 48(1):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550802539775
Hazer O, Kartal Ş (2010) Use of amidoximated hydrogel for removal and recovery of U(VI) ion from water samples. Talanta 82(5):1974–1979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.08.023
Chi F, Hu S, Xiong J, Wang X (2013) Adsorption behavior of uranium on polyvinyl alcohol-g-amidoxime: Physicochemical properties, kinetic and thermodynamic aspects. Sci China Chem 56(11):1495–1503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-5003-9
Karadağ E, Nalbantoğlu A, Kundakcı S, Üzüm ÖB (2016) Uranyl Ion sorption characteristics of novel polymer/montmorillonite/carboxymethyl cellulose-composite biosorbent-based AAm/AMPS hydrogels and semi-IPNs. Adv Polym Technol 37(2):575–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21698
Ye T, Huang B, Wang Y, Zhou L, Liu Z (2020) Rapid removal of uranium(VI) using functionalized luffa rattan biochar from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf, A 606:125480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125480
Tan J, Xie S, Wang G, Yu CW, Zeng T, Cai P, Huang H (2020) Fabrication and optimization of the thermo-sensitive hydrogel carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) for U(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Polymers 12(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010151
Atta AM, Wahab ZHAE, El Shafey ZA, Zidan WI, Akl ZF (2010) Characterization and evaluation of acrylic acid Co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane-1-sulfonic Acid Hydrogels for Uranium Recovery. J Dispers Sci Technol 31(10):1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690903269560
Tatarchuk T, Shyichuk A, Mironyuk I, Naushad M (2019) A review on removal of uranium(VI) ions using titanium dioxide based sorbents. J Mol Liq 293:111563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111563
Saraydın D, Işıkver Y, Karadağ E (2018) A study on the correlation between adsorption and swelling for poly(Hydroxamic Acid) hydrogels-triarylmethane dyes systems. J Polym Environ 26(9):3924–3936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1257-9
Kundakci S, Üzüm ÖB, Karadağ E (2008) Swelling and dye sorption studies of acrylamide/2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid/bentonite highly swollen composite hydrogels. React Funct Polym 68(2):458–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.11.008
Işikver Y (2017) Removal of some cationic dyes from aqueous solution by acrylamide- or 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-based copolymeric hydrogels. Fibers Polym 18(11):2070–2078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-7215-7
Isikver Y, Saraydin D, Sahiner N (2001) Poly(hydroxamic acid) hydrogels from poly(acrylamide): preparation and characterization. Polym Bull 47(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890170023
Saraydın D, Işıkver Y, Karadağ E (2022) An evaluation on S-type adsorption isotherm in the model of crosslinked polyhydroxamates/oxazine dyes/water interactions. Adsorption 28(5–6):249–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-022-00367-7
Saraydın D, Işıkver Y, Karadağ E (2017) Adsorption of phenazine dyes using poly(hydroxamic acid) hydrogels from aqueous solutions. Polym Eng Sci 58(3):310–318. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24574
Sahoo TR, Prelot B (2020) Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater. Nanomater Detect Removal Wastew Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-818489-9.00007-4
Hazer O, Soykan C, Kartal Ş (2007) Synthesis and swelling behavior analysis of Poly(acrylamidoxime-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane Sulfonic Acid) hydrogels. J Macromol Sci, Part A 45(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601320701683223
Nesic A, Panic V, Ostojic S, Micic D, Pajic-Lijakovic I, Onjia A, Velickovic S (2016) Physical-chemical behavior of novel copolymers composed of methacrylic acid and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid. Mater Chem Phys 174:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.02.063
Öztop HN, Akyildiz F, Saraydin D (2020) Poly(acrylamide/vinylsulfonic acid) hydrogel for invertase immobilization. Microsc Res Tech 83(12):1487–1498. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23542
Haerifar M, Azizian S (2013) Mixed surface reaction and diffusion-controlled kinetic model for adsorption at the solid/solution interface. J Phys Chem C 117(16):8310–8317. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp401571m
Ho Y (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136(3):681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Plazinski W, Rudzinski W, Plazinska A (2009) Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 152(1–2):2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2009.07.009
Wu F-C, Tseng R-L, Juang R-S (2009) Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 153(1–3):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.042
Crini G, Peindy H, Gimbert F, Robert C (2007) Removal of C.I. basic green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep Purif Technol 53(1):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.018
Choudhary S, Sharma K, Kumar V, Bhatia JK, Sharma S, Sharma V (2019) Microwave-assisted synthesis of gum gellan-cl-poly(acrylic-co- methacrylic acid) hydrogel for cationic dyes removal. Polym Bull 77(9):4917–4935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02998-3
Giles CH, MacEwan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) 786. Studies in adsorption Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc (Resumed). https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9600003973
Politzer P, Truhlar DG (Eds) (1981) Chemical applications of atomic and molecular electrostatic potentials: reactivity, structure, scattering and energies of organic, inorganic and biological systems, Plenum, New York
Ehresmann B, Martin B, Horn AHC, Clark T (2003) Local molecular properties and their use in predicting reactivity. J Mol Model 9(5):342–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-003-0153-x
Akman F (2016) Spectroscopic investigation, HOMO–LUMO energies, natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis and thermodynamic properties of two-armed macroinitiator containing coumarin with DFT quantum chemical calculations. Can J Phys 94(6):583–593. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjp-2016-0041
Gaussian 16, Revision C.01, Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Li X, Caricato M, Marenich AV, Bloino J, Janesko BG, Gomperts R, Mennucci B, Hratchian HP, Ortiz JV, Izmaylov AF, Sonnenberg JL, Williams-Young D, Ding F, Lipparini F, Egidi F, Goings J, Peng B, Petrone A, Henderson T, Ranasinghe D, Zakrzewski VG, Gao J, Rega N, Zheng G, Liang W, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Throssell K, Montgomery JA, Jr, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark MJ, Heyd JJ, Brothers EN, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith TA, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell AP, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Millam JM, Klene M, Adamo C, Cammi R, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Fox DJ (2019) Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT
Dennington R, Keith TA, Millam JM (2016) GaussView, Version 6, Semichem, Inc., Shawnee Mission, KS
Frisch MJ, Trucks G, Schlegel H, Scuseria G, Robb M, Cheeseman J, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson G (2009) Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT
Stephens PJ, Devlin FJ, Chabalowski CF, Frisch MJ (1994) Ab initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields. J Phys Chem 98(45):11623–11627. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100096a001
Raghavachari K (2000) Perspective on “Density functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange.” Theor Chim Acta 103(3–4):361–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002149900065
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Dr. Dursun Saraydın for his ideas in some experiments. The authors also thank Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nihat Karakuş for his help in the calculation of MEP maps.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was produced from Nihat Alkan’s Master’s Thesis, which was completed under the supervision of YI. The corresponding author YI was responsible for ensuring that the descriptions are accurate and agreed upon by all authors. YI contributed to investigation, conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, and project administration. NA contributed to resources, visualization, official analysis, original drafting. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Işıkver, Y., Alkan, N. Chemically functionalized poly(AAm-AMPSA) superadsorbent hydrogels for removal of uranyl from aqueous solutions. Polym. Bull. 81, 1019–1042 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-05000-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-05000-3