Abstract
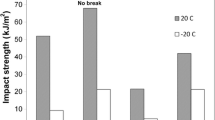
Four samples, including homopolymerized PP (PP-1), random impact copolymerized PP (PP-2), random impact copolymerized PP of ethylene-propylene (PP-3), and random impact copolymerized PP of ethylene-propylene-butylene (PP-4), which were prepared by 75 KG Spheripol process pilot plant using ZN104M as catalyst, were adopted to study the structure and performance, i.e., the influence of the different polypropylene molecular chain structures on the crystallization behavior of random impact copolymer polypropylene, and the changes in mechanical and optical performance due to the different aggregation structures of random impact copolymer polypropylene, and following results were achieved. Firstly, when ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR) and copolymerization monomers of ethylene and butylene were added in turn, the regularity of PP molecular chains decreased in different degree with the order of PP-1 > PP-2 > PP-3 > PP-4, and which further led to the same pattern for the crystallization peak temperature and the crystallinity. Secondly, half-crystallization time (T1/2) of the same cooling rate and the crystallization activation energy increased with the addition of EPR, ethylene and butylene. Crystallization activation energies were calculated to be 12.05 kJ mol−1, 12.09 kJ mol−1, 12.38 kJ mol−1 and 12.64 kJ mol−1 for PP-1, PP-2, PP-3 and PP-4, respectively. Last but the most importantly, the addition of EPR, ethylene and butylene would enhance the impact strength, but decrease the transmittance, whereas the haze changed little. Based on the theory between structure and performance, the reason that caused above results were analyzed. This work provided some guidance for the development of high-performance polypropylene used in identical fields.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia E, Shangguan Y, Xiong J, Chen F, Zheng Q (2018) Fabrication of polypropylene blends with excellent low-temperature toughness and balanced toughness-rigidity by a combination of EPR and SEEPS. J Appl Polym Sci 135(3):45714
Nasresfahani A, Hutchinson RA (2020) Deterministic approach to estimate functionality of chains produced by radical copolymerization in the presence of secondary reactions. Macromolecules 53(14):5674–5686
Ran J, Fu C, Ding L, Cao P, Xu T (2018) Dual hydrophobic grafted chains facilitating quaternary ammonium aggregations of hydroxide conducting polymers: a theoretical and experimental investigation. J Mater Chem A 6(14):5714–5723
Sauceda HE, Chmiela S, Poltavsky I, Müller K-R, Tkatchenko A (2019) Molecular force fields with gradient-domain machine learning: construction and application to dynamics of small molecules with coupled cluster forces. J Chem Phys 150(11):114102
Farani AY, Mohammadi Y, Ghahremani F (2019) Modeling farmers’ responsible environmental attitude and behaviour: a case from Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(27):28146–28161
Nan Y, Li S, Zhu M, Li B, Yang S (2019) Endowing the lithium metal surface with self-healing property via an in situ gas-solid reaction for high-performance lithium metal batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(32):28878–28884
Zhang L, Lin Y, Cheng L, Yang Z, Matsuyama H (2019) A comprehensively fouling-and solvent-resistant aliphatic polyketone membrane for high-flux filtration of difficult oil-in-water micro-and nanoemulsions. J Membr Sci 582:48–58
Zhang T, Wu H, Fang Q, Huang T, Gong Z, Peng Y (2017) UHP-SFRC panels subjected to aircraft engine impact: experiment and numerical simulation. Int J Impact Eng 109:276–292
Li Y, Li Y, Han C, Yu Y, Xiao L (2019) Morphology and properties in the binary blends of polypropylene and propylene–ethylene random copolymers. Polym Bull 76(6):2851–2866
Li Y, Zhang G, Fu X, Guo W (2015) Preparation and properties of core-shell particles filled β-nucleated polypropylene random copolymer composites. Polym Polym Compos 23(1):1–10
Cao J, Zheng Y, Lin T (2016) Synergistic toughening effect of β-nucleating agent and long chain branching on polypropylene random copolymer. Polym Testing 55:318–327
Pastor-García MT, Suárez I, Expósito MT, Coto B, García-Muñoz RA (2021) Engineered PP impact copolymers in a single reactor as efficient method for determining their structure and properties. Eur Polym J 157:110642
Graziano A, Jaffer S, Sain M (2019) Review on modification strategies of polyethylene/polypropylene immiscible thermoplastic polymer blends for enhancing their mechanical behavior. J Elastomers Plast 51(4):291–336
Gahleitner M, Tranninger C, Doshev P (2019) Polypropylene copolymers. In: Karger-Kocsis J, Bárány T (eds) Polypropylene handbook: morphology, blends and composites. Springer, pp 295–355
Bláha M, Zedník J, Vohlídal J (2015) Self-doping of polyaniline prepared with the FeCl3/H2O2 system and the origin of the Raman band of emeraldine salt at around 1375 cm-1. Polym Int 64(12):1801–1807
Kunimitsu T, Toyoda K, Ikaga T, Kim K, Ohkoshi Y, Koike K (2020) High strength fiber obtained from a high stereoregularity metallocene catalyst-synthesized polypropylene. Polymer 202:122654
Du Juan G, Jia Lin Z, Min Feng D (2017) Study on assay method of polymeric monomer content in transparent polypropylene. China Plast Ind 45(4):100–102
Du Juan G, Jia Lin Z (2017) Study on the determination method of polymeric monomer content in butane-ethylene-propylene random polypropylene. China Plast Ind 45(6):85–88
Wang W, Zhou S, Xin Z, Shi Y, Zhao S, Meng X (2016) Preparation and foaming mechanism of foamable polypropylene based on self-assembled nanofibrils from sorbitol nucleating agents. J Mater Sci 51(2):788–796
Jian Z, Deng-Fu C, Cheng-Qian Z, Weng-Sing H, Ming-Rong H (2015) The effects of heating/cooling rate on the phase transformations and thermal expansion coefficient of C-Mn as-cast steel at elevated temperatures. J Mater Res 30(13):2081–2089
Yan HD, Zhang C, Li WK, Zha JW (2020) Effect of trap level density on breakdown strength and space charge distribution of polypropylene/low-density polyethylene composites. Polym Compos 41(2):780–787
Lee S, Jiang Y, Durniak M, Wetzel C, Brueck S (2018) Initial stage of cubic GaN for heterophase epitaxial growth induced on nanoscale v-grooved Si (001) in metal-organic vapor-phase epitaxy. Nanotechnology 30(2):025711
Zeaiter A, Nardin P, Yazdi MAP, Billard A (2019) Outstanding shortening of the activation process stage for a TiFe-based hydrogen storage alloy. Mater Res Bull 112:132–141
Dai X, Cao Y, Shi X, Wang X (2016) Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics, thermal degradation behavior and mechanical properties of poly (lactic acid)/MOF composites prepared by melt-blending methods. RSC Adv 6(75):71461–71471
Vyazovkin S (2020) Activation energies and temperature dependencies of the rates of crystallization and melting of polymers. Polymers 12(5):1070
Chen F, Zhu H, Chen W, Ou H, Cui Z (2021) Multiscale modeling of discontinuous dynamic recrystallization during hot working by coupling multilevel cellular automaton and finite element method. Int J Plast 145:103064
Howell L, Osborne E, Franklin A, Hébrard É (2021) Pattern recognition of chemical waves: finding the activation energy of the autocatalytic step in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. J Phys Chem B 125(6):1667–1673
Ptáček P, Opravil T, Šoukal F (2016) Introduction of novel kinetic approach to calculation of activation energy and its application to the sinter-crystallization of strontian feldspar. Ceram Int 42(15):16969–16980
El-Yazbi AF, Aboukhalil FM, Khamis EF, Youssef RM, El-Sayed MA (2021) Simultaneous determination of mometasone furoate and salicylic acid in complex matrix using green analytical method. Microchem J 163:105900
Khoo CY, Liu H, Sasangka WA, Made RI, Tamura N, Kunz M, Budiman AS et al (2016) Impact of deposition conditions on the crystallization kinetics of amorphous GeTe films. J Mater Sci 51(4):1864–1872
Lupi L, Peters B, Molinero V (2016) Pre-ordering of interfacial water in the pathway of heterogeneous ice nucleation does not lead to a two-step crystallization mechanism. J chem phys 145(21):211910
Xie C, Li W, Zheng D, Wang K, Yang Y, Shen F, Xie L et al (2019) Study of crystallization behavior and kinetics of magnetic FeCoCrNiZr high entropy amorphous alloy. J Non-Cryst Solids 514:20–24
Retson T, Hoek J, Sterling R, Van Bockstaele E (2015) Amygdalar neuronal plasticity and the interactions of alcohol, sex, and stress. Brain Struct Funct 220(6):3211–3232
Gao Q, Jian Z, Xu J, Zhu M, Chang F, Han A (2016) Crystallization kinetics of the Cu50Zr50 metallic glass under isothermal conditions. J Solid State Chem 244:116–119
Bai D, Diao X, Ju Y, Liu H, Bai H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2018) Low-temperature sintering of stereocomplex-type polylactide nascent powder: the role of optical purity in directing the chain interdiffusion and cocrystallization across the particle interfaces. Polymer 150:169–176
Deblieck R, Remerie K, Van den Fonteyne W, Boerakker M (2021) A morphology-based model to describe the low-temperature impact behaviour of rubber-toughened polypropylene. Polymers 13(13):2218
Deblieck RA, Van Beek D, Remerie K, Ward IM (2011) Failure mechanisms in polyolefines: the role of crazing, shear yielding and the entanglement network. Polymer 52(14):2979–2990
Gao G, Zhang S, Wang L, Lin J, Qi H, Zhu J, Du L et al (2020) Developing highly tough, heat-resistant blend thermosets based on silicon-containing arylacetylene: a material genome approach. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(24):27587–27597
Shi L, Li Q, Duan H, Zhang W, Yang W, Li H, Chang C (2018) The correlation between mechanical properties and structure of Fe-Ni-PB amorphous alloys: Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. J Non-Cryst Solids 491:1–6
Strubel P, Thieme S, Biemelt T, Helmer A, Oschatz M, Brückner J, Althues H et al (2015) ZnO hard templating for synthesis of hierarchical porous carbons with tailored porosity and high performance in lithium-sulfur battery. Adv Func Mater 25(2):287–297
Geng Z, Cui Z, Li Z, Zhu S, Liang Y, Lu WW, Yang X (2015) Synthesis, characterization and the formation mechanism of magnesium-and strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite. J Mater Chem B 3(18):3738–3746
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent Project of Lanzhou (2019-RC-53), and the Innovation Foundation of China National Petroleum Corporation (2019D-5007-0408).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Fan, J., Chen, Y. et al. The structure and performance study of PP random impact resistance copolymer. Polym. Bull. 80, 2637–2663 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04187-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04187-1